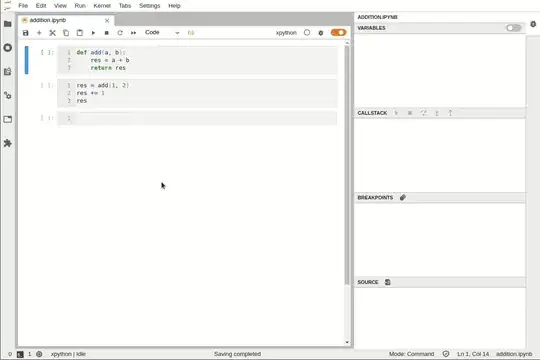
In Jupyter notebook, if I have
print("hello")
quit()
in the first cell and
print("Good bye")
in the second, when I do "Run all" it prints hello and also Good bye.
In other words, quit() seems to only stop the execution of the cell itself, not the whole script.
Is there some way to add a breakpoint to your code so that it stops executing when it gets to it?