I wrote some code to capture frames from a webcam using GStreamer 1.0 (PyGST). It is important for me to know the exact time of capture. For this, I set the v4l2src property do-timestamp, and I use appsink to write the buffer PTS to a text file.
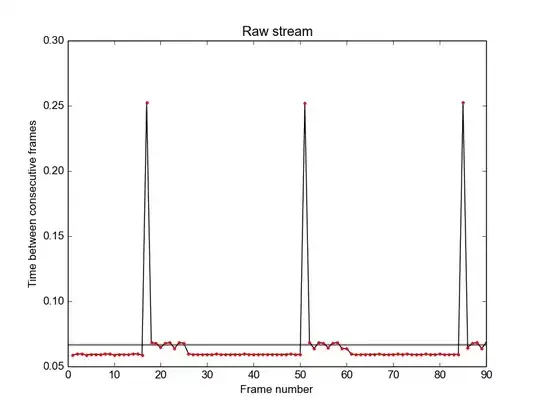
However, the timestamps are not monotonically increasing. E.g. the timestamp of frame 16 is 0.88199 s, and the timstamp of frame 17 is 0.77462 s, i.e. 0.10737 s EARLIER than previous frame. (I have a figure showing the problem, but lack the reputation necessary to post it.)
Is it correct that PTS of captured GstBuffers are not always monotonically increasing? If this is not normal behavior, does anyone know what I messed up?
I use a Logitech c920 webcam. The frames are h.264 encoded on the camera. The code looks roughly like this:
import gi
gi.require_version('Gst', '1.0')
from gi.repository import GObject, Gst, Gtk
GObject.threads_init()
Gst.init(None)
class Webcam:
def __init__(self, video_dev='/dev/video0', fps=30):
ts_log_fname = 'webcam_timestamps.log'
vid_fname = 'webcam.mkv'
self.ts_log = open(ts_log_fname, 'w')
self.ts_log.write('video filename: %s\n '
'\nframe_number, cam_running_ts\n' % vid_fname)
self.n_frames = 0
# Create GStreamer pipline
self.pipeline = Gst.Pipeline()
# Create bus to get events from GStreamer pipeline
self.bus = self.pipeline.get_bus()
self.bus.add_signal_watch()
self.bus.connect('message::error', self.on_error)
self.bus.enable_sync_message_emission()
self.bus.connect('sync-message::element', self.on_sync_message)
###########################
# Callable function
###########################
def on_new_sample(appsink):
"""
Function called from the pipeline by appsink.
Writes the timestampes of frame capture to a log file.
"""
# Get the buffer
smp = appsink.emit('pull-sample')
buf = smp.get_buffer()
# Nanoseconds to seconds
timestamp = np.float64(1e-9) * buf.pts
self.n_frames += 1
self.ts_log.write('%d,%0.9f\n' % (self.n_frames, timestamp))
return False
###########################
# Create GStreamer elements
###########################
# Video source:
self.v4l2src0 = Gst.ElementFactory.make('v4l2src', None)
self.v4l2src0.set_property('device', video_dev)
self.v4l2src0.set_property('do-timestamp', 'true')
# Video source filters:
vid0caps = Gst.Caps.from_string('video/x-h264,width=%d,height=%d,'
'framerate=%d/1' % (1280, 720, fps))
self.vid0filter = Gst.ElementFactory.make('capsfilter', None)
self.vid0filter.set_property('caps', vid0caps)
# Parse video:
self.vid0parse = Gst.ElementFactory.make('h264parse', None)
# Split:
self.tee0 = Gst.ElementFactory.make('tee', None)
self.tee0.set_property('name', 't0')
####
# Display branch
####
# Decode
self.vid0decode = Gst.ElementFactory.make('avdec_h264', None)
# Scale to display size:
self.disp0scale = Gst.ElementFactory.make('videoscale', None)
# Display filter caps:
disp0caps = Gst.Caps.from_string('video/x-raw,width=%d,height=%d' %
(800, 600))
# Sinks:
self.disp0sink = Gst.ElementFactory.make('autovideosink', None)
self.disp0sink.set_property('filter-caps', disp0caps)
####
# File branch
####
self.mux = Gst.ElementFactory.make('matroskamux', None)
