Is it possible to detect if an application is opened with the runas command?
And how can I detect which user is used?
runas /netonly /user:DOM\usr "C:\App.exe"
Is it possible to detect if an application is opened with the runas command?
And how can I detect which user is used?
runas /netonly /user:DOM\usr "C:\App.exe"
You can check for the user that is running the application, using
System.Security.Principal.WindowsIdentity.GetCurrent()
Note that using /netonly, there is no way to get the supplied credentials on a local process. The LSA takes care of that, and as far as I know, you just can't do it from your local process.
There are some good explanations on why on this link , but the why basically comes down to: while the credentials you supply are stored, they are not even checked until you do any kind of remote authentication (using SSPI), and those are checked only on the actual remote computer.
You can even do:
runas /netonly /user:FAKE\fake something.exe
And the credentials will not even be checked... so you basically don't get an auth token till you do the remote auth
Only solution I can see is trying to run a remote process which will return the user credentials.
You can see it on Windows Event Viewer under Windows Log > Security :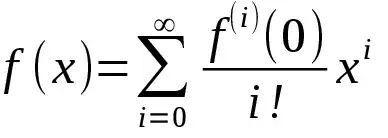
Whenever you run the runas command with /netonly you will se under Event ID 4624 or even under 4648.
in this example I used the follow command to open an instance of VS 2022 Community Edition:
runas /netonly /user:MYDOMAIN\MYUSER "C:\Program Files\Microsoft Visual Studio\2022\Community\Common7\IDE\DEVENV.EXE"
If you have impersonated programmatically throught .NET you should see it under the same EventID as showed above.
Note: in this example you don't have to debug the app to get the EventID raised. Only need to run the command.
Also in case you want to check the event viewer values or even created one by your on in .NET you may use EventLog class:
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/api/system.diagnostics.eventlog?view=windowsdesktop-7.0