I am using Java to read in WAV data. With the WAV data being little-endian and Java using big-endian, I was looking to convert the values upon reading them in, as shown below, which I will then manipulate.
However, it seems to be working only partially for certain values.
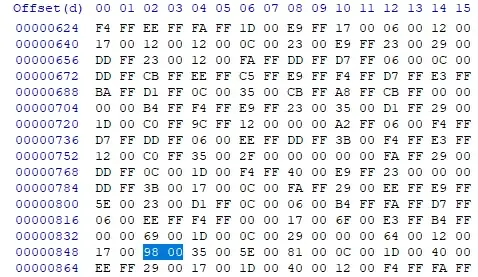
The first image shows the original WAV data, which should be read in as 98 00 and then swapped, to get 00 98, which would equate to 152 in decimal. My code below is however receiving the value -104 in decimal, which eqautes to simply 98 in hex. Note that this code should be able to take in negative values, as this is important to the use of the WAV data once it is read in.
This can equally seen a bit further down the same line as the higlighted values when the first value in the byte is above 80.
public boolean read (String filename) {
try {
FileInputStream input = new FileInputStream(new File(filename));
if (!(riff_header.read(input))) {
return false;
}
nSamples = (riff_header.getData_size() / riff_header.getBytes_samp());
System.out.println("Number of samples: " + nSamples);
sample = new int[nSamples];
System.out.println("Sizeof sample: " + sample.length);
// Should sample two bytes at a time (if 1 channel WAV)
byte[] bytes = new byte[riff_header.getBytes_samp()];
// incrementing by bytes_samp every iteration ( in this case, for test_file.wav = 2 bytes)
for (int i = 0; i < riff_header.getData_size(); i+=riff_header.getBytes_samp()) {
if (i / riff_header.getBytes_samp() == 402) {
System.out.println("break");
}
input.read(bytes);
// note - working backwards through array - endian order
int joined = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < bytes.length; j++) {
joined = joined | (int) (((bytes[(bytes.length - 1) - j]) << ((bytes.length - 1) - j) * 8));
}
sample[i / riff_header.getBytes_samp()] = joined;
}
input.close();
return true;
Howw