How do I display the current date and time in an Android application?
23 Answers
Okay, not that hard as there are several methods to do this. I assume you want to put the current date & time into a TextView.
String currentDateTimeString = java.text.DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance().format(new Date());
// textView is the TextView view that should display it
textView.setText(currentDateTimeString);
There is more to read in the documentation that can easily be found here . There you'll find more information on how to change the format used for conversion.
- 30,998
- 16
- 147
- 256
- 10,451
- 11
- 42
- 58
-
43Please - be more explicit! What's the error? Did you import the wrong DateFormat class? It's `java.text.DateFormat` and NOT `android.text.format.DateFormat`! And it's `java.util.Date` and NOT `java.sql.Date`! Just a little hint on asking questions: try to be precise, e.g.: declare what you mean by "display" in your question. And when you type in my lines - both Date and DateFormat must, of course, be imported - if there's a choice of 2 for each, the least you could try is any combination: it's just 4! – Zordid Feb 16 '10 at 11:08
-
sorry sir, i got date not time.similarly can we get time ? – BIBEKRBARAL Feb 17 '10 at 06:30
-
28Have a look at http://developer.android.com/reference/java/text/SimpleDateFormat.html - there you can see how to define **exactly** what you want to be in your output string. E.g. for time use `"HH:mm:ss"`! Completely: `currentTimeString = new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss").format(new Date());` – Zordid Feb 17 '10 at 08:14
-
2There's also `DateFormat.getTimeInstance()` and `DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance()`. – Felix Jun 20 '11 at 14:15
-
How efficient is this? Let's say you need to get time from a constantly firing method. Is there anything more efficient than creating a new Date object each time? – keshav.bahadoor Jun 25 '16 at 20:24
public class XYZ extends Activity {
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
//setContentView(R.layout.main);
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
System.out.println("Current time => "+c.getTime());
SimpleDateFormat df = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
String formattedDate = df.format(c.getTime());
// formattedDate have current date/time
Toast.makeText(this, formattedDate, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
// Now we display formattedDate value in TextView
TextView txtView = new TextView(this);
txtView.setText("Current Date and Time : "+formattedDate);
txtView.setGravity(Gravity.CENTER);
txtView.setTextSize(20);
setContentView(txtView);
}
}

-
2android.os.Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.N (24). – kangear Feb 10 '17 at 07:57
-
How to declare `SimpleDateFormat` because I have got can not find symbol class – dubis Aug 11 '17 at 08:36
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
Thread myThread = null;
Runnable runnable = new CountDownRunner();
myThread= new Thread(runnable);
myThread.start();
}
public void doWork() {
runOnUiThread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try{
TextView txtCurrentTime= (TextView)findViewById(R.id.lbltime);
Date dt = new Date();
int hours = dt.getHours();
int minutes = dt.getMinutes();
int seconds = dt.getSeconds();
String curTime = hours + ":" + minutes + ":" + seconds;
txtCurrentTime.setText(curTime);
}catch (Exception e) {}
}
});
}
class CountDownRunner implements Runnable{
// @Override
public void run() {
while(!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()){
try {
doWork();
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}catch(Exception e){
}
}
}
}
- 310,957
- 84
- 592
- 636
- 537
- 4
- 2
-
@Harshit this function comes with the Android SDK as long as your class extends Activity – Carlos P Jan 08 '12 at 16:24
-
2I know this is old question, but if somebody will find it in google like me, he should know that the methods Date.getX are deprecated. – tobi Jul 20 '12 at 09:28
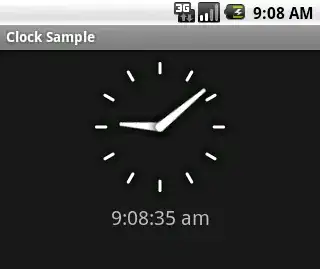
The obvious choices for displaying the time are the AnalogClock View and the DigitalClock View.
