-1.#IND is Microsoft's way of outputting an indeterminate value, specifically NaN.
One of the ways this can happen is with 0 / 0 but I would check all operations to see where the issue lies:
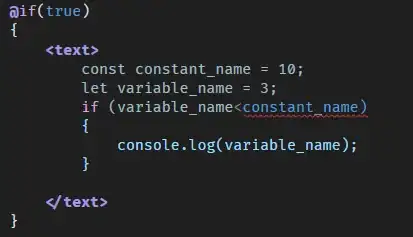
double secant_method(double(*f)(double), double a, double b){
double c;
printf("DBG =====\n");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){
printf("\nDBG -----\n");
printf("DBG i: %d\n",i);
printf("DBG a: %30f\n",a);
printf("DBG b: %30f\n",b);
printf("DBG c: %30f\n",c);
printf("DBG f(a): %30f\n",f(a));
printf("DBG a-b: %30f\n",a-b);
printf("DBG f(b): %30f\n",f(b));
printf("DBG f(a)-f(b): %30f\n",f(a)-f(b));
printf("DBG f(a)*(a-b): %30f\n",f(a)*(a-b));
printf("DBG f(a)*(a-b)/(f(a)-f(b)): %30f\n",f(a)*(a-b)/(f(a)-f(b)));
c = a - f(a) * (a - b) / (f(a) - f(b));
b = a; a = c;
}
return c;
}
Once you have that debug output, then you can figure out what the actual issue is, and adopt strategies to avoid it.
When I do that, I see (at the end):
DBG -----
DBG i: 8
DBG a: 1.556773264394211375716281509085
DBG b: 1.556773264393484179635152031551
DBG c: 1.556773264394211375716281509085
DBG f(a): -0.000000000000000987057657830803
DBG a-b: 0.000000000000727196081129477534
DBG f(b): -0.000000000008196943991622962500
DBG f(a)-f(b): 0.000000000008195956933965131697
DBG f(a)*(a-b): -0.000000000000000000000000000718
DBG f(a)*(a-b)/(f(a)-f(b)): -0.000000000000000087577871187781
DBG -----
DBG i: 9
DBG a: 1.556773264394211375716281509085
DBG b: 1.556773264394211375716281509085
DBG c: 1.556773264394211375716281509085
DBG f(a): -0.000000000000000987057657830803
DBG a-b: 0.000000000000000000000000000000
DBG f(b): -0.000000000000000987057657830803
DBG f(a)-f(b): 0.000000000000000000000000000000
DBG f(a)*(a-b): -0.000000000000000000000000000000
DBG f(a)*(a-b)/(f(a)-f(b)): nan
Root found: nan
So you can see, on the tenth iteration, a and b have become equal and hence so have f(a) and f(b). So you're getting the expression:
something * 0 / 0
which, as mentioned, will give you 0 / 0 or NaN.
In terms of how to fix it, you just need to avoid dividing by zero since that will give you eithere NaN or an infinity. So you could use the following function instead:
double secant_method(double(*f)(double), double a, double b){
double c;
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
if (f(a) == f(b)) break;
c = a - f(a) * (a - b) / (f(a) - f(b));
b = a; a = c;
}
return c;
}
A thousand loops should be more than enough to get a decent answer and it will opt out early if you're ever about to divide by zero.
If you want more precision, you could either look into the long double type or switch to using one of the arbitrary precision arithmetic libraries such as GMP or MPIR.
