I'm experimenting with OpenCV and Python's bindings. This code is intended to rotate an image with a command line argument value. However, it is saving as an exact copy of the input image, with no rotation whatsoever.
This code is adapted from this answer
import cv2 as cv
def rotateImage(self, image, angle):
print "Rotating image to angle: %s" % (angle)
print type(image) #image is numpy.ndarray
print type(angle) #angle is float
center = tuple(np.array(image.shape[0:2])/2)
matrix = cv.getRotationMatrix2D(center, angle, 1.0)
rotate = cv.warpAffine(image, matrix, image.shape[0:2], flags=cv.INTER_LINEAR)
fileList = self.filename.split(".")
newFile = fileList[0] + "_rotate_%s." % (int(angle)) + fileList[1]
print "Saving to %s" % (newFile)
cv.imwrite(newFile, rotate)
My issue is the image saved after rotation isn't the one being input.
Input image: 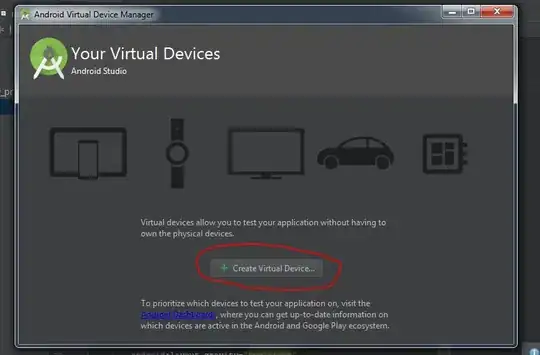
Output: 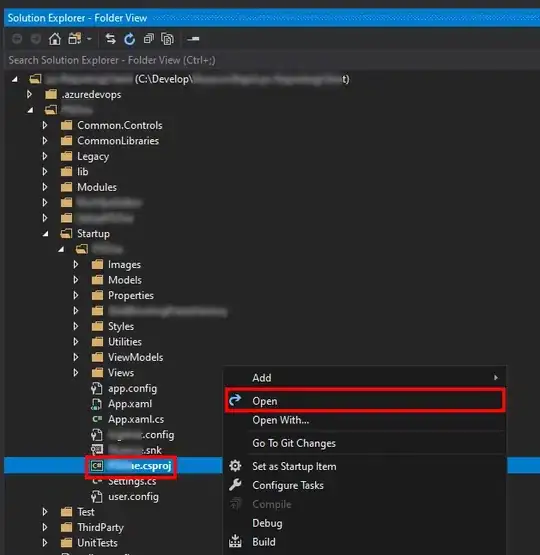
Given these input and output, how can I alter the image dimensions to allow for 30 and 45 degree rotations?