Using the MongoDB Java Driver library is there a way to stream writes of bson objects to a file and then later stream reads of bson objects from that file. Looking at the documentation I see nothing about how to encode a sequence of bson objects to a file similar to having a sequence of json objects in a file.
Asked
Active
Viewed 2,647 times
9
-
This might be helpful https://jaihirsch.github.io/straw-in-a-haystack/mongodb/2014/09/16/generate-bson-files-with-java/ – Rajind Ruparathna Feb 01 '18 at 03:45
-
and perhaps https://stackoverflow.com/questions/38689874/how-could-i-write-a-bsondocument-object-into-a-file-and-read-it-again-using-ja – Rajind Ruparathna Feb 01 '18 at 03:47
-
Writing/reading bson objects is what the driver already does.. and the file it uses is the data file. Mongo is a document database, everything is bson document. So if you have the bson object, or a sequence of objects, using the driver, you can persist it in the db file. What else is the db for? – mcku Feb 07 '18 at 22:05
2 Answers
2
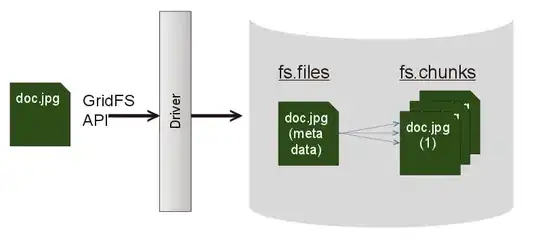
MongoDB GridFS is a specification for storing and retrieving files.
Use GridFS to store a file « GridFS uses two collections to save a file to a database: fs.files and fs.chunks. Based on the size of the file the data get stored into multiple individual “chunks”.
* MongoDB Files using GridFS. Refer to MyPost
For more information on GridFS go through my Github wiki.
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
mongoDB_GRIDFS("D:\\Yash\\JavaCSV.csv");
}
public static void mongoDB_GRIDFS(String csvlocation) throws IOException{
Mongo Mongo = new Mongo( "localhost" , 27017 ); // Connect to MongoDB
DB db = Mongo.getDB( "DBName" ); // Get database
String bucketName = "BucketName";
GridFS gridFs = new GridFS(db,bucketName); //Create instance of GridFS implementation
String imageName = "image1";
upload(gridFs, csvlocation, imageName);
download(gridFs, imageName);
Mongo.close();
}
public static void upload(GridFS gridFs, String csvlocation, String imageName) throws IOException{
GridFSInputFile gridFsInputFile = gridFs.createFile(new File(csvlocation));
gridFsInputFile.setId("777");
gridFsInputFile.setFilename(imageName); //Set a name on GridFS entry
gridFsInputFile.save(); //Save the file to MongoDB
}
public static void download(GridFS gridFs, String imageName) throws IOException{
GridFSDBFile outputImageFile = gridFs.findOne(imageName);
String outcsvLocation = "D:\\Yash\\mongoCSV.csv";//Location of the file read from MongoDB to be written
outputImageFile.writeTo(new File(outcsvLocation));
}
CSV file to JSON Object and JSON String to CSV File.
- CSV file to JSON refer to class
CSV_FileOperations.. - JSON to CSV File refer to method
Json2Csv(String fileName, String jsonString).
JSON to BSON and BSON to JSON.
MongoDB Java Driverjar comes with utility methods for parsing JSON to BSON and serializing BSON to JSON.
- BSON Library « A standalone BSON library, with a new Codec infrastructure that you can use to build high-performance encoders and decoders without requiring an intermediate Map instance.
DBObject dbObj = new Document("myKey", "myValue");
String db_json = com.mongodb.util.JSON.serialize( dbObj );
DBObject bson = ( DBObject ) com.mongodb.util.JSON.parse( jsonData );
System.out.println("BSON Object : "+ bson);
sample output:
BSON Object : [ { "Key2" : "21" , "Key1" : "11" } , { "Key2" : "22" , "Key1" : "12"}]
Json : {"K1":"V1","K2":"V2"}
Map : {K1=V1, K2=V2}
Yash
- 9,250
- 2
- 69
- 74
1
Based on the documention for MongoDb Java driver: BSON I wrote following example. Is this what you are looking for?
