I'm trying to convert MATLAB code to equivalent python.
I have 3 arrays and I want to compute interp2d:
nuA = np.asarray([2.439,2.5,2.6,2.7,2.8,3.0,3.2,3.5,4.0,5.0,6.0,8.0,10,15,25])
nuB = np.asarray([0,0.1,0.2,0.3,0.5,0.7,1])
a, b = np.meshgrid(nuA, nuB)
betaTab = np.transpose(np.asarray([[0.0,2.16,1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0],[0.0,1.592,3.39,1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0],[0.0,0.759,1.8,1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0],[0.0,0.482,1.048,1.694,1.0,1.0,1.0],[0.0,0.36,0.76,1.232,2.229,1.0,1.0],[0.0,0.253,0.518,0.823,1.575,1.0,1.0],[0.0,0.203,0.41,0.632,1.244,1.906,1.0],[0.0,0.165,0.332,0.499,0.943,1.56,1.0],[0.0,0.136,0.271,0.404,0.689,1.23,2.195],[0.0,0.109,0.216,0.323,0.539,0.827,1.917],[0.0,0.096,0.19,0.284,0.472,0.693,1.759],[0.0,0.082,0.163,0.243,0.412,0.601,1.596],[0.0,0.074,0.147,0.22,0.377,0.546,1.482],[0.0,0.064,0.128,0.191,0.33,0.478,1.362],[0.0,0.056,0.112,0.167,0.285,0.428,1.274]]))
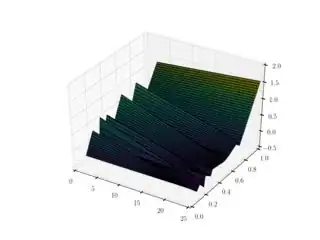
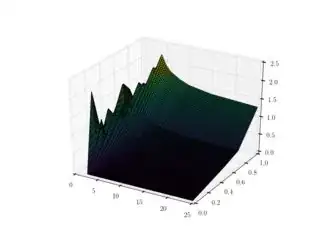
ip = scipy.interpolate.interp2d(a,b,betaTab)
when I try to run it, this warning is displayed:
/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/scipy/interpolate/fitpack.py:981: RuntimeWarning: No more knots can be added because the additional knot would
coincide with an old one. Probable cause: s too small or too large
a weight to an inaccurate data point. (fp>s)
kx,ky=1,1 nx,ny=4,14 m=105 fp=21.576347 s=0.000000
warnings.warn(RuntimeWarning(_iermess2[ierm][0] + _mess))
I know that interp2d is different from matlab interp2 and in python RectBivariateSpline function is preferred. But I can't use the latter function because of the length of my data. Also, the final result of ip(xi,yi) is different from the MATLAB answer.
How can I compute interp2d without warning and compute it correctly?