jTextArea1.setText(ss[i]); is doing just that, it's "setting" the text to the value you are suppling, generally you either want to use JTextArea#append to append more text to the JTextArea or a StringBuilder to build a String within the loop, which you can apply in a single step through setText... however...
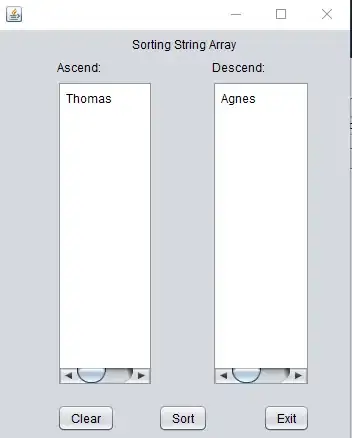
This is probably more complex then you were thinking, but your basic problem just screams JList. See How to Use Lists for more details.
Now, it would be very easy to simply create 3 Lists of values, using the original, unsorted list, populate the other two and use Collections.sort to sort them, but where's the fun in that.
Instead, I use a custom ListModel which can sort another ListModel in the order you want. The power of this is, the original is never changed, so it's order is preserved, but if you change either list (add/remove rows), they will both be updated
import java.awt.EventQueue;
import java.awt.GridBagConstraints;
import java.awt.GridBagLayout;
import java.awt.GridLayout;
import java.text.Collator;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
import javax.swing.AbstractListModel;
import javax.swing.DefaultListModel;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.JList;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.JScrollPane;
import javax.swing.ListModel;
import javax.swing.UIManager;
import javax.swing.UnsupportedLookAndFeelException;
import javax.swing.event.ListDataEvent;
import javax.swing.event.ListDataListener;
public class SortExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SortExample();
}
public SortExample() {
EventQueue.invokeLater(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
UIManager.setLookAndFeel(UIManager.getSystemLookAndFeelClassName());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException | UnsupportedLookAndFeelException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
JFrame frame = new JFrame("Testing");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.add(new TestPane());
frame.pack();
frame.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
});
}
public class TestPane extends JPanel {
private JList unsorted;
private JList ascending;
private JList descending;
public TestPane() {
String[] ss = {"Agnes",
"Alfred",
"Bernard",
"Bill",
"Ezra",
"Herman",
"Lee",
"Mary",
"Thomas"};
List<String> listOfValues = Arrays.asList(ss);
Collections.shuffle(listOfValues);
DefaultListModel model = new DefaultListModel();
for (String value : listOfValues) {
model.addElement(value);
}
setLayout(new GridBagLayout());
GridBagConstraints gbc = new GridBagConstraints();
gbc.gridx = 0;
gbc.gridy = 0;
add(new JLabel("Unsorted"), gbc);
gbc.gridx++;
add(new JLabel("Ascending"), gbc);
gbc.gridx++;
add(new JLabel("Descending"), gbc);
unsorted = new JList(model);
ascending = new JList(new SortedListModel(model, SortedListModel.SortOrder.Ascending));
descending = new JList(new SortedListModel(model, SortedListModel.SortOrder.Descending));
gbc.weightx = 1;
gbc.weighty = 1;
gbc.fill = GridBagConstraints.BOTH;
gbc.gridx = 0;
gbc.gridy++;
add(new JScrollPane(unsorted), gbc);
gbc.gridx++;
add(new JScrollPane(ascending), gbc);
gbc.gridx++;
add(new JScrollPane(descending), gbc);
}
}
/**
* SortedListModel decorates an unsorted ListModel to provide a sorted
* model. You can create a SortedListModel from models you already have.
* Place the SortedListModel into a JList, for example, to provide a sorted
* view of your underlying model.
*
* @author John O'Conner
*/
public static class SortedListModel extends AbstractListModel {
private ListDataHandler hndListData;
private List<SortedListEntry> sortedModel;
private ListModel unsortedModel;
private Comparator comparator;
private SortOrder sortOrder;
public enum SortOrder {
Unsorted,
Ascending,
Descending;
}
private SortedListModel() {
setSortOrder(SortOrder.Unsorted);
setComparator(Collator.getInstance());
}
/**
* Create a SortedListModel from an existing model using a default text
* comparator for the default Locale. Sort in ascending order.
*
* @param model the underlying, unsorted ListModel
*/
public SortedListModel(ListModel model) {
this(model, SortOrder.Ascending, null);
}
/**
* Create a SortedListModel from an existing model using a specific
* comparator and sort order. Use a default text comparator.
*
* @param model the unsorted list model
* @param sortOrder that should be used
*/
public SortedListModel(ListModel model, SortOrder sortOrder) {
this(model, sortOrder, null);
}
/**
* Create a SortedListModel from an existing model. Sort the model in
* the specified sort order using the given comparator.
