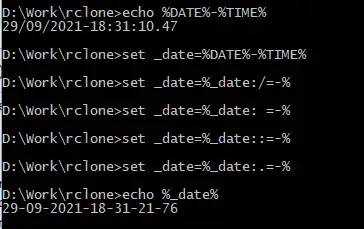
In situations like this use a simple, standard programming approach:
Instead of expending a huge effort parsing an unknown entity, simply save the current configuration, reset it to a known state, extract the info and then restore the original state. Use only standard Windows resources.
Specifically, the date and time formats are stored under the registry key
HKCU\Control Panel\International\ in [MS definition] "values": "sTimeFormat" and "sShortDate".
Reg is the console registry editor included with all Windows versions.
Elevated privileges are not required to modify the HKCU key
Prompt $N:$D $T$G
::Save current config to a temporary (unique name) subkey, Exit if copy fails
Set DateTime=
Set ran=%Random%
Reg copy "HKCU\Control Panel\International" "HKCU\Control Panel\International-Temp%ran%" /f
If ErrorLevel 1 GoTO :EOF
::Reset the date format to your desired output format (take effect immediately)
::Resetting the time format is useless as it only affect subsequent console windows
::Reg add "HKCU\Control Panel\International" /v sTimeFormat /d "HH_mm_ss" /f
Reg add "HKCU\Control Panel\International" /v sShortDate /d "yyyy_MM_dd" /f
::Concatenate the time and (reformatted) date strings, replace any embedded blanks with zeros
Set DateTime=%date%__%time:~0,2%_%time:~3,2%_%time:~6,2%
Set DateTime=%DateTime: =0%
::Restore the original config and delete the temp subkey, Exit if restore fails
Reg copy "HKCU\Control Panel\International-Temp%ran%" "HKCU\Control Panel\International" /f
If ErrorLevel 1 GoTO :EOF
Reg delete "HKCU\Control Panel\International-Temp%ran%" /f
Simple, straightforward and should work for all regions.
For reasons I don't understand, resetting the "sShortDate" value takes effect immediately in
a console window but resetting the very similar "sTimeFormat" value does NOT take effect
until a new console window is opened. However, the only thing changeable is the delimiter -
the digit positions are fixed.Likewise the "HH" time token is supposed to prepend leading zeros but it doesn't.
Fortunately, the workarounds are easy.