I use C# to make connection to a db and then a Ad hoc SQL to get data. This simple SQL query is very convenient to debug since I can log the SQL query string. If I use parametrized SQL query command, is there any way to log sql query string for debug purpose?
4 Answers
I think this is about it. Place this code where you have configured the query command and you'll have the into debugSQL the SQL statement which will be executed
string debugSQL = cmd.CommandText;
foreach (SqlParameter param in cmd.Parameters)
{
debugSQL = debugSQL.Replace(param.ParameterName, param.Value.ToString());
}
- 4,440
- 3
- 35
- 56
-
2You can make an extension method: `public static string ToSQL(this IDbCommand Cmd) { ... }` and put above code in {...}. You'll want to format `debugSQL.Value` to output strings specific to types in your DB. – laifukang Apr 22 '14 at 07:42
-
3debugSQL.ParameterName and debugSQL.Value should be param.ParameterName and param.Value – JoeHz Apr 24 '17 at 06:13
-
2@JoeHz Ah! little typo. Thanks! – ɐsɹǝʌ ǝɔıʌ Apr 28 '17 at 11:05
SQL Server
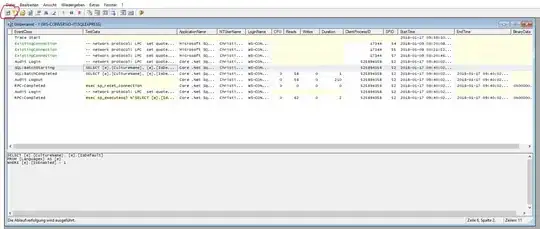
For SQL Server you could user the SQL Server Profiler:
Start a new Trace Session, and you will see everyting which gets executed. You can also filter it.
More Information here.
Everything other
General, you looking for a query profiler. You can search for <RDBMS NAME> query profiler and should find something usefull.
- 16,510
- 17
- 74
- 111
-
3Thanks (have an upvote), but does that mean that C# just holds on to the substituted query and doesn't let me see it at all? – NH. Jan 17 '18 at 15:59
-
1A parameter will be send to SQL server as a "variable". There is not such a concept as replace the sql query string before sending it to sql server. If you want something on c# site, it is very dependent on the library you are using. For plain ADO.NET look at [equisde's answer](https://stackoverflow.com/a/20490398/2441442). Maybe you could do something fancy with the [`DebugDisplayAttribute`](https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/x810d419.aspx) – Christian Gollhardt Jan 17 '18 at 16:13
Using the "debug" flag of your library is often the simplest solution. But you're dependent on the library which can lie to you or at least conceal a few things it will do (for instance, psycopg silently changes the default isolation level).
On the DBMS side, you can always activate logging. The good thing with it is that you will get the exact SQL request, whatever your client library does. In that respect, it is better than the "debug" flag of the library. But, on some DBMS, logging statements can be very slow (this is the case with PostgreSQL).
Another solution is to use a sniffer on the network, if you have sufficient privilege. Wireshark can decode the protocols of many DBMS and present the actual SQL request.
On PostgreSQL, activating logging is done in postgresql.conf by:
log_statement = 'all' # none, ddl, mod, all
I typically use also:
log_connections = on
log_disconnections = on
log_duration = on
log_hostname = on
- 34,164
- 12
- 67
- 91
The answer by equisde was helpful, but to handle bool and char types, I needed this variation:
string debugSQL = dbCommand.CommandText;
foreach (SqlParameter param in dbCommand.Parameters)
{
string val = param.Value.ToString();
switch (param.DbType)
{
case System.Data.DbType.AnsiString:
val = "'" + val + "'";
break;
case System.Data.DbType.Boolean:
val = (val == "True" ? "1" : "0");
break;
}
debugSQL = debugSQL.Replace("@" + param.ParameterName, val);
}
- 125
- 1
- 6