That's usually more work but you can achieve some impressive results. This program, built on MPIR:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <mpir.h>
void secant_method(mpf_t result, void(*f)(mpf_t, mpf_t), mpf_t a, mpf_t b){
mpf_t c, fa, fb, temp1, temp2;
mpf_init (fa);
mpf_init (fb);
mpf_init (temp1);
mpf_init (temp2);
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++){
printf("DBG i: %d\n",i);
f (fa, a);
f (fb, b);
if (mpf_cmp (fa, fb) == 0) break;
mpf_set (temp1, a);
mpf_sub (temp1, temp1, b);
mpf_set (temp2, fa);
mpf_sub (temp2, temp2, fb);
mpf_set (result, fa);
mpf_mul (result, result, temp1);
mpf_div (result, result, temp2);
mpf_sub (result, result, a);
mpf_neg (result, result);
mpf_set (b, a);
mpf_set (a, result);
}
}
void test (mpf_t result, mpf_t x){
mpf_t temp;
mpf_set (result, x);
mpf_pow_ui (result, result, 3);
mpf_init_set (temp, x);
mpf_mul_ui (temp, temp, 4);
mpf_add (result, result, temp);
mpf_set_ui (temp, 10);
mpf_sub (result, result, temp);
mpf_clear (temp);
}
int main(){
mpf_t ans, a, b;
mpf_set_default_prec (8000);
mpf_init_set_ui (ans, 0);
mpf_init_set_ui (a, 0);
mpf_init_set_ui (b, 2);
secant_method (ans, &test, a, b);
mpf_out_str (stdout, 10, 0, ans);
return 0;
}
outputs much more precision, about two and a half thousand digits:
DBG i: 1
:
DBG i: 19
0.155677326439421146326886324730853302634853266143
22856485101283627988036767055520913212330822780959
93349183787687346999781239000417393618333668026011
02048595843228945228507966189601958673920851932189
20626590635658264390975889008832048255537650792123
54916373054888140164770654992918100928227714960414
65208113116379497717707745267800989233875981344305
90022883167106124203999713536673991376957068731244
91919087980169395013246250812213656324598765244218
15974098310512802880727074335472786858740154287363
31949470951650710072488856623955478366217474755111
76368234254761541647442609230138418167182918204711
66713459423756284737546964906061587903876515793884
14091165347411853670752820576131460960421137744435
73729141652832258144582021037373967987171478026002
48487515446248979731517957120705447608265161099693
33098235693813752370774508652788986557620510981156
19907950657355934071535840759135251701581523712307
00051674680667972152582339710574822560693109306285
91240827697915787078746087225027856691436076089912
35551789799825731841345891629028445554314717823386
07885164744100235567602875364878328805811271289098
87558119684442289199181352023304600847178256323082
57317198584882656089836229208443415369358460418542
84083408696290686178971039756668669303212658278679
39542421457300944206839268283788585029652481323614
65995074020560963212330914882733926627309382310653
39023265929195094492468196461296569155421718696631
73798097369621805062145075113127308161572398104766
37356504104570136778437926442139603916930640425421
15655156674699552536588332891562053247342008145504
44336211031437923307615880759201695011419324719812
46482293928341901673056596202744639074280785106031
90197472588293352508389295101867514582271001202777
85575614897203080940643669476500979934666490279524
88486176409290187337498631681392563044899541391612
88438904336237873504970887963071622208868799638373
42186338496601471274609131141920820263780493617795
89714798662834913192777810386631915415021934333441
01797098172897161215116673422762953435902633516501
73788202968876596925999628999004575114529754782488
59959395407324243559011982543407738505315960009874
36510513519775603567237051670918870105777288994910
85524037720122749091827520695838000086150188462000
63190624219373460624686216781527327604063990319908
56547016812115842640285111265677758613385414834511
69237199199725030839166586376374587900611430229333
87296847315023767826706323911923435564643861604120
017381909481e1
And, if you take that number and pass it back into the test() function, you get a number rather close to zero, about -1.15 x 10-2408. So I would say that's a pretty big improvement on using double.
And, for what it's worth, it only takes about a tenth of a second CPU time so it's at least feasible to do this with arbitrary precision arithmetic.
For even more precision, just change the default precision settings for MPIR, currently set as:
mpf_set_default_prec (8000);
Bumping that up to 100,000 gives an answer with over 30,000 significant digits, and a final "close-to-zero" answer of about -5 x 10-30103.