I'm essentially looking for a "@Ignore" type annotation with which I can stop a particular field from being persisted. How can this be achieved?
10 Answers
@Transient complies with your needs.
- 7,745
- 3
- 28
- 34
- 616,129
- 168
- 910
- 942
-
33But then jackson will not serialize the field when converting to JSON...how to solve? – MobileMon Jan 20 '16 at 03:44
-
that depends on your app desing. if you annotate your entity class - it applies everywhere; but if you anotate dao that use entity - it's another story. in short: use DAO when you have multiple storages – Andrii Plotnikov Jul 07 '16 at 10:31
-
Doesn't work on List fields. For Collection type fields, hibernate actually creates a new intermediate table. Any workaround for that ? – zulkarnain shah Aug 29 '17 at 09:12
-
@MobileMon You can solve it, check my answer https://stackoverflow.com/a/41850392/3871754 – Kamil Nękanowicz Jul 01 '19 at 10:48
-
1@MobileMon Preferably you shouldn't be using the same entity for both database and API purposes (single responsibility). – J_S May 06 '20 at 12:36
-
Thanks for the keyword. Static fields soved my problems both when the datatable and entity is created. https://www.objectdb.com/java/jpa/entity/fields#Transient_Fields – serdarsen Jul 01 '20 at 04:27
-
I needed to ignore a List type property for persistence, but include it in my JSON response. When I went to add a Transient annotation to my model property using Eclipse IDE, it suggested four 'Transient' options to import. This SO question/answer helped me choose the correct implementation of Transient: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/42750977/transient-annotation-org-springframework-data-annotation-transient-annotation/42753469 – Tim Nov 03 '20 at 22:08
To ignore a field, annotate it with @Transient so it will not be mapped by hibernate.
but then jackson will not serialize the field when converting to JSON.
If you need mix JPA with JSON(omit by JPA but still include in Jackson) use @JsonInclude :
@JsonInclude()
@Transient
private String token;
TIP:
You can also use JsonInclude.Include.NON_NULL and hide fields in JSON during deserialization when token == null:
@JsonInclude(JsonInclude.Include.NON_NULL)
@Transient
private String token;
- 6,254
- 7
- 34
- 51
-
4I'm running JAX-RS 2.0.1 / Jersey 2.25.1 / Jackson 2.8.7 and with that stack `@JsonInclude` is not necessary: `@Transient` fields are still included in JSON. (You still got my vote: the technique itself might be very useful in other circumstances). – Dima Korobskiy Apr 18 '17 at 16:06
-
2
-
hi,I am trying to use this,but it is not getting serialized with @Transient field – Mohammad Adil Jan 01 '19 at 06:27
-
-
1Tried this in Spring Boot 2.1.7 but didn't work. But still you get my vote because it may work in other scenarios. – Aditya Ekbote Aug 28 '19 at 11:08
-
1`@Transient` fields are only excluded when the jackson-datatype-hibernate module is on the classpath and registered with the ObjectMapper, which might be the default for a Spring Boot application with Jackson and Hibernate, and why setting `@JsonInclude` as well is optional for others. – Jan-Willem Gmelig Meyling Feb 20 '20 at 07:47
To ignore a field, annotate it with @Transient so it will not be mapped by hibernate.
Source: Hibernate Annotations.
- 35,493
- 19
- 190
- 259
- 291
- 3
- 2
This answer comes a little late, but it completes the response.
In order to avoid a field from an entity to be persisted in DB one can use one of the two mechanisms:
@Transient - the JPA annotation marking a field as not persistable
transient keyword in java. Beware - using this keyword, will prevent the field to be used with any serialization mechanism from java. So, if the field must be serialized you'd better use just the @Transient annotation.
- 5,001
- 4
- 34
- 49
-
1how about i just want to ignore the persistence on get method?. For example : myjparepository.save() wil save the model as usual , and myjparepository.find(id) will ignore the field that I want? – xtiger Feb 01 '16 at 04:15
-
@xtiger you can create a custom query to archive that functionality. Here's an example [link](https://docs.spring.io/spring-data/jpa/docs/current/reference/html/#jpa.query-methods.at-query) – Mohale May 23 '18 at 11:16
There are multiple solutions depending on the entity attribute type.
