I would like to know how to loop through each line in a text file using a Windows batch file and process each line of text in succession.
12 Answers
I needed to process the entire line as a whole. Here is what I found to work.
for /F "tokens=*" %%A in (myfile.txt) do [process] %%A
The tokens keyword with an asterisk (*) will pull all text for the entire line. If you don't put in the asterisk it will only pull the first word on the line. I assume it has to do with spaces.
If there are spaces in your file path, you need to use usebackq. For example.
for /F "usebackq tokens=*" %%A in ("my file.txt") do [process] %%A
- 6,511
- 28
- 39
- 51
- 7,885
- 5
- 28
- 33
-
47A minor addition: to make this work from the command line interactively, replace `%%A` with `%A` in the above command. Otherwise you'll get `%%A was unexpected at this time.`. – vadipp Nov 12 '12 at 12:02
-
25FYI, if you need to do a multi-line command, after "DO" you can put an open parenthesis "(" and a few lines later, end it with a close parenthesis ")" -- and you can just put your code block inside those (indented to your tastes). – BrainSlugs83 Jan 27 '13 at 04:49
-
If you have issues with files in the same folder with nested batch files, or files that have spaces in their names, look at my solution below. – Marvin Thobejane Mar 10 '14 at 12:04
-
6Thanks for that pattern. I have found that I can't put quotes(") around a the file name -- For file names with spaces just gives me the file name. E.g. `for /F "tokens=*" %%A in ("myfile.txt") do echo A = %%A` --> `A = myfile.txt`. Any ideas how to thwart this? – will Apr 19 '16 at 02:52
-
2Make sure the file you working is encoded in ANSI or UTF8. I was scratching my head as to why this wasn't working until I tried viewing the file using the TYPE command and output wasn't what I was expecting. At this point I noticed the file had been encoded in "UCS-2 BE BOM" for some reason! – Dan Stevens May 03 '16 at 15:49
-
Remember variables in batch file should be in UPPERCASE , I was trying `for /F "tokens=*" %%Region in (RegionsFile.txt) do echo %%Region` and it was throwing `%Region was unexpected at this time` – Shrikant Prabhu Oct 14 '16 at 00:43
-
Lines in file to process should end in '\n' instead of just '\r'. My .bat file was failing, opened the file in text editor and it looked fine. After a while realised it failed because wrong line endings. – Ricardo stands with Ukraine May 06 '18 at 05:38
-
@will It is a late response but for that case you would need to use `usebackq`. For example; `for /F "usebackq tokens=*" %%A in ("myfile.txt") do echo A = %%A` – Dan Jun 25 '18 at 08:31
-
@Dan ... thanks mate, yes I've come across `usebackq` in the past. You are absolutely right for the general case. My use-case is just to define some environment variables based on the existing `set` environment. Luckily, I didn't need to go that far. I'm glad your reminded, I'll put a comment for when I come back to _extend_ or _clone_ the script. – will Jun 26 '18 at 12:00
-
@will ... One follow-up point. After a few _experiences_ with that script pattern, I've decided to name the input _`source`-d_ file I'm reading with `for /F ...` as: "**`.src`**" extension, for "_soruce_". That way I can also have `xxx.cmd` that runs from a shortcut: `cmd /k xxx.cmd`, and executes a corresponding: `xxx.src` ... When needs be. – will Jun 26 '18 at 12:04
-
If you find this answer not working, check the encoding of the file you're trying to loop through. I've had issues with some of the less common encodings. UTF-8 is _usually_ safe to convert to. – kayleeFrye_onDeck Nov 12 '18 at 21:27
-
4It's worth pointing out that the index parameter in your loop must be a single character. So for example %%i is fine but %%index will fail. – Vincent Mar 06 '20 at 20:12
-
1This doesn't work for lines in file starting with semicolon ; and blank lines. – Zimba Apr 15 '20 at 03:25
From the Windows command line reference:
To parse a file, ignoring commented lines, type:
for /F "eol=; tokens=2,3* delims=," %i in (myfile.txt) do @echo %i %j %k
This command parses each line in Myfile.txt, ignoring lines that begin with a semicolon and passing the second and third token from each line to the FOR body (tokens are delimited by commas or spaces). The body of the FOR statement references %i to get the second token, %j to get the third token, and %k to get all of the remaining tokens.
