In fact technically you can store C++ arrays in a vector Not directly, but with a simple workaround. And it makes a lot of sense. Question is already answered by anon, but some explanations still needed. Wrapping the array in a class will make the vector data to meet the requirements of a multidimensional array. STL in C++ 11 and upper already provides such a wrapper std::array.
The vector of vectors fits many purposes, but is not the answer and in some cases it is just wrong. Is an unpleasant experience to fall in the trap of fixing errors caused by not understanding clearly the difference between arrays and pointers, or between multidimensional arrays and arrays of arrays. Vectors of vectors contains vectors as elements: each contains a copy of size, capacity, pointer to data pointing to random segments of data in memory. These segments will not be placed one after another like in a multidimensional array. That will cause problems to interoperability with other programming languages or libraries that are not C++ vector aware.
But a vector of arrays will point always to a contiguous segment of memory, containing all segments of a multidimensional array in correct order in a single place. Technically the data pointer will point to something identical to multidimensional array. There is no good reason to keep the size of each array element while it is known to be the same for all elements. At least it is redundant, but it is not that a big problem. The bigger problem, it breaks the structure of the multidimensional array.
So, making a vector of array can be done indirectly, by wrapping the array in a class or by using existing std::array. It will store the data im memory identically to a bidimensional array. This approach is already widely used by many libraries. At low level it will be easily interoperable with APIs that are not C++ vector aware. So without using std::array it will look like this:
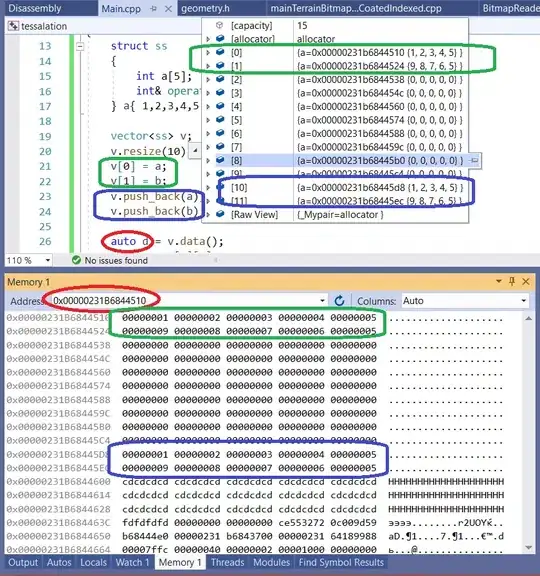
int main()
{
struct ss
{
int a[5];
int& operator[] (const int& i) { return a[i]; }
} a{ 1,2,3,4,5 }, b{ 9,8,7,6,5 };
vector<ss> v;
v.resize(10);
v[0] = a;
v[1] = b;
//all the rest is uninitialised array
v.push_back(a); // pushes to the end, with reallocation
v.push_back(b); // pushes to the new end, with reallocation
auto d = v.data();
// cin >> v[1][3]; //input any element from stdin
cout << "show two element: "<< v[1][2] <<":"<< v[1][3] << endl;
return 0;
}
In memory it looks very predictable, twelve arrays, two on the beginning and two on the end initialised, the other eight in the middle uninitialised, filled with zeroes
C++11 and upper has std::array, no need to reinvent:
....
#include<array>
....
int main()
{
vector<array<int, 5>> v;
v.reserve(10); //set capacity
v.resize(2);
v[0] = array<int, 5> {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
v[1] = array<int, 5> {9, 8, 7, 6, 5};
//note, since size does not exceed capacity
//this push_back will cause no reallocation and no relocation:
v.push_back(array<int, 5>{ 7, 2, 53, 4, 5 });
///cin >> v[1][1];
auto d = v.data();
Now, this is why vectors of vectors is not the answer. Supposing following code
int main()
{
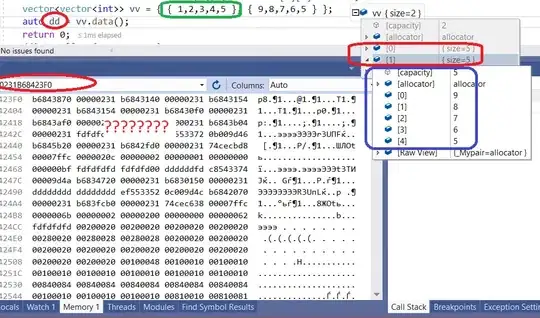
vector<vector<int>> vv = { { 1,2,3,4,5 }, { 9,8,7,6,5 } };
auto dd = vv.data();
return 0;
}
How data is stored in memory can never be guessed, it is definitely not a multidimensional array