For example, the following layout:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<AnalogClock
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<DigitalClock
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center"
android:textSize="20sp"/>
</LinearLayout>
Looks like this:
- 1
- 1
- 190,537
- 57
- 313
- 299
-
4
-
5I feel like a stupid shit after reading this obvious answer! I implemented my own runnable, putting it to sleep for a given amount of time and so on when the obvious answer was a XML-one-liner! Many thanks (more than a year after your post) :-) – dbm Feb 22 '11 at 08:08
-
6In 2015 it's deprecated and It is recommended you use TextClock instead. :) – Evilripper Feb 27 '15 at 09:45
-
1AnalogClock is deprecated in API level 23. and AnalogClock and DigitalClock only show current time, but not current date. – Zafer Mar 23 '18 at 19:14
In case you want a single line of code:
String date = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(Calendar.getInstance().getTime());
The result is "2016-09-25 16:50:34"
- 30,738
- 21
- 105
- 131
- 1,905
- 1
- 17
- 30
My own working solution:
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
String sDate = c.get(Calendar.YEAR) + "-"
+ c.get(Calendar.MONTH)
+ "-" + c.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH)
+ " at " + c.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY)
+ ":" + c.get(Calendar.MINUTE);
Hope this helps!
-
I wonder why c.get(Calendar.MONTH) returns 5 when it is supposedly 6? My device has correct time settings. – Kris Jun 09 '11 at 10:45
-
Oh yeah, but why do they have to do that when the other variables were accurate. :) – Kris Jun 13 '11 at 06:11
-
1Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance(); int month = c.get(Calendar.MONTH) + 1; String sDate = month + "-" + c.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH) + "-" + c.get(Calendar.YEAR) + "-" + c.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY) + ":" + c.get(Calendar.MINUTE); that works fine – user577732 Jul 01 '11 at 03:27
If you want to get the date and time in a specific pattern you can use
Date d = new Date();
CharSequence s = DateFormat.format("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss", d.getTime());
- 5,669
- 7
- 58
- 90
From How to get full date with correct format?:
Please, use
android.text.format.DateFormat.getDateFormat(Context context)
android.text.format.DateFormat.getTimeFormat(Context context)
to get valid time and date formats in sense of current user settings (12/24 time format, for example).
import android.text.format.DateFormat;
private void some() {
final Calendar t = Calendar.getInstance();
textView.setText(DateFormat.getTimeFormat(this/*Context*/).format(t.getTime()));
}
- 1
- 1
- 7,227
- 3
- 36
- 39
Here is the code which worked for me. Please try this. It is a simple method which takes time and date from a system call.
public static String getDatetime() {
Calendar c = Calendar .getInstance();
System.out.println("Current time => "+c.getTime());
SimpleDateFormat df = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mms");
String formattedDate = df.format(c.getTime());
return formattedDate;
}
- 2,976
- 2
- 22
- 43
- 127
- 2
- 11
Use:
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
int seconds = c.get(Calendar.SECOND);
int minutes = c.get(Calendar.MINUTE);
int hour = c.get(Calendar.HOUR);
String time = hour + ":" + minutes + ":" + seconds;
int day = c.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);
int month = c.get(Calendar.MONTH);
int year = c.get(Calendar.YEAR);
String date = day + "/" + month + "/" + year;
// Assuming that you need date and time in a separate
// textview named txt_date and txt_time.
txt_date.setText(date);
txt_time.setText(time);
- 30,738
- 21
- 105
- 131
- 89
- 1
- 2
String formattedDate = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(Calendar.getInstance().getTime());
Use formattedDate as your String filled with the date.
In my case: mDateButton.setText(formattedDate);
- 4,115
- 6
- 33
- 42
- 71
- 1
- 1
Actually, you're best off with the TextClock widget. It handles all of the complexity for you and will respect the user's 12/24hr preferences. http://developer.android.com/reference/android/widget/TextClock.html
- 1,239
- 1
- 13
- 20
To display the current date function:
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
SimpleDateFormat df = new SimpleDateFormat("dd-MMM-yyyy");
String date = df.format(c.getTime());
Date.setText(date);
You must want to import
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.util.Calendar;
You must want to use
TextView Date;
Date = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.Date);
- 2,231
- 3
- 23
- 34
- 101
- 1
- 7
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
int month=c.get(Calendar.MONTH)+1;
String sDate = c.get(Calendar.YEAR) + "-" + month+ "-" + c.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH) +
"T" + c.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY)+":"+c.get(Calendar.MINUTE)+":"+c.get(Calendar.SECOND);
This will give date time format like 2010-05-24T18:13:00
- 658
- 8
- 7
Simply copy this code and hope this works fine for you.
