I am trying to make an outbound API request to a third-party service from within a Lambda function, but the function always times out without any error.
This previously happened when trying to perform a s3.putObject operation within a different function (still within the same VPC / subnets), and I managed to get around that by adding an Endpoint with a service name com.amazonaws.us-east-1.s3 and connecting it to the route table that is associated with the VPC that this Lambda function resides in.
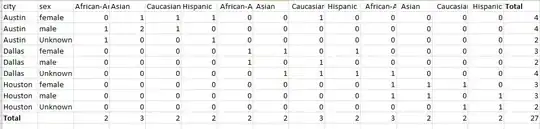
Within the Lambda dashboard inside Network box -> Security Groups section, I see this warning:
When you enable VPC, your Lambda function will lose default internet access. If you require external internet access for your function, ensure that your security group allows outbound connections and that your VPC has a NAT gateway.
I believe that this security group allows outbound connections, based off of the Outbound rules table right underneath:
For that second requirement, I can confirm this VPC has a NAT gateway, because on the VPC Dashboard, within NAT Gateways tab, the one that appears there has a VCP associated with it, and that VPC is the same one hosting the Lambda function.
I followed a guide to create a Flow Log to monitor traffic in and out of the VPC, hoping to see that those outbound requests are indeed rejected. However, after doing so and inspecting the CloudWatch logs, all of the records end in either ACCEPT OK or NODATA.
How can I grant internet access to my VPC Lambda function? is the guide I originally tried to follow, but I got stuck on step 4 under To create a public or private subnet:
From the Change to: drop-down menu, choose an appropriate route table: For a private subnet, the default route should point to a NAT gateway or NAT instance:
Destination: 0.0.0.0/0 Target: nat-… (or eni-…) For a public subnet, the default route should point to an internet gateway:
Destination: 0.0.0.0/0 Target: igw-…
For all four of the subnets within this VPC, clicking the drop-down to the right of Change to: only showed one option, the one already selected, rtb-xxxxxxxx. After clicking on the link to that route table, and clicking the Routes tab next to Summary, I see this:
What might I be doing wrong that is blocking the Lambda function's access to the Internet?