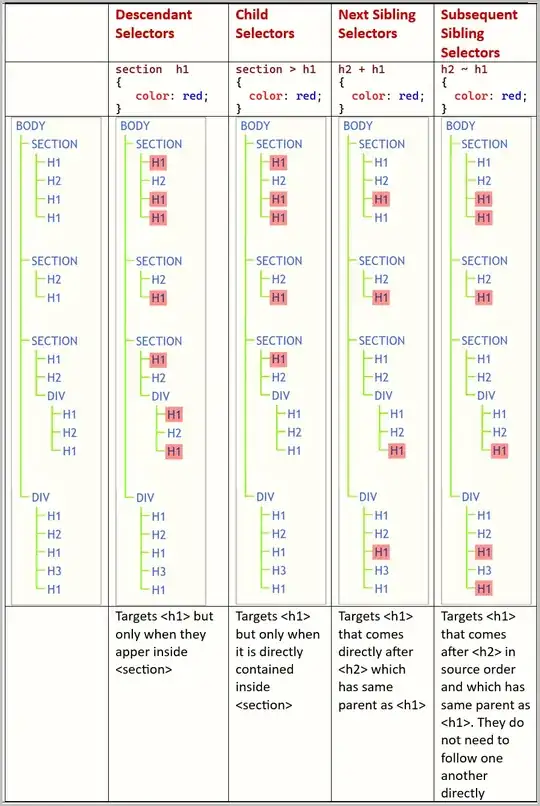
I am a bit confused between these 2 selectors.
Does the descendent selector:
div p
select all p within a div whether or not it's an immediate descedent? So if the p is inside another div it will still be selected?
Then the child selector:
div > p
Whats the difference? Does a child mean immediate child? Eg.
<div><p>
vs
<div><div><p>
will both be selected, or not?