I'm trying to simulate a realistic key press event. For that reason I'm using SendInput() method, but for greater result I need to specify the delay between keyDOWN and KeyUP events! These numbers below show the elapsed time in milliseconds between DOWN and UP events (these are real/valid):
96 95 112 111 119 104 143 96 95 104 120 112 111 88 104 119 111 103 95 104 95 127 112 143 144 142 143 128 144 112 111 112 120 128 111 135 118 147 96 135 103 64 64 87 79 112 88 111 111 112 111 104 87 95
We can simplify the output:
delay 64 - 88 ms -> 20% of a time
delay 89 - 135 ms -> 60% of a time
delay 136 - 150 ms -> 20 % of a time
How do I trigger an event according to probabilities from above? Here is the code I'm using right now:
private void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
textBox2.Focus();
Random r = new Random();
int rez = r.Next(0, 5); // 0,1,2,3,4 - five numbers total
if (rez == 0) // if 20% (1/5)
{
Random r2 = new Random();
textBox2.AppendText(" " + rez + " " + r2.Next(64, 88) + Environment.NewLine);
// do stuff
}
else if (rez == 4)//if 20% (1/5)
{
Random r3 = new Random();
textBox2.AppendText(" " + rez + " " + r3.Next(89, 135) + Environment.NewLine);
// do stuff
}
else // if 1 or 2 or 3 (3/5) -> 60%
{
Random r4 = new Random();
textBox2.AppendText(" " + rez + " " + r4.Next(136, 150) + Environment.NewLine);
// do stuff
}
}
There is a huge problem with this code. In theory, after millions of iterations - the resulting graph will look similar to this:
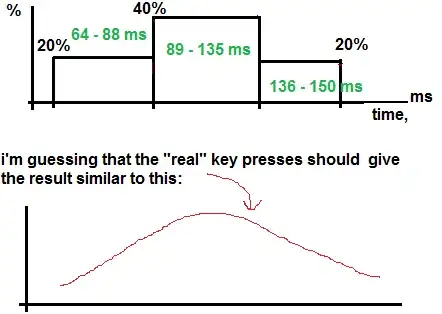
How to deal with this problem?
EDIT: the solution was to use distribution as people suggested.
here is java implementation of such code:
http://docs.oracle.com/javase/1.4.2/docs/api/java/util/Random.html#nextGaussian%28%29
and here is C# implementation:
How to generate normally distributed random from an integer range?
although I'd suggest to decrease the value of "deviations" a little.
here is interesting msdn article
http://blogs.msdn.com/b/ericlippert/archive/2012/02/21/generating-random-non-uniform-data-in-c.aspx
everyone thanks for help!