So you want this:
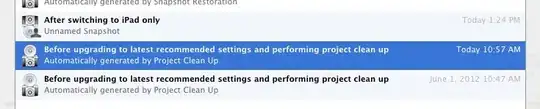
You should use a UICollectionView. You can't use UICollectionViewFlowLayout (the only layout that's provided in the public SDK) because it is designed to only scroll in one direction, so you need to implement a custom UICollectionViewLayout subclass that arranges the elements to scroll in both directions if needed.
For full details on building a custom UICollectionViewLayout subclass, you should watch these: videos from WWDC 2012:
Anyway, I'll just dump an example implementation of GridLayout here for you to start with. For each IndexPath, I use the section as the row number and the item as the column number.
class GridLayout: UICollectionViewLayout {
var cellHeight: CGFloat = 22
var cellWidths: [CGFloat] = [] {
didSet {
precondition(cellWidths.filter({ $0 <= 0 }).isEmpty)
invalidateCache()
}
}
override var collectionViewContentSize: CGSize {
return CGSize(width: totalWidth, height: totalHeight)
}
override func layoutAttributesForElements(in rect: CGRect) -> [UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes]? {
// When bouncing, rect's origin can have a negative x or y, which is bad.
let newRect = rect.intersection(CGRect(x: 0, y: 0, width: totalWidth, height: totalHeight))
var poses = [UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes]()
let rows = rowsOverlapping(newRect)
let columns = columnsOverlapping(newRect)
for row in rows {
for column in columns {
let indexPath = IndexPath(item: column, section: row)
poses.append(pose(forCellAt: indexPath))
}
}
return poses
}
override func layoutAttributesForItem(at indexPath: IndexPath) -> UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes? {
return pose(forCellAt: indexPath)
}
override func shouldInvalidateLayout(forBoundsChange newBounds: CGRect) -> Bool {
return false
}
private struct CellSpan {
var minX: CGFloat
var maxX: CGFloat
}
private struct Cache {
var cellSpans: [CellSpan]
var totalWidth: CGFloat
}
private var _cache: Cache? = nil
private var cache: Cache {
if let cache = _cache { return cache }
var spans = [CellSpan]()
var x: CGFloat = 0
for width in cellWidths {
spans.append(CellSpan(minX: x, maxX: x + width))
x += width
}
let cache = Cache(cellSpans: spans, totalWidth: x)
_cache = cache
return cache
}
private var totalWidth: CGFloat { return cache.totalWidth }
private var cellSpans: [CellSpan] { return cache.cellSpans }
private var totalHeight: CGFloat {
return cellHeight * CGFloat(collectionView?.numberOfSections ?? 0)
}
private func invalidateCache() {
_cache = nil
invalidateLayout()
}
private func rowsOverlapping(_ rect: CGRect) -> Range<Int> {
let startRow = Int(floor(rect.minY / cellHeight))
let endRow = Int(ceil(rect.maxY / cellHeight))
return startRow ..< endRow
}
private func columnsOverlapping(_ rect: CGRect) -> Range<Int> {
let minX = rect.minX
let maxX = rect.maxX
if let start = cellSpans.firstIndex(where: { $0.maxX >= minX }), let end = cellSpans.lastIndex(where: { $0.minX <= maxX }) {
return start ..< end + 1
} else {
return 0 ..< 0
}
}
private func pose(forCellAt indexPath: IndexPath) -> UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes {
let pose = UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes(forCellWith: indexPath)
let row = indexPath.section
let column = indexPath.item
pose.frame = CGRect(x: cellSpans[column].minX, y: CGFloat(row) * cellHeight, width: cellWidths[column], height: cellHeight)
return pose
}
}
To draw the separating lines, I added hairline views to each cell's background:
class GridCell: UICollectionViewCell {
static var reuseIdentifier: String { return "cell" }
override init(frame: CGRect) {
super.init(frame: frame)
label.frame = bounds.insetBy(dx: 2, dy: 2)
label.autoresizingMask = [.flexibleWidth, .flexibleHeight]
contentView.addSubview(label)
let backgroundView = UIView(frame: CGRect(origin: .zero, size: frame.size))
backgroundView.backgroundColor = .white
self.backgroundView = backgroundView
rightSeparator.backgroundColor = .gray
backgroundView.addSubview(rightSeparator)
bottomSeparator.backgroundColor = .gray
backgroundView.addSubview(bottomSeparator)
}
func setRecord(_ record: String) {
label.text = record
}
override func layoutSubviews() {
super.layoutSubviews()
let thickness = 1 / (window?.screen.scale ?? 1)
let size = bounds.size
rightSeparator.frame = CGRect(x: size.width - thickness, y: 0, width: thickness, height: size.height)
bottomSeparator.frame = CGRect(x: 0, y: size.height - thickness, width: size.width, height: thickness)
}
private let label = UILabel()
private let rightSeparator = UIView()
private let bottomSeparator = UIView()
required init?(coder aDecoder: NSCoder) {
fatalError("init(coder:) has not been implemented")
}
}
Here's my demo view controller:
class ViewController: UIViewController {
var records: [[String]] = (0 ..< 20).map { row in
(0 ..< 6).map {
column in
"Row \(row) column \(column)"
}
}
var cellWidths: [CGFloat] = [ 180, 200, 180, 160, 200, 200 ]
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
let layout = GridLayout()
layout.cellHeight = 44
layout.cellWidths = cellWidths
let collectionView = UICollectionView(frame: view.bounds, collectionViewLayout: layout)
collectionView.isDirectionalLockEnabled = true
collectionView.backgroundColor = UIColor(white: 0.