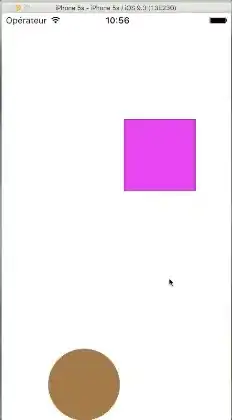
I want to be able to drag the objects on the screen, but they wont. I tried everything but still cant.
Here are the code.
func panGesture(gesture: UIPanGestureRecognizer) {
switch gesture.state {
case .began:
print("Began.")
for i in 0..<forms.count {
if forms[i].frame.contains(gesture.location(in: view)) {
gravity.removeItem(forms[i])
}
}
case .changed:
let translation = gesture.translation(in: forms[1])
gesture.view!.center = CGPoint(x: gesture.view!.center.x + translation.x, y: gesture.view!.center.y + translation.y)
gesture.setTranslation(CGPoint.zero, in: self.view)
print("\(gesture.view!.center.x)=\(gesture.view!.center.y)")
print("t;: \(translation)")
case .ended:
for i in 0..<forms.count {
if forms[i].frame.contains(gesture.location(in: view)) {
gravity.addItem(forms[i])
}
}
print("Ended.")
case .cancelled:
print("Cancelled")
default:
print("Default")
}
}
Also they have gravity. The forms are squares and circles.
Explanation: in .began - i disable the gravity for selected form. in .changed - i try to change the coordinates. in .end - i enable again gravity.
ScreenShot.