Class for the logic:
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import org.apache.commons.io.IOUtils;
import org.bson.BsonBinaryReader;
import org.bson.BsonBinaryWriter;
import org.bson.BsonReader;
import org.bson.BsonWriter;
import org.bson.codecs.Codec;
import org.bson.codecs.DecoderContext;
import org.bson.codecs.EncoderContext;
import org.bson.codecs.StringCodec;
import org.bson.codecs.configuration.CodecRegistries;
import org.bson.codecs.configuration.CodecRegistry;
import org.bson.codecs.pojo.PojoCodecProvider;
import org.bson.io.BasicOutputBuffer;
public class Bson {
FileOutputStream fop;
FileInputStream fip;
BsonWriter writer;
BsonReader reader;
Codec<Person> codec;
EncoderContext ec;
DecoderContext dc;
BasicOutputBuffer output;
public Bson() {
PojoCodecProvider provider = PojoCodecProvider.builder()
.register(Person.class)
.build();
CodecRegistry registry = CodecRegistries
.fromRegistries(CodecRegistries.fromCodecs(new StringCodec()),
CodecRegistries.fromProviders(provider));
codec = provider.get(Person.class, registry);
ec = EncoderContext.builder().build();
dc = DecoderContext.builder().build();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Bson bson = new Bson();
// write data
bson.initBsonWriter();
bson.encodePerson(new Person("John", "Doe"));
bson.encodePerson(new Person("John2", "Doe2"));
bson.encodePerson(new Person("John3", "Doe3"));
bson.closeFop();
// read data
bson.initBsonReader();
Person person = bson.decodePerson();
System.out.println(person);
person = bson.decodePerson();
System.out.println(person);
person = bson.decodePerson();
System.out.println(person);
bson.closeFip();
}
public void initBsonWriter() throws IOException {
openFop();
output = new BasicOutputBuffer();
writer = new BsonBinaryWriter(output);
writer.writeStartDocument();
writer.writeName("values");
writer.writeStartArray();
}
public void initBsonReader() throws IOException {
openFip();
reader = new BsonBinaryReader(ByteBuffer.wrap(IOUtils.toByteArray(fip)));
reader.readStartDocument();
reader.readName();
reader.readStartArray();
}
public void encodePerson(Person p) {
codec.encode(writer, p, ec);
}
public Person decodePerson() {
return codec.decode(reader, dc);
}
public void openFop() throws IOException {
File file = new File("example.bson");
fop = new FileOutputStream(file);
// if file doesnt exists, then create it
if (!file.exists()) {
file.createNewFile();
}
}
public void closeFop() throws IOException {
writer.writeEndArray();
writer.writeEndDocument();
output.pipe(fop);
fop.flush();
fop.close();
}
public void openFip() throws IOException {
File file = new File("example.bson");
fip = new FileInputStream(file);
}
public void closeFip() throws IOException {
fip.close();
}
}
POJO to store some data:
public class Person {
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
public Person() { }
public Person(final String firstName, final String lastName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public void setFirstName(final String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(final String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [firstName=" + firstName + ", lastName=" + lastName + "]";
}
}
Adrian Farmadin
- 407
- 2
- 11
-
Does this work if there is more than one bson object written to the file? – user782220 Feb 06 '18 at 00:39
-
I modified the example. Now is in file created one main document containing an array of `Person` objects. I used `wirter`to create the main document so you can easily stream objects to the array. – Adrian Farmadin Feb 06 '18 at 19:58
-
@user782220 now when my example supports streaming multiple BSON object to the file, is it what you are looking for? Or did I missed something? – Adrian Farmadin Feb 07 '18 at 17:39