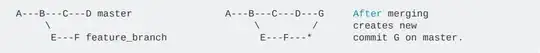Case: If you need to ignore the merge commit created by default, follow these steps.
Say, a new feature branch is checked out from master having 2 commits already,
Checkout a new feature_branch
Feature branch then adds two commits-->
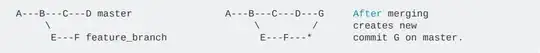
Now if you want to merge feature_branch changes to master, Do git merge feature_branch sitting on the master.
This will add all commits into master branch (4 in master + 2 in feature_branch = total 6) + an extra merge commit something like 'Merge branch 'feature_branch'' as the master is diverged.
If you really need to ignore this merge commit and add as new commit like 'Integrated feature branch changes into master', Run git merge feature_merge --no-commit.
With --no-commit, it perform the merge and stop just before creating a merge commit, We will have all the added changes in feature branch now in master and get a chance to create a new merge commit as our own.
Edit 2023: You can now have the option to change the merge commit interactively in newer versions of git without specifying the --no-commit option.
Read here for more : https://git-scm.com/docs/git-merge