If the file names that you supply contain spaces, use quotation marks around the text (for example, "File Name"). To use quotation marks, you must use usebackq. Otherwise, the quotation marks are interpreted as defining a literal string to parse.
By the way, you can find the command-line help file on most Windows systems at:
"C:\WINDOWS\Help\ntcmds.chm"
- 60,973
- 31
- 151
- 169
-
9to [clarify](http://ss64.com/nt/for_cmd.html) the _"to use quotation marks, you must use `usebackq`"_: `for /f "usebackq" %%a in ("Z:\My Path Contains Spaces\xyz\abc.txt")` – drzaus Feb 21 '14 at 16:15
-
In a Batch File you MUST use %% instead of % : (Type help for)
for /F "tokens=1,2,3" %%i in (myfile.txt) do call :process %%i %%j %%k
goto thenextstep
:process
set VAR1=%1
set VAR2=%2
set VAR3=%3
COMMANDS TO PROCESS INFORMATION
goto :EOF
What this does: The "do call :process %%i %%j %%k" at the end of the for command passes the information acquired in the for command from myfile.txt to the "process" 'subroutine'.
When you're using the for command in a batch program, you need to use double % signs for the variables.
The following lines pass those variables from the for command to the process 'sub routine' and allow you to process this information.
set VAR1=%1
set VAR2=%2
set VAR3=%3
I have some pretty advanced uses of this exact setup that I would be willing to share if further examples are needed. Add in your EOL or Delims as needed of course.
- 10,997
- 11
- 73
- 124
- 381
- 3
- 2
Improving the first "FOR /F.." answer: What I had to do was to call execute every script listed in MyList.txt, so it worked for me:
for /F "tokens=*" %A in (MyList.txt) do CALL %A ARG1
--OR, if you wish to do it over the multiple line:
for /F "tokens=*" %A in (MuList.txt) do (
ECHO Processing %A....
CALL %A ARG1
)
Edit: The example given above is for executing FOR loop from command-prompt; from a batch-script, an extra % needs to be added, as shown below:
---START of MyScript.bat---
@echo off
for /F "tokens=*" %%A in ( MyList.TXT) do (
ECHO Processing %%A....
CALL %%A ARG1
)
@echo on
;---END of MyScript.bat---
- 557
- 8
- 10
@MrKraus's answer is instructive. Further, let me add that if you want to load a file located in the same directory as the batch file, prefix the file name with %~dp0. Here is an example:
cd /d %~dp0
for /F "tokens=*" %%A in (myfile.txt) do [process] %%A
NB:: If your file name or directory (e.g. myfile.txt in the above example) has a space (e.g. 'my file.txt' or 'c:\Program Files'), use:
for /F "tokens=*" %%A in ('type "my file.txt"') do [process] %%A
, with the type keyword calling the type program, which displays the contents of a text file. If you don't want to suffer the overhead of calling the type command you should change the directory to the text file's directory. Note that type is still required for file names with spaces.
I hope this helps someone!
- 1
- 1
- 2,010
- 1
- 19
- 13
-
There's no need to prefix the filename as the batch file will look in the current folder by default. – foxidrive May 28 '13 at 12:56
-
1@foxidrive: Okay, I hear you. Although care should be taken. For example if a directory was changed it would look in that directory rather than the one the batch file is in. The solution then would be calling `**cd /d %~dp0**` before the for loop. This would make sure you are referencing a file in the directory the batch file is in. Thanks for the observation – Marvin Thobejane Jul 18 '13 at 12:01
-
3
-
I can't get the `type` work around working, I've had to quote my filename because it's in a different directory that contains spaces(Damn you `Program Files`). I'm getting an error `The system cannot find the file \`type.` – scragar Jul 03 '14 at 15:48
-
1@scragar, have you got the right quote? it needs to be a ' not a `. On my keyboard it's on the same key as @ – FrinkTheBrave Jul 10 '14 at 14:17
-
@FrinkTheBrave That was the issue, it's backticks in the answer, so I assumed that was correct, thanks. – scragar Jul 10 '14 at 14:24
-
@scragar or you can use the `usebackq` option of the for loop. the code would start with `for /F "usebackq tokens=*"` then you can use backquotes around the command, single quotes around strings and double quotes around file paths. – robotik Sep 06 '16 at 16:42
-
@foxidrive: in Win 10 batch file doesn't look in current folder by default. Instead it looks at folder registered in Win Registry. Default is user homedir. – Zimba Apr 15 '20 at 03:15
The accepted answer is good, but has two limitations.
