I have a .sql file from a MySQL dump containing tables, definitions and data to be inserted in these tables. How can I convert this database represented in the dump file to a SQL Server database?
- 25,246
- 15
- 42
- 71
- 3,250
- 8
- 33
- 50
-
1Do you have access to the original database as well? Or is the export file basically all you have? – Whakkee Apr 12 '10 at 11:46
-
I have de acces to the original DB too. I just thought that using the dump might be easier – marionmaiden Apr 12 '10 at 11:49
9 Answers
Use SQL Server Migration Assistant (SSMA)
In addition to MySQL it supports Oracle, Sybase and MS Access.
It appears to be quite smart and capable of handling even nontrivial transfers. It also got some command line interface (in addition to GUI) so theoretically it can be integrated into some batch load process.
This the current download link for MySQL version https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=54257
The current (June 2016) stable version 6.0.1 crashes with the current (5.3.6) MySQL ODBC driver while transferring data. Everything 64 bit. The 5.3 version with the 5.1.13 ODBC driver works fine.
- 5,675
- 2
- 39
- 37
-
13This tool only works if you can install an ODBC connector from your PC to your MySQL DB. If you just have a .sql dump file you cannot use SSMA. – Jake Munson Feb 21 '13 at 18:20
-
11MySQL engine is free software, and there is a version for windows too. Installing it and loading the dump is a trivial job. If you are hoping to find a tool (even a commercial, let alone free) that will reliably convert an arbitrary MySQL script to its SQL Server equivalent - well, good luck with that. – Zar Shardan Feb 22 '13 at 01:16
-
1Good point. And that is what I ended up doing yesterday. Short of writing your own custom conversion utility, installing MySQL seems to be the best option. SSMA was a pain in the butt to use, but I eventually got it to work. – Jake Munson Feb 22 '13 at 16:07
-
Agree, it's not the most user friendly piece of software, but gets the job done. – Zar Shardan Feb 24 '13 at 02:14
-
2SSMA is a great option, this should be the accepted answer. I didn't find it hard to use at all. – DonBecker Apr 25 '13 at 15:14
-
4It requires the SQL Server Agent that does not comes with SQL Server Express. – Vinicius Rocha Sep 02 '13 at 23:13
-
@Vinicius, I just migrated my data from MySQL 5.6 to SQL Server Express 2008 R2. What is the problem you are having? – Rosdi Kasim Dec 19 '13 at 08:32
-
This is an old thread, but exactly how might I go about doing this with a locally hosted MySQL database (using WAMP)? – muttley91 Aug 05 '14 at 04:33
-
@Vinicius: It's not enabled by default, but if you start it in Administrator Tools > Services, it works with Express fine. – Aquarion Dec 05 '14 at 10:27
-
@rar: Same thing. The SSMA will connect to any MySQL server. You'll need to install the ODBC connectors for windows from mysql.com. Pay attention to version numbers, the SSMA only supports a limited range. – Aquarion Dec 05 '14 at 10:28
-
This worked for me using MS SQL 2014 and the 7.6.0 version of the Migration Assistant and the 5.3 MySQL ODBC connector. It's a kludgy interface but it does the job. – Jason Feb 26 '18 at 17:56
-
The links are obsolete. Use this: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=54255 – Shadi Alnamrouti Mar 26 '19 at 16:47
-
@ShadiNamrouti Thanks, updated the links. Yours was for Access though. – Zar Shardan Apr 05 '19 at 17:17
I suggest you to use mysqldump like so:
mysqldump --compatible=mssql
phpMyAdmin is still a web-app and could potentially have some limitations for large databases (script execution time, allocatable memory and so on).
- 4,501
- 6
- 50
- 90
- 238
- 1
- 3
-
6Alas, this gives me all sorts of compatabilty problems. The script will contain backticks around column names, data types that don't exist in MSSQL, will violate the max-1000-inserts constraint, auto_increment keywords, etc. etc. This answer is a logical suggestion, but I'm afraid it doesn't work too well (at least: it didn't for me). – Jeroen Nov 03 '12 at 08:16
-
1mysqldump --compatible=ansi "Produce output that is more compatible with other database systems or with older MySQL servers. The only permitted value for this option is ansi, which has the same meaning as the corresponding option for setting the server SQL mode." – Thomas Taylor May 22 '20 at 22:57
-
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/mysqldump.html#option_mysqldump_compatible - this does not do what you think it does – Vetsin Apr 20 '21 at 17:00
I found a way for this on the net
It demands a little bit of work, because it has to be done table by table. But anyway, I could copy the tables, data and constraints into a SQL Server database.
Here is the link
http://www.codeproject.com/KB/database/migrate-mysql-to-mssql.aspx
- 25,246
- 15
- 42
- 71
- 3,250
- 8
- 33
- 50
-
1That is when both Mysql and SQL are in one machine or they are connected through a network. This is not useful when two different machine exist and you have a Dump file from mysql. right? – Espanta Nov 06 '15 at 09:37
Here is my approach for importing .sql files to SQL Server:
Export table from MySQL with
--compatible=mssqland--extended-insert=FALSEoptions:mysqldump -u [username] -p --compatible=mssql --extended-insert=FALSE db_name table_name > table_backup.sqlSplit the exported file with PowerShell by 300000 lines per file:
$i=0; Get-Content exported.sql -ReadCount 300000 | %{$i++; $_ | Out-File out_$i.sql}Run each file in SQL Server Management Studio
There are few tips how to speed up the inserts.