Basic attributes
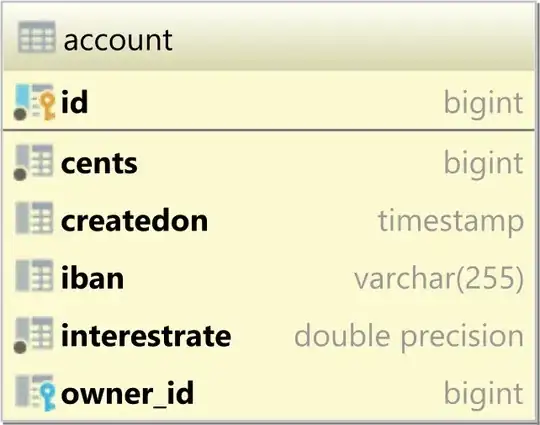
Consider you have the following account table:
The account table is mapped to the Account entity like this:
@Entity(name = "Account")
public class Account {
@Id
private Long id;
@ManyToOne
private User owner;
private String iban;
private long cents;
private double interestRate;
private Timestamp createdOn;
@Transient
private double dollars;
@Transient
private long interestCents;
@Transient
private double interestDollars;
@PostLoad
private void postLoad() {
this.dollars = cents / 100D;
long months = createdOn.toLocalDateTime()
.until(LocalDateTime.now(), ChronoUnit.MONTHS);
double interestUnrounded = ( ( interestRate / 100D ) * cents * months ) / 12;
this.interestCents = BigDecimal.valueOf(interestUnrounded)
.setScale(0, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_EVEN).longValue();
this.interestDollars = interestCents / 100D;
}
//Getters and setters omitted for brevity
}
The basic entity attributes are mapped to table columns, so properties like id, iban, cents are basic attributes.
But the dollars, interestCents, and interestDollars are computed properties, so you annotate them with @Transient to exclude them from SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE SQL statements.
So, for basic attributes, you need to use
@Transientin order to exclude a given property from being persisted.
Associations
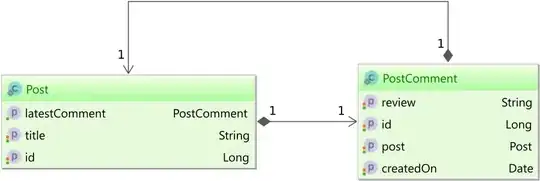
Assuming you have the following post and post_comment tables:
You want to map the latestComment association in the Post entity to the latest PostComment entity that was added.
To do that, you can use the @JoinFormula annotation:
@Entity(name = "Post")
@Table(name = "post")
public class Post {
@Id
private Long id;
private String title;
@ManyToOne(fetch = FetchType.LAZY)
@JoinFormula("(" +
"SELECT pc.id " +
"FROM post_comment pc " +
"WHERE pc.post_id = id " +
"ORDER BY pc.created_on DESC " +
"LIMIT 1" +
")")
private PostComment latestComment;
//Getters and setters omitted for brevity
}
When fetching the Post entity, you can see that the latestComment is fetched, but if you want to modify it, the change is going to be ignored.
So, for associations, you can use
@JoinFormulato ignore the write operations while still allowing reading the association.
@MapsId
Another way to ignore associations that are already mapped by the entity identifier is to use @MapsId.
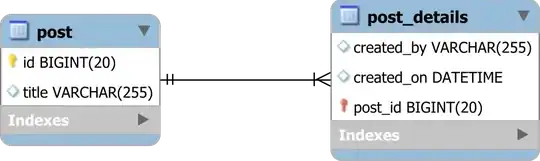
For instance, consider the following one-to-one table relationship:
The PostDetails entity is mapped like this:
@Entity(name = "PostDetails")
@Table(name = "post_details")
public class PostDetails {
@Id
private Long id;
@Column(name = "created_on")
private Date createdOn;
@Column(name = "created_by")
private String createdBy;
@OneToOne(fetch = FetchType.LAZY)
@MapsId
private Post post;
public PostDetails() {}
public PostDetails(String createdBy) {
createdOn = new Date();
this.createdBy = createdBy;
}
//Getters and setters omitted for brevity
}
Notice that both the id attribute and the post association map the same database column, which is the post_details Primary Key column.
To exclude the id attribute, the @MapsId annotation will tell Hibernate that the post association takes care of the table Primary Key column value.
So, when the entity identifier and an association share the same column, you can use
@MapsIdto ignore the entity identifier attribute and use the association instead.
Using insertable = false, updatable = false
Another option is to use insertable = false, updatable = false for the association which you want to be ignored by Hibernate.