*
* @param model
* @param sortOrder
* @param comp
*
*/
public SortedListModel(ListModel model, SortOrder sortOrder, Comparator comp) {
this();
setComparator(comp);
setModel(model);
setSortOrder(sortOrder);
}
public void setModel(ListModel model) {
if (unsortedModel == null || !unsortedModel.equals(model)) {
if (unsortedModel != null) {
fireIntervalRemoved(this, 0, unsortedModel.getSize() - 1);
unsortedModel.removeListDataListener(getListDataHandler());
}
unsortedModel = model;
if (unsortedModel != null) {
unsortedModel.addListDataListener(getListDataHandler());
}
// get base model info
int size = model.getSize();
List<SortedListEntry> sortedModel = getSortedModel();
sortedModel.clear();
for (int x = 0; x < size; ++x) {
SortedListEntry entry = new SortedListEntry(x);
int insertionPoint = findInsertionPoint(entry);
sortedModel.add(insertionPoint, entry);
}
}
}
protected ListDataHandler getListDataHandler() {
if (hndListData == null) {
hndListData = new ListDataHandler();
}
return hndListData;
}
public SortOrder getSortOrder() {
return sortOrder;
}
protected List<SortedListEntry> getSortedModel() {
if (sortedModel == null) {
sortedModel = new ArrayList<SortedListEntry>(25);
}
return sortedModel;
}
public ListModel getModel() {
return unsortedModel;
}
/**
* Retrieve the sorted entry from the original model
*
* @param index index of an entry in the sorted model
* @return element in the original model to which our entry points
*/
public Object getElementAt(int index) throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {
Object element = null;
if (getModel() != null) {
int modelIndex = toUnsortedModelIndex(index);
element = getModel().getElementAt(modelIndex);
}
return element;
}
/**
* Retrieve the size of the underlying model
*
* @return size of the model
*/
public int getSize() {
int size = getSortedModel().size();
return size;
}
/**
* Convert sorted model index to an unsorted model index.
*
* @param index an index in the sorted model
* @return modelIndex an index in the unsorted model
*
*/
public int toUnsortedModelIndex(int index) throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {
int modelIndex = -1;
SortedListEntry entry = getSortedModel().get(index);
modelIndex = entry.getIndex();
return modelIndex;
}
/**
* Convert an array of sorted model indices to their unsorted model
* indices. Sort the resulting set of indices.
*
* @param sortedSelectedIndices indices of selected elements in the
* sorted model or sorted view
* @return unsortedSelectedIndices selected indices in the unsorted
* model
*/
public int[] toUnsortedModelIndices(int[] sortedSelectedIndices) {
int[] unsortedSelectedIndices = new int[sortedSelectedIndices.length];
int x = 0;
for (int sortedIndex : sortedSelectedIndices) {
unsortedSelectedIndices[x++] = toUnsortedModelIndex(sortedIndex);
}
// sort the array of indices before returning
Arrays.sort(unsortedSelectedIndices);
return unsortedSelectedIndices;
}
/**
* Convert an unsorted model index to a sorted model index.
*
* @param unsortedIndex an element index in the unsorted model
* @return sortedIndex an element index in the sorted model
*/
public int toSortedModelIndex(int unsortedIndex) {
int sortedIndex = -1;
int x = -1;
for (SortedListEntry entry : getSortedModel()) {
++x;
if (entry.getIndex() == unsortedIndex) {
sortedIndex = x;
break;
}
}
return sortedIndex;
}
/**
* Convert an array of unsorted model selection indices to indices in
* the sorted model. Sort the model indices from low to high to
* duplicate JList's getSelectedIndices method
*
* @param unsortedModelIndices
* @return an array of selected indices in the sorted model
*/
public int[] toSortedModelIndices(int[] unsortedModelIndices) {
int[] sortedModelIndices = new int[unsortedModelIndices.length];
int x = 0;
for (int unsortedIndex : unsortedModelIndices) {
sortedModelIndices[x++] = toSortedModelIndex(unsortedIndex);
}
Arrays.sort(sortedModelIndices);
return sortedModelIndices;
}
private void resetModelData() {
int index = 0;
for (SortedListEntry entry : getSortedModel()) {
entry.setIndex(index++);
}
}
public void setComparator(Comparator comp) {
if (comparator == null || !comparator.equals(comp)) {
comparator = comp;
if (comparator == null) {
setSortOrder(SortOrder.Unsorted);
comparator = Collator.getInstance();
resetModelData();
} else if (getModel() != null) {
Collections.sort(getSortedModel());
}
if (getModel() != null) {
fireContentsChanged(ListDataEvent.CONTENTS_CHANGED, 0, getSortedModel().size() - 1);
}
}
}
/**
* Change the sort order of the model at runtime
*
* @param value
*/
public void setSortOrder(SortOrder value) {
if (sortOrder != value) {
sortOrder = value;
if (value == SortOrder.Unsorted) {
resetModelData();
} else if (getModel() != null) {
Collections.sort(getSortedModel());
}
if (getModel() != null) {
fireContentsChanged(ListDataEvent.CONTENTS_CHANGED, 0, getSortedModel().size() - 1);
}
}
}
/**
* Update the sorted model whenever new items are added to the
* original/decorated model.
