I have been following a tutorial explaining a custom ios control. There is no problem with the tutorial but I got really confused about the frame/bounds clipping (not part of the tutorial).
I have a UIView instance in the scene in the storyboard. This UIView is sized at 120 x 120. I am adding a custom control (extending UIControl) to this container view with addSubview. I began to experiment with setting different widths and height to the frame and bounds of the custom control, this is the initializer of the control:
public override init(frame: CGRect) {
super.init(frame: frame)
createSublayers()
}
...and produces this result (red is the parent, blue circle is the child):
Now I change the init to this:
public override init(frame: CGRect) {
super.init(frame: frame)
createSublayers()
self.frame.size.width = 40
self.frame.size.height = 40
println("frame: \(self.frame)")
println("bounds: \(self.bounds)")
self.clipsToBounds = true
}
And that produces this result:
 and prints:
frame: (0.0,0.0,40.0,40.0)
bounds: (0.0,0.0,40.0,40.0)
and prints:
frame: (0.0,0.0,40.0,40.0)
bounds: (0.0,0.0,40.0,40.0)
But when I change the initliazer to this:
public override init(frame: CGRect) {
super.init(frame: frame)
createSublayers()
self.bounds.size.width = 40
self.bounds.size.height = 40
println("frame: \(self.frame)")
println("bounds: \(self.bounds)")
self.clipsToBounds = true
}
I get this:
 and prints: frame: (40.0,40.0,40.0,40.0)
bounds: (0.0,0.0,40.0,40.0)
and prints: frame: (40.0,40.0,40.0,40.0)
bounds: (0.0,0.0,40.0,40.0)
I cannot seem to comprehend why this view is centered in its parent view when I change its bounds. What exactly is causing it? Is the 'frame' clipped always towards its center? Or is this view centered in its parent after the bounds have been modified and that causes the update of the 'frame'? Is it some property that can be changed? How could I manage to put it to top-left corner, for example (exactly in the same way as when I modify the 'frame')? Thanks a lot!
EDIT:
class ViewController: UIViewController {
@IBOutlet var knobPlaceholder: UIView!
@IBOutlet var valueLabel: UILabel!
@IBOutlet var valueSlider: UISlider!
@IBOutlet var animateSwitch: UISwitch!
var knob: Knob!
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
knob = Knob(frame: knobPlaceholder.bounds)
knobPlaceholder.addSubview(knob)
knobPlaceholder.backgroundColor = UIColor.redColor();
}
@IBAction func sliderValueChanged(slider: UISlider) {
}
@IBAction func randomButtonTouched(button: UIButton) {
}
}
And the knob:
public class Knob: UIControl {
private let knobRenderer = KnobRenderer()
private var backingValue: Float = 0.0
/** Contains the receiver’s current value. */
public var value: Float {
get {
return backingValue
}
set {
setValue(newValue, animated: false)
}
}
/** Sets the receiver’s current value, allowing you to animate the change visually. */
public func setValue(value: Float, animated: Bool) {
if value != backingValue {
backingValue = min(maximumValue, max(minimumValue, value))
}
}
/** Contains the minimum value of the receiver. */
public var minimumValue: Float = 0.0
/** Contains the maximum value of the receiver. */
public var maximumValue: Float = 1.0
public override init(frame: CGRect) {
super.init(frame: frame)
createSublayers()
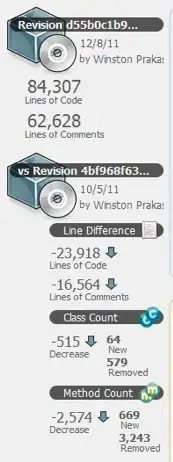
self.bounds.size.width = 40
self.bounds.size.height = 40
println("frame: \(self.frame)")
println("bounds: \(self.bounds)")
self.clipsToBounds = true
}
public required init(coder aDecoder: NSCoder) {
fatalError("init(coder:) has not been implemented")
}
func createSublayers() {
knobRenderer.update(bounds)
knobRenderer.strokeColor = tintColor
knobRenderer.startAngle = -CGFloat(M_PI * 11.0 / 8.0);
knobRenderer.endAngle = CGFloat(M_PI * 3.0 / 8.0);
knobRenderer.pointerAngle = knobRenderer.startAngle;
knobRenderer.lineWidth = 2.0
knobRenderer.pointerLength = 6.0
layer.addSublayer(knobRenderer.trackLayer)
layer.addSublayer(knobRenderer.pointerLayer)
}
}
private class KnobRenderer {
let trackLayer = CAShapeLayer()
let pointerLayer = CAShapeLayer()
var strokeColor: UIColor {
get {
return UIColor(CGColor: trackLayer.strokeColor)
}
set(strokeColor) {
trackLayer.strokeColor = strokeColor.CGColor
pointerLayer.strokeColor = strokeColor.CGColor
}
}
var lineWidth: CGFloat = 1.0 {
didSet {
update();
}
}
var startAngle: CGFloat = 0.0 {
didSet {
update();
}
}
var endAngle: CGFloat = 0.0 {
didSet {
update()
}
}
var backingPointerAngle: CGFloat = 0.0
var pointerAngle: CGFloat {
get { return backingPointerAngle }
set { setPointerAngle(newValue, animated: false) }
}
func setPointerAngle(pointerAngle: CGFloat, animated: Bool) {
backingPointerAngle = pointerAngle
}
var pointerLength: CGFloat = 0.0 {
didSet {
update()
}
}
init() {
trackLayer.fillColor = UIColor.clearColor().CGColor
pointerLayer.fillColor = UIColor.clearColor().CGColor
}
func updateTrackLayerPath() {
let arcCenter = CGPoint(x: trackLayer.bounds.width / 2.0, y: trackLayer.bounds.height / 2.0)
let offset = max(pointerLength, trackLayer.lineWidth / 2.0)
let radius = min(trackLayer.bounds.height, trackLayer.bounds.width) / 2.0 - offset;
trackLayer.path = UIBezierPath(arcCenter: arcCenter, radius: radius, startAngle: startAngle, endAngle: endAngle, clockwise: true).CGPath
}
func updatePointerLayerPath() {
let path = UIBezierPath()
path.moveToPoint(CGPoint(x: pointerLayer.bounds.width - pointerLength - pointerLayer.lineWidth / 2.0, y: pointerLayer.bounds.height / 2.0))
path.addLineToPoint(CGPoint(x: pointerLayer.bounds.width, y: pointerLayer.bounds.height / 2.0))
pointerLayer.path = path.CGPath
}
func update(bounds: CGRect) {
let position = CGPoint(x: bounds.width / 2.0, y: bounds.height / 2.0)
trackLayer.bounds = bounds
trackLayer.position = position
pointerLayer.bounds = bounds
pointerLayer.position = position
update()
}
func update() {
trackLayer.lineWidth = lineWidth
pointerLayer.lineWidth = lineWidth
updateTrackLayerPath()
updatePointerLayerPath()
}
}