For instance, we can map the previous one-to-one association like this:
@Entity(name = "PostDetails")
@Table(name = "post_details")
public class PostDetails {
@Id
@Column(name = "post_id")
private Long id;
@Column(name = "created_on")
private Date createdOn;
@Column(name = "created_by")
private String createdBy;
@OneToOne
@JoinColumn(name = "post_id", insertable = false, updatable = false)
private Post post;
//Getters and setters omitted for brevity
public void setPost(Post post) {
this.post = post;
if (post != null) {
this.id = post.getId();
}
}
}
The insertable and updatable attributes of the @JoinColumn annotation will instruct Hibernate to ignore the post association since the entity identifier takes care of the post_id Primary Key column.
- 142,745
- 71
- 566
- 911
-
_Notice that both the id attribute and the post association map the same database column, which is the post_comment Primary Key column._ Is this correct in context of `post` and `post_details` tables as example? – David Mar 20 '20 at 18:49
-
1
-
I tried all of these with DB2 and the only one that I could get to work with the DB2 database is @JoinColumn. PrimaryKeyColumn also did not work. Mostly the generated generated SQL was incorrect. – Cummings Dec 09 '20 at 20:44
-
Thanks for this excellent and exhaustive answer! In the `@MapsId` example, the screenshot shows a `post_id` column, and the code example the `@Id private Long id` and `@OneToOne(fetch = FetchType.LAZY) @MapsId private Post post;` attributes. To make the code example consistent with the screenshot, shouldn't the id-attribute be `@Id private Long post_id`? Maybe I'm missing something, because I don't understand how Hibenate would use the DB column `post_id` (see screenshot) without annotating field `post` with `@JoinColumn(name="post_id")`. – t0r0X Aug 05 '22 at 10:46
-
If you test it, you'll see it works just fine because the id name is taken from the relationship. – Vlad Mihalcea Aug 07 '22 at 12:16
Sometimes you want to:
- Serialize a column
- Ignore column from being persisted:
Use @Column(name = "columnName", insertable = false, updatable = false)
A good scenario is when a certain column is automatically calculated by using other column values
- 201
- 3
- 4
-
-
1This is the best solution for me: I want to ignore the column during EntityManager operations but still use it to automatically create the schema – xtian Aug 25 '21 at 10:57
use @Transient to make JPA ignoring the field.
but! Jackson will not serialize that field as well. to solve just add @JsonProperty
an example
@Transient
@JsonProperty
private boolean locked;
- 1,752
- 18
- 17
To complete the above answers, I had the case using an XML mapping file where neither the @Transient nor transient worked...
I had to put the transient information in the xml file:
<attributes>
(...)
<transient name="field" />
</attributes>
- 2,549
- 3
- 22
- 23
None of the above answers worked for me using Hibernate 5.2.10, Jersey 2.25.1 and Jackson 2.8.9. I finally found the answer (sort of, they reference hibernate4module but it works for 5 too) here. None of the Json annotations worked at all with @Transient. Apparently Jackson2 is 'smart' enough to kindly ignore stuff marked with @Transient unless you explicitly tell it not to. The key was to add the hibernate5 module (which I was using to deal with other Hibernate annotations) and disable the USE_TRANSIENT_ANNOTATION feature in my Jersey Application:
ObjectMapper jacksonObjectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
Hibernate5Module jacksonHibernateModule = new Hibernate5Module();
jacksonHibernateModule.disable(Hibernate5Module.Feature.USE_TRANSIENT_ANNOTATION);
jacksonObjectMapper.registerModule(jacksonHibernateModule);
Here is the dependency for the Hibernate5Module:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-datatype-hibernate5</artifactId>
<version>2.8.9</version>
</dependency>
- 614
- 9
- 17
-
After trying every other method mention above and others `@JsonProperty` `@JsonInclude` `@JsonSerialize + @JsonDeserialize` `mapper.configure(MapperFeature.PROPAGATE_TRANSIENT_MARKER, false));` this solution finally worked. Thanks! – Aceonline Oct 11 '17 at 11:32
Apparently, using Hibernate5Module, the @Transient will not be serialize if using ObjectMapper. Removing will make it work.
import javax.persistence.Transient;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonInclude.Include;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j
public class TransientFieldTest {
@Test
public void Print_Json() throws JsonProcessingException {
ObjectMapper objectEntityMapper = new ObjectMapper();
//objectEntityMapper.registerModule(new Hibernate5Module());
objectEntityMapper.setSerializationInclusion(Include.NON_NULL);
log.info("object: {}", objectEntityMapper.writeValueAsString( //
SampleTransient.builder()
.id("id")
.transientField("transientField")
.build()));
}
@Getter
@Setter
@Builder
private static class SampleTransient {
private String id;
@Transient
private String transientField;
private String nullField;
}
}
- 21
- 1