It drops empty lines and lines beginning with ;
To read lines of any content, you need the delayed expansion toggling technic.
@echo off
SETLOCAL DisableDelayedExpansion
FOR /F "usebackq delims=" %%a in (`"findstr /n ^^ text.txt"`) do (
set "var=%%a"
SETLOCAL EnableDelayedExpansion
set "var=!var:*:=!"
echo(!var!
ENDLOCAL
)
Findstr is used to prefix each line with the line number and a colon, so empty lines aren't empty anymore.
DelayedExpansion needs to be disabled, when accessing the %%a parameter, else exclamation marks ! and carets ^ will be lost, as they have special meanings in that mode.
But to remove the line number from the line, the delayed expansion needs to be enabled.
set "var=!var:*:=!" removes all up to the first colon (using delims=: would remove also all colons at the beginning of a line, not only the one from findstr).
The endlocal disables the delayed expansion again for the next line.
The only limitation is now the line length limit of ~8191, but there seems no way to overcome this.
- 78,592
- 17
- 171
- 225
-
Win 10 doesn't allow `setlocal` on commandline. When I run code on CMD, I get !var! instead of blanks. How to fix? – Zimba Apr 15 '20 at 03:11
-
line length limit can be overcome by splitting file to temp files of max line length 8190 before processing. Then recombined to one file. – Zimba Apr 15 '20 at 06:10
-
Zimba:- I think you want to create a batch file and paste the entire code snippet. I am sure you figure this out already. Yet, it might help the next person. Jeb:- The echo line currently reads:- echo (!var! I think it should read:- echo !var! I am not sure why we will need to emit the extra ( Nice One. Thanks for placing in the public domain duds like me. – Daniel Adeniji Oct 20 '21 at 23:46
-
1@DanielAdeniji `echo(!var!` is correct (without spaces), it avoids problems with content in var like `ON`, `OFF` or `/?` See also: [ECHO. FAILS to give text or blank line - Instead use ECHO/](https://www.dostips.com/forum/viewtopic.php?p=4554#p4554) – jeb Oct 21 '21 at 08:41
-
1
Or, you may exclude the options in quotes:
FOR /F %%i IN (myfile.txt) DO ECHO %%i
- 1,224
- 2
- 14
- 31
-
1Two percent signs next to each other %% are treated like a single percent sign in a command (not a batch file). – Paul Feb 24 '18 at 08:09
Here's a bat file I wrote to execute all SQL scripts in a folder:
REM ******************************************************************
REM Runs all *.sql scripts sorted by filename in the current folder.
REM To use integrated auth change -U <user> -P <password> to -E
REM ******************************************************************
dir /B /O:n *.sql > RunSqlScripts.tmp
for /F %%A in (RunSqlScripts.tmp) do osql -S (local) -d DEFAULT_DATABASE_NAME -U USERNAME_GOES_HERE -P PASSWORD_GOES_HERE -i %%A
del RunSqlScripts.tmp
-
You could get rid of the temp file by letting the for loop work on the dir command. `for /F %%A in ('dir /B /O:n *.sql') do osql...`. Note the single quotes around the dir command. – JMichael Jan 12 '23 at 08:24
If you have an NT-family Windows (one with cmd.exe as the shell), try the FOR /F command.
- 39,422
- 4
- 33
- 40
The accepted anwser using cmd.exe and
for /F "tokens=*" %F in (file.txt) do whatever "%F" ...
works only for "normal" files. It fails miserably with huge files.
For big files, you may need to use Powershell and something like this:
[IO.File]::ReadLines("file.txt") | ForEach-Object { whatever "$_" }
or if you have enough memory:
foreach($line in [System.IO.File]::ReadLines("file.txt")) { whatever "$line" }
This worked for me with a 250 MB file containing over 2 million lines, where the for /F ... command got stuck after a few thousand lines.
For the differences between foreach and ForEach-Object, see Getting to Know ForEach and ForEach-Object.
