Both the interfaces seem to compare objects for equality, so what are the major differences between them?
5 Answers
IEquatable tests whether two objects are equal.
IComparable imposes a total ordering on the objects being compared.
For example, IEquatable would tell you that 5 is not equal to 7. IComparable would tell you that 5 comes before 7.
- 43,259
- 14
- 84
- 117
In addition to Greg D's answer:
You might implement IComparable without implementing IEquatable for a class where a partial ordering makes sense, and where you very definitely want the consumer to infer that just because CompareTo() returns zero, this does not imply that the objects are equal (for anything other than sorting purposes).
- 1,266
- 1
- 12
- 24
- 234,701
- 27
- 340
- 448
-
12That sounds much more like a special-case comparer than like an object implementing `IComparable` properly. Can you come up with a meaningful example where `CompareTo(…) == 0` does **not** imply equality? I certainly can’t. In fact, the interface contract (as per MSDN) **requires** that `CompareTo(…) == 0` implies equality. To put it bluntly, in such a case as yours, use a special `Comparator` object, do *not* implement `IComparable`. – Konrad Rudolph Mar 09 '10 at 17:05
-
2@Konrad - I did indicate several caveats - that the type doesn't implement IEquatable (so obviously, the originator doesn't want to include an equality test), and that CompareTo results are used for sorting, *not* to evaluate equality. You also get into questions of which equality is relevant (reference, value, ignoring "arbitrary" attributes - a blue book of 500 pages in length may be "equal" to a red book of 500 pages in length, for the purposes of IComparable) – Damien_The_Unbeliever Mar 09 '10 at 18:35
-
4Your last sentence is wrong, and this is the particular mistake I wanted to point out: `IComparable` is wholly inappropriate here. What you’ve got is a very *particular* ordering that only applies in one special situation. For such situations, implementing a general `IComparable` is wrong. This is what `IComparer`s are there for. For example, people cannot be ordered meaningfully. But they *can* be ordered according to their salary, their shoe size, the number of their freckles or their weight. Hence, we would implement different `IComparer`s for all these cases. – Konrad Rudolph Mar 09 '10 at 19:08
-
2@Konrad Rudolph: What about something like a "ScheduledEvent" class, which is supposed to do "something" at some particular time? The semantics of the type would imply a very strong natural semantic ordering based upon when the action was supposed to take place, but one could easily have different events occur at the same time. One could require the use of a manually-specified IComparer, but I would aver that having a comparator built into the class would be more convenient. – supercat Nov 23 '11 at 22:33
-
4@supercat Convenience is important, but it isn’t everything. Correctness (as in, logical consistency) is more important and the static type system is an important tool for verifying this logical consistency. By violating the documented contract of interfaces that you implement, you are subverting the type system. This is *not* a good idea, and I would never recommend it. Use an external comparer for such situations. – Konrad Rudolph Nov 23 '11 at 23:02
-
@KonradRudolph what do you mean by external comparer? – user1131926 Aug 18 '14 at 15:12
-
@user1131926 A class implementing the [`IComparer` interface](http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/8ehhxeaf%28v=vs.110%29.aspx). – Konrad Rudolph Sep 02 '14 at 11:53
-
1This is an old thread but I must concur with @KonradRudolph here, he is absolutely right. The comparison logic in some cases should reside in dedicated, separate `IComparer` implementations rather than being imposed as the default one. In fact, I believe that as soon as an object becomes a bit complex, it's generally good reason enough not to have it implement `IComparable` at all and systematically use a separate comparer. – Crono Dec 06 '19 at 15:23
-
@KonradRudolph - I agree that logically `CompareTo(...) == 0` should imply equality. Earlier you asked for an example where that might not be the case. How about names that are case-preserving, but case-insensitive for equality? In other words, I can have a name "a" and "A", (case is preserved), and they're considered equal (perhaps by converting both to uppercase, just for the equality check). However, for sorting purposes, we want to treat them case sensitively, so they're sorted logically according to cultural rules. Would that justify equality and comparison yielding different results? – prlcutting Jan 20 '23 at 15:57
-
@KonradRudolph - also, your first commented cited the MSDN docs as saying that `IComparable` was required to imply equality for a return value of zero. Clearly it's now 13 years later since you made that observation, but it's worth noting that today the MS docs on [IComparable](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/api/system.icomparable) and [IComparable
](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/api/system.icomparable-1) no longer make such an assertion. I don't know if this indicates a softening in MS's thinking on this. – prlcutting Jan 20 '23 at 16:03 -
1@prlcutting Your example is excellent, the same is true for Unicode collation, where you would for instance want the strings `angstrom`, `ångström`, etc. to compare equal, but when sorting them you would generally sort unadorned Latin letters before their modified variants. I still think this merits using a specific comparer rather than putting these semantics into the `IComparable` implementation: the latter just seems error-prone. It's interesting that the MSDN wording has been softened in that regard. – Konrad Rudolph Jan 20 '23 at 16:37
As stated on the MSDN Page for IEquatable:
The IComparable interface defines the
CompareTomethod, which determines the sort order of instances of the implementing type. The IEquatable interface defines theEqualsmethod, which determines the equality of instances of the implementing type.
Equals vs. CompareTo
- 13,628
- 5
- 51
- 85
IComparable <T> defines a type specific comparison method which can be used to order or sort objects.
IEquatable <T> defines a generalized method which can be used to implement for determining equality.
Let's say you have Person class
public class Person
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
}
Person p1 = new Person() { Name = "Person 1", Age = 34 };
Person p2 = new Person() { Name = "Person 2", Age = 31 };
Person p3 = new Person() { Name = "Person 3", Age = 33 };
Person p4 = new Person() { Name = "Person 4", Age = 26 };
List<Person> people = new List<Person> { p1, p2, p3, p4 };
To sort these objects you can use people.Sort();.
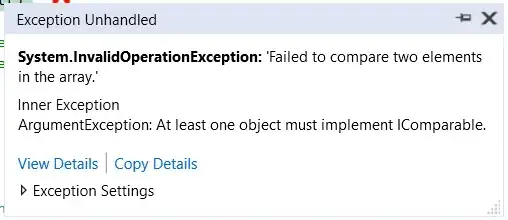
But this will thrown an an exception.
Framework doesn't know how to sort these objects. You need to tell how to sort implementing IComparable interface.
public class Person : IComparable
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
public int CompareTo(object obj)
{
Person otherPerson = obj as Person;
if (otherPerson == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException();
}
else
{
return Age.CompareTo(otherPerson.Age);
}
}
}
This will sort the array properly with Sort() method.
Next to compare two objects you can use Equals() method.
var newPerson = new Person() { Name = "Person 1", Age = 34 };
var newPersonIsPerson1 = newPerson.Equals(p1);
This will return false because Equals method doesn't know how to compare two objects. Therefore you need to implement IEquatable interface and tell the framework how to do the comparison. Extending on the previous example it'll look like this.
public class Person : IComparable, IEquatable<Person>
{
//Some code hidden
public bool Equals(Person other)
{
if (Age == other.Age && Name == other.Name)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
}
- 6,846
- 9
- 64
- 87
-
1Thanks for this great explanation. Question: why does `IEquatable` use a generic `
` and `IComparable` does not? – veuncent Sep 12 '19 at 08:39