*
*/
private void unsortedIntervalAdded(ListDataEvent e) {
int begin = e.getIndex0();
int end = e.getIndex1();
int nElementsAdded = end - begin + 1;
/* Items in the decorated model have shifted in flight.
* Increment our model pointers into the decorated model.
* We must increment indices that intersect with the insertion
* point in the decorated model.
*/
for (SortedListEntry entry : getSortedModel()) {
int index = entry.getIndex();
// if our model points to a model index >= to where
// new model entries are added, we must bump up their index
if (index >= begin) {
entry.setIndex(index + nElementsAdded);
}
}
// now add the new items from the decorated model
for (int x = begin; x <= end; ++x) {
SortedListEntry newEntry = new SortedListEntry(x);
int insertionPoint = findInsertionPoint(newEntry);
getSortedModel().add(insertionPoint, newEntry);
fireIntervalAdded(ListDataEvent.INTERVAL_ADDED, insertionPoint, insertionPoint);
}
}
/**
* Update this model when items are removed from the original/decorated
* model. Also, let our listeners know that we've removed items.
*/
private void unsortedIntervalRemoved(ListDataEvent e) {
int begin = e.getIndex0();
int end = e.getIndex1();
int nElementsRemoved = end - begin + 1;
/*
* Move from end to beginning of our sorted model, updating
* element indices into the decorated model or removing
* elements as necessary
*/
int sortedSize = getSortedModel().size();
boolean[] bElementRemoved = new boolean[sortedSize];
for (int x = sortedSize - 1; x >= 0; --x) {
SortedListEntry entry = getSortedModel().get(x);
int index = entry.getIndex();
if (index > end) {
entry.setIndex(index - nElementsRemoved);
} else if (index >= begin) {
getSortedModel().remove(x);
bElementRemoved[x] = true;
}
}
/*
* Let listeners know that we've removed items.
*/
for (int x = bElementRemoved.length - 1; x >= 0; --x) {
if (bElementRemoved[x]) {
fireIntervalRemoved(ListDataEvent.INTERVAL_REMOVED, x, x);
}
}
}
/**
* Resort the sorted model if there are changes in the original unsorted
* model. Let any listeners know about changes. Since I don't track
* specific changes, sort everywhere and redisplay all items.
*/
private void unsortedContentsChanged(ListDataEvent e) {
Collections.sort(getSortedModel());
fireContentsChanged(ListDataEvent.CONTENTS_CHANGED, 0, getSortedModel().size() - 1);
}
/**
* Internal helper method to find the insertion point for a new entry in
* the sorted model.
*/
private int findInsertionPoint(SortedListEntry entry) {
int insertionPoint = getSortedModel().size();
if (getSortOrder() != SortOrder.Unsorted) {
insertionPoint = Collections.binarySearch((List) getSortedModel(), entry);
if (insertionPoint < 0) {
insertionPoint = -(insertionPoint + 1);
}
}
return insertionPoint;
}
public Comparator getComparator() {
return comparator;
}
public class SortedListEntry implements Comparable {
private int index;
private SortedListEntry() {
}
public SortedListEntry(int index) {
this.index = index;
}
public int getIndex() {
return index;
}
public void setIndex(int index) {
this.index = index;
}
public int compareTo(Object o) {
int comparison = 0;
if (getModel() != null && getComparator() != null) {
// retrieve the element that this entry points to
// in the original model
Object thisElement = getModel().getElementAt(index);
SortedListEntry thatEntry = (SortedListEntry) o;
// retrieve the element that thatEntry points to in the original
// model
Object thatElement = getModel().getElementAt(thatEntry.getIndex());
if (getComparator() instanceof Collator) {
thisElement = thisElement.toString();
thatElement = thatElement.toString();
}
// compare the base model's elements using the provided comparator
comparison = getComparator().compare(thisElement, thatElement);
// convert to descending order as necessary
if (getSortOrder() == SortOrder.Descending) {
comparison = -comparison;
}
}
return comparison;
}
}
protected class ListDataHandler implements ListDataListener {
public void intervalAdded(ListDataEvent e) {
unsortedIntervalAdded(e);
}
public void intervalRemoved(ListDataEvent e) {
unsortedIntervalRemoved(e);
}
public void contentsChanged(ListDataEvent e) {
unsortedContentsChanged(e);
}
}
}
}
The concept of using a "proxy" model like this goes WAY back to Java 1.3, before we had things like RowSorter, which you might be able to use for this instead, but I've never had the time to go back an investigate it.
Using proxy models like this is a great way of adding new functionality to components, without the need to modify the existing code