This works for me in ASP Net Core:
I had similar problem.
In startup.cs - ConfigureServices:
services.AddCors();
In startup.cs - Configure:
// global cors policy
app.UseCors(x => x
.AllowAnyMethod()
.AllowAnyHeader()
.SetIsOriginAllowed(origin => true) // allow any origin
//.WithOrigins("https://localhost:44351")); // Allow only this origin can also have multiple origins separated with comma
.AllowCredentials()); // allow credentials
Install NuGet Package: Microsoft.AspNetCore.Cors
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.AspNetCore.Cors" Version="2.2.0" />
Now its possible to call the api from the browser using ex. Javascript.
Found here:
https://jasonwatmore.com/post/2020/05/20/aspnet-core-api-allow-cors-requests-from-any-origin-and-with-credentials
Example - accessing from JS fetch api:
In the JS APP: - fetch api:
mode: 'cors',
credentials: 'include'
EDIT:
I have tried to understand CORS and this is how I understand it now - Please correct me if I am wrong:
The images are only for reference - the addresses are not the same as in the text.
CORS:
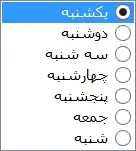
1. Client makes request to get the webpage from - https://localhost:5050
2. Client gets the webpage
3. Client tries to fetch “GET” data from https://localhost:5050 by using POST or GET and all is fine.
4. We have an API at https://localhost:6060 and we want to use it together with the webpage from - https://localhost:5050
5. Client tries to fetch “GET” data from the API - https://localhost:6060
6. Client Gets CORS Error Message - Because as Default only the Origin “the address” https://localhost:6060 is the only one that is allowed to fetch, get, post etc. Like swagger etc. that is on the same address can get the data but other addresses cant. But how is it possible that other APIs can use this API without CORS configuration on the server. This is because CORS is related to the browsers and its the browser that stops the response, so using it with other APIs without CORS is no problem.
7. To allow webpages to access the API, its the Server that needs to be configured for this.
8. The server needs to add a Access-Control-Allow-Origin: https:/address:port header and return the allowed Origin “Address” which is the one that is sending the request.
9. ASP net Core is configured in the startup.cs in the Configure method:
In ASP net Core is configured in the startup.cs in the Configure method:
// CORS - Allow calling the API from WebBrowsers
app.UseCors(x => x
.AllowAnyMethod()
.AllowAnyHeader()
.AllowCredentials()
//.WithOrigins("https://localhost:44351")); // Allow only this origin can also have multiple origins seperated with comma
.SetIsOriginAllowed(origin => true));// Allow any origin
10. This means when the server returns an response it will add Access-Control-Allow-Origin: with the address of the allowed origin.
11. Than the browser will get the response and will look for Access-Control-Allow-Origin:
If this header is there and the value is as the origin of the address that sent the request “the webpage address”. Then the response is allowed by the browser.
12. If there is no Access-Control-Allow-Origin: header that means that the server is not CORS configured and should be configured before consuming API data from browsers other APIs can GET and POST data but clients through browsers can't.
13. If there is Access-Control-Allow-Origin: header with the response but the value is not as the current address, “the web page address” then this means that the server is not configured for this particular website.
Conclussion:
So the server needs to be configured in order for the website to use the API. This is default browser behavior and will look for Access-Control-Allow-Origin: header if it's not present the browser will refuse to show the response to the client. If the Access-Control-Allow-Origin: is present but the origin value is not the same as the website address the browser will refuse showing the response to the client. This means that in any case the server should be configured with CORS configuration in order for Clients to access the API through web browsers. Other APIs etc. can get data from the API because they are not web browsers and there is no web browser blocking the response.
Misconfiguratin of CORS:
Like @ TwoFingerRightClick said, its not good to have Allow All Origins together with Allow Credentials.
Why allow credentials with allow all origins is not so good. In the post they talk about how user data can be stolen if CORS is misconfigured like I have done in the code above. I use Credentials and Allow all origins which is misconfiguratin of CORS. So allow all origins should be used without Allow credentials. If Allow credentials is needed we need to specify the Origins which we allow credentials from. So we need to use the commented line //.WithOrigins("https://localhost:44351")); // Allow only this origin can also have multiple origins separated with comma
Allow Credentials - Allows Cookies with request and response.
The Post: https://we45.com/blog/3-ways-to-exploit-cors-misconfiguration


