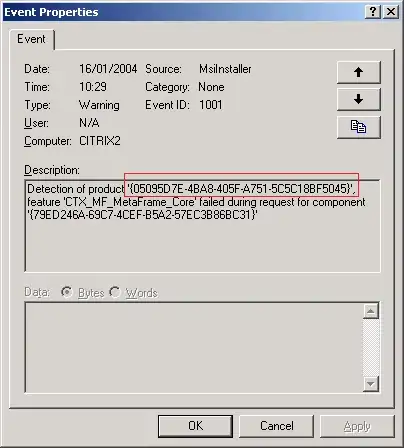
Example {
@SerializedName("Some1")
@Expose
private Some1 some1;
@SerializedName("Some3")
@Expose
private Some3 some3;
public Some1 getSome1() {
return some1;
}
public void setSome1(Some1 some1) {
this.some1 = some1;
}
public Some3 getSome3() {
return some3;
}
public void setSome3(Some3 some3) {
this.some3 = some3;
}
}
-----------------------------------com.example.Some1.java----------------
import com.google.gson.annotations.Expose;
import com.google.gson.annotations.SerializedName;
public class Some1 {
@SerializedName("data")
@Expose
private String data;
@SerializedName("title")
@Expose
private String title;
public String getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(String data) {
this.data = data;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
}
-----------------------------------com.example.Some3.java----------------
import com.google.gson.annotations.Expose;
import com.google.gson.annotations.SerializedName;
public class Some3 {
@SerializedName("data")
@Expose
private String data;
@SerializedName("title")
@Expose
private String title;
public String getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(String data) {
this.data = data;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
}
This is activity code for you, ENJOY!!!
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
String json = "{\n" +
" \"Some1\": {\n" +
" \"data\": \"dta\",\n" +
" \"title\": \"ttl\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"Some3\": {\n" +
" \"data\": \"dta2\",\n" +
" \"title\": \"ttl2\"\n" +
" }\n" +
"}";
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Example mExample = new Gson().fromJson(json, Example.class);
Toast.makeText(this, mExample.toString(), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
You can also use this website to generate class link