(credits: Read file line by line in PowerShell )
- 13,452
- 5
- 76
- 69
Modded examples here to list our Rails apps on Heroku - thanks!
cmd /C "heroku list > heroku_apps.txt"
find /v "=" heroku_apps.txt | find /v ".TXT" | findstr /r /v /c:"^$" > heroku_apps_list.txt
for /F "tokens=1" %%i in (heroku_apps_list.txt) do heroku run bundle show rails --app %%i
Full code here.
- 372
- 4
- 5
-
Per [comment to another question above](http://stackoverflow.com/questions/155932/random-string-to-show-comment-highlighting#comment47265_155954) - You can skip the file creation/reading and just use `for /f "tokens=1" %%i in ('find /v "=" heroku_apps.txt ^| find /v ".TXT" ^| findstr /r /v /c:"^$"') do...` (Note the addition of `^`'s used to escape the pipe, so that it is passed to the `for` and not directly to the command processor) – user66001 Feb 03 '13 at 09:13
To print all lines in text file from command line (with delayedExpansion):
set input="path/to/file.txt"
for /f "tokens=* delims=[" %i in ('type "%input%" ^| find /v /n ""') do (
set a=%i
set a=!a:*]=]!
echo:!a:~1!)
Works with leading whitespace, blank lines, whitespace lines.
Tested on Win 10 CMD
- 2,854
- 18
- 26
-
God try, but your first sample removes leading `]]]` from lines, the second sample drops empty lines and lines beginning with space – jeb Feb 02 '20 at 11:58
-
The 2nd one is meant to remove blank lines. 1st one could modify `delims` if any lines in text file begins with `]` eg. replace with some character that doesn't, or a control character like backspace or bell; they're not normally found in text files. The reason for `delims=]` is to remove placeholders created by `/n` of `find` command to preserve blank lines. – Zimba Feb 02 '20 at 16:43
-
@jeb: bracket ]]] problem fixed. See update, to print all lines in text file. Works on Win 10 CMD too. – Zimba Apr 15 '20 at 05:44
-
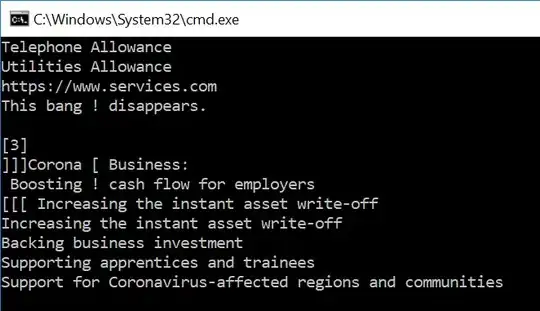
But now it fails with exclamation marks in the text, like `This bang ! disappears`. Btw, you don't need the `delim=[` because `set a=!a:*]=]!` would remove it too, and `echo:!a:~1!` is not necessary, you could change your replacement to `set a=!a:*]=!` – jeb Oct 06 '20 at 06:25
-
@jeb: Just checked, still works even with exclamations. See scnshot in edit. Do you have delayed expansion on? The idea for `delim=[` was to preserve lines with whitespace only, which is to be removed with `set a=!a:*]=]!` since it's not part of content. Reason for `set a=!a:*]=]!` is `set a=!a:*]=!` didn't work in initial testing. Both works now in the final code with the right `echo` format. – Zimba Oct 06 '20 at 13:42
-
You are right, my bang test string works on the command line (it was too simple), but these new ones all fail `The caret ^ is removed, but the bang ! stays`, `Use !cd! or %cd%` and `\..\..\..\windows\system32\calc.exe` – jeb Oct 07 '20 at 08:41
-
The `calc.exe` line works ok for me. The caret & cd lines can be fixed with `"`, `^` & string substitution (in my case), but like other implementations of CMD would need a specialized solution for the OS it's run on. BTW, the `!cd!` problem extends to any valid variable eg. `%windir%` or `!windir!`. – Zimba Oct 07 '20 at 15:18
-
The `calc.exe` bug depends on your windows dir and in which dir you start the code (same drive and directory depth), but can be easily solved by using `echo(!var!`. The other problems are not trivial to solve, as it's the delayed expansion behavior. – jeb Oct 07 '20 at 17:10
-
The calc.exe line works ok for me, not a bug. The caret & cd lines I fixed with ", ^ & string substitution, and may not work for all flavors of CMD – Zimba Oct 08 '20 at 14:55