Other approach is to use mysqldump –where option. By using this option you can split your table on any condition which is supported by where SQL clause.
-
-
try `--databases [db_name]` keyword as it explained in this answer: http://stackoverflow.com/a/26096339/155687 – Vladislav Mar 27 '17 at 06:57
If you do an export with PhpMyAdmin, you can switch sql compatibility mode to 'MSSQL'. That way you just run the exported script against your MS SQL database and you're done.
If you cannot or don't want to use PhpMyAdmin, there's also a compatibility option in mysqldump, but personally I'd rather have PhpMyAdmin do it for me.
- 1,867
- 1
- 16
- 18
-
1This answer worked for me, with minimal modifications to the generated script. Brought it into SQL Server 2012. Didn't see the compatibility mode before. – Kiel Jun 29 '16 at 14:04
I had a very similar issue today - I needed to copy a big table(5 millions rows) from MySql into MS SQL.
Here are the steps I've done(under Ubuntu Linux):
Created a table in MS SQL which structure matches the source table in MySql.
Installed MS SQL command line: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/linux/sql-server-linux-setup-tools#ubuntu
Dumped table from MySql to a file:
mysqldump \
--compact \
--complete-insert \
--no-create-info \
--compatible=mssql \
--extended-insert=FALSE \
--host "$MYSQL_HOST" \
--user "$MYSQL_USER" \
-p"$MYSQL_PASS" \
"$MYSQL_DB" \
"$TABLE" > "$FILENAME"
In my case the dump file was quite large, so I decided to split it into a number of small pieces(1000 lines each) -
split --lines=1000 "$FILENAME" part-Finally I iterated over these small files, did some text replacements, and executed the pieces one by one against MS SQL server:
export SQLCMD=/opt/mssql-tools/bin/sqlcmd x=0 for file in part-* do echo "Exporting file [$file] into MS SQL. $x thousand(s) processed" # replaces \' with '' sed -i "s/\\\'/''/g" "$file" # removes all " sed -i 's/"//g' "$file" # allows to insert records with specified PK(id) sed -i "1s/^/SET IDENTITY_INSERT $TABLE ON;\n/" "$file" "$SQLCMD" -S "$AZURE_SERVER" -d "$AZURE_DB" -U "$AZURE_USER" -P "$AZURE_PASS" -i "$file" echo "" echo "" x=$((x+1)) done echo "Done"
Of course you'll need to replace my variables like $AZURE_SERVER, $TABLE , e.t.c. with yours.
Hope that helps.
- 599
- 3
- 11
For me it worked best to export all data with this command:
mysqldump -u USERNAME -p --all-databases --complete-insert --extended-insert=FALSE --compatible=mssql > backup.sql
--extended-insert=FALSE is needed to avoid mssql 1000 rows import limit.
I created my tables with my migration tool, so I'm not sure if the CREATE from the backup.sql file will work.
In SQL Server's SSMS I had to imported the data table by table with the IDENTITY_INSERT ON to write the ID fields:
SET IDENTITY_INSERT dbo.app_warehouse ON;
GO
INSERT INTO "app_warehouse" ("id", "Name", "Standort", "Laenge", "Breite", "Notiz") VALUES (1,'01','Bremen',250,120,'');
SET IDENTITY_INSERT dbo.app_warehouse OFF;
GO
If you have relationships you have to import the child first and than the table with the foreign key.
- 25,246
- 15
- 42
- 71
- 63
- 7
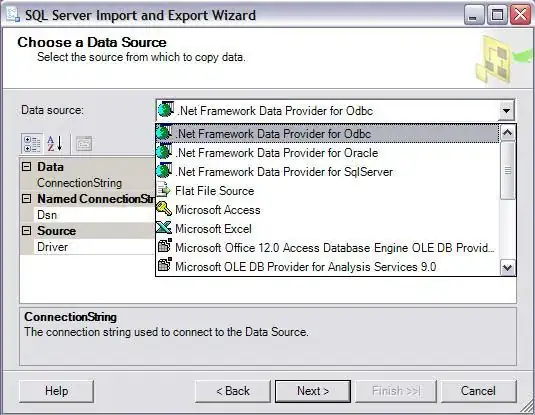
Also you can use 'ODBC' + 'SQL Server Import and Export Wizard'. Below link describes it: https://www.mssqltips.com/sqlservertutorial/2205/mysql-to-sql-server-data-migration/
- 2,403
- 3
- 19
- 19
Run:
mysqldump -u root -p your_target_DB --compatible=mssql > MSSQL_Compatible_Data.sql
Do you want to see a process bar?
pv mysqldump -u root -p your_target_DB --compatible=mssql > MSSQL_Compatible_Data.sql
- 10,216
- 13
- 73
- 113