self.file0sink = Gst.ElementFactory.make('filesink', None)
self.file0sink.set_property('location', vid_fname)
self.file0sink.set_property('sync', False)
####
# Timestamp branch
####
# Create appsink
self.ts0sink = Gst.ElementFactory.make('appsink', None)
# Setting properties of appsink
ts0caps = vid0caps # use same caps as for camera
self.ts0sink.set_property('caps', ts0caps)
self.ts0sink.set_property("max-buffers", 20) # Limit memory usage
# Tell sink to emit signals
self.ts0sink.set_property('emit-signals', True)
self.ts0sink.set_property('sync', False) # No sync
# Connect appsink to my function (writing timestamps)
self.ts0sink.connect('new-sample', on_new_sample)
self.queue0 = Gst.ElementFactory.make('queue', None)
self.queue1 = Gst.ElementFactory.make('queue', None)
self.disp_queue = Gst.ElementFactory.make('queue', None)
self.file_queue = Gst.ElementFactory.make('queue', None)
self.ts_queue = Gst.ElementFactory.make('queue', None)
# Add elements to the pipeline
self.pipeline.add(self.v4l2src0)
self.pipeline.add(self.vid0filter)
self.pipeline.add(self.vid0parse)
self.pipeline.add(self.tee0)
self.pipeline.add(self.vid0decode)
self.pipeline.add(self.disp0scale)
self.pipeline.add(self.disp0sink)
self.pipeline.add(self.mux)
self.pipeline.add(self.file0sink)
self.pipeline.add(self.ts0sink)
self.pipeline.add(self.queue0)
self.pipeline.add(self.queue1)
self.pipeline.add(self.disp_queue)
self.pipeline.add(self.file_queue)
self.pipeline.add(self.ts_queue)
###############
# Link elements
###############
# video source
if not self.v4l2src0.link(self.vid0filter):
print('video source to video filter link failed')
if not self.vid0filter.link(self.vid0parse):
print('video filter to video parse link failed')
if not self.vid0parse.link(self.tee0):
print('video parse to tee link failed')
# tee
if not self.tee0.link(self.disp_queue):
print('tee to display queue link failed')
if not self.tee0.link(self.file_queue):
print('tee to file queue link failed')
if not self.tee0.link(self.ts_queue):
print('tee to ts queue link failed')
# video display sink
if not self.disp_queue.link(self.vid0decode):
print('dispaly queue to video decode link failed')
if not self.vid0decode.link(self.disp0scale):
print('decode to videoscale link failed')
if not self.disp0scale.link(self.queue0):
print('disp0scale to queue0 link failed')
if not self.queue0.link_filtered(self.disp0sink, disp0caps):
print('queue0 to display-sink link failed')
# file sink
if not self.file_queue.link(self.mux):
print('file queue to mux link failed')
if not self.mux.link(self.queue1):
print('mux to queue1 link failed')
if not self.queue1.link(self.file0sink):
print('queue1 to file-sink link failed')
# timestamp sink
if not self.ts_queue.link(self.ts0sink):
print('ts queue to ts-sink link failed')
def run(self):
self.offset_t = datetime.now().timestamp() - self.t_start
self.pipeline.set_state(Gst.State.PLAYING)
def quit(self):
self.pipeline.set_state(Gst.State.NULL)
self.ts_log.close()
def on_sync_message(self, bus, msg):
if msg.get_structure().get_name() == 'prepare-window-handle':
msg.src.set_property('force-aspect-ratio', True)
def on_error(self, bus, msg):
print('on_error():', msg.parse_error())