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("dd:MMMM:yyyy HH:mm:ss a");
String strDate = sdf.format(c.getTime());
- 1,894
- 3
- 17
- 35
This would give the current date and time:
public String getCurrDate()
{
String dt;
Date cal = Calendar.getInstance().getTime();
dt = cal.toLocaleString();
return dt;
}
- 30,738
- 21
- 105
- 131
- 83
- 1
- 2
Try the below code:
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat(
"yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss");
Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance();
System.out.println("time => " + dateFormat.format(cal.getTime()));
String time_str = dateFormat.format(cal.getTime());
String[] s = time_str.split(" ");
for (int i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
System.out.println("date => " + s[i]);
}
int year_sys = Integer.parseInt(s[0].split("/")[0]);
int month_sys = Integer.parseInt(s[0].split("/")[1]);
int day_sys = Integer.parseInt(s[0].split("/")[2]);
int hour_sys = Integer.parseInt(s[1].split(":")[0]);
int min_sys = Integer.parseInt(s[1].split(":")[1]);
System.out.println("year_sys => " + year_sys);
System.out.println("month_sys => " + month_sys);
System.out.println("day_sys => " + day_sys);
System.out.println("hour_sys => " + hour_sys);
System.out.println("min_sys => " + min_sys);
- 30,738
- 21
- 105
- 131
- 37,851
- 12
- 116
- 113
String currentDateandTime = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date());
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), currentDateandTime, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
- 1,794
- 20
- 37
You Can try this way
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
SimpleDateFormat mdformat = new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss");
String strDate = "Current Time : " + mdformat.format(calendar.getTime());
- 3,066
- 20
- 27
If you wish to work with date/time in android I recommend you to use ThreeTenABP which is a version of java.time.* package (available starting from API 26 on android) shipped with Java 8 available as a replacement for java.util.Date and java.util.Calendar.
LocalDate localDate = LocalDate.now();
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofLocalizedDate(FormatStyle.MEDIUM);
String date = localDate.format(formatter);
textView.setText(date);
- 579
- 6
- 8
-
1Just to set it straight, I am sure you meant the correct thing: java.time is *built in* from Android API level 26. ThreeTenABP is what you use to get virtually the same functionality *on lower API levels*. So the code can work on both low and high levels. – Ole V.V. Dec 16 '19 at 14:08
-
2And since the question was about displaying date *and time*, for that purpose one may use for example a `ZonedDateTime` instead of `LocalDate` and `DateTimeFormatter.ofLocalizedDateTime` instead of `ofLocalizedDate`. Otherwise the code will be the same. – Ole V.V. Dec 16 '19 at 14:49
For Show Current Date and Time on Textview
/// For Show Date
String currentDateString = DateFormat.getDateInstance().format(new Date());
// textView is the TextView view that should display it
textViewdate.setText(currentDateString);
/// For Show Time
String currentTimeString = DateFormat.getTimeInstance().format(new Date());
// textView is the TextView view that should display it
textViewtime.setText(currentTimeString);
Check full Code Android – Display the current date and time in an Android Studio Example with source code
- 2,427
- 1
- 13
- 9
To get current Time/Date just use following code snippet:
To use Time:
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormatTime = new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm", Locale.getDefault());
String strTime = simpleDateFormatTime.format(now.getTime());
To use Date:
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormatDate = new SimpleDateFormat("E, MMM dd, yyyy", Locale.getDefault());
String strDate = simpleDateFormatDate.format(now.getTime());
and you are good to go.
- 4,245
- 1
- 29
- 48
SimpleDateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat("dd/MM/yyyy");
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
Date date = Calendar.getInstance().getTime();
String sDate = format.format(date);//31-12-9999
int mYear = c.get(Calendar.YEAR);//9999
int mMonth = c.get(Calendar.MONTH);
mMonth = mMonth + 1;//12
int hrs = c.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY);//24
int min = c.get(Calendar.MINUTE);//59
String AMPM;
if (c.get(Calendar.AM_PM) == 0) {
AMPM = "AM";
} else {
AMPM = "PM";
}
- 1,033
- 10
- 11