Read this out about all the ways in which you can set up the new HEAD
How to move HEAD back to a previous location? (Detached head)
Basically you need to decide to which commit you want to switch to and simply checkout this commit in a various ways as explained in the above link.
git checkout
git checkout <commit_id>
git checkout -b <new branch> <commit_id>
git checkout HEAD~X // x is the number of commits t go back
This will checkout new branch pointing to the desired commit.
This command will checkout to a given commit.
At this point you can create a branch and start to work from this point on.
# Checkout a given commit.
# Doing so will result in a `detached HEAD` which mean that the `HEAD`
# is not pointing to the latest so you will need to checkout branch
#in order to be able to update the code.
git checkout <commit-id>
# create a new branch forked to the given commit
git checkout -b <branch name>
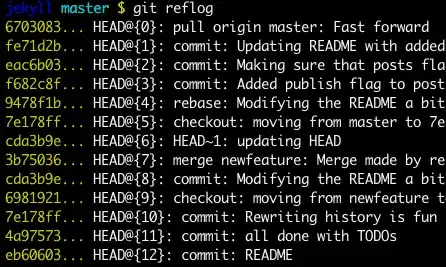
git reflog
You can always use the reflog as well
git reflog
git checkout HEAD@{...}
This will get you back to your desired commit
git reset HEAD --hard <commit_id>
"Move" your head back to the desired commit.
# This will destroy any local modifications.
# Don't do it if you have uncommitted work you want to keep.
git reset --hard 0d1d7fc32
# Alternatively, if there's work to keep:
git stash
git reset --hard 0d1d7fc32
git stash pop
# This saves the modifications, then reapplies that patch after resetting.
# You could get merge conflicts, if you've modified things which were
# changed since the commit you reset to.
- Note: (Since Git 2.7)
you can also use the git rebase --no-autostash as well.
Here is a general schema of what can be done.
