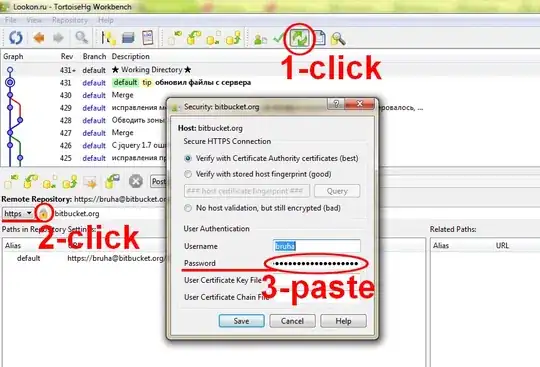
Both existing answers suggest storing your username and password unencrypted in plain-text, which is a bit of a no-no.
You should use the Keyring extension instead, as it has been specifically designed for securely saving authentication passwords. It already comes bundled with TortoiseHg, so all you have to do is activate it by writing the following in your mercurial.ini file:
[extensions]
mercurial_keyring=
You will also have to associate your username with the push url by editing your repository-specific .hg\hgrc file like in the example below:
[paths]
default = https://<your_username>@bitbucket.org/tortoisehg/thg
For more details on associating your username with the url, see the Repository Configuration (SMTP) section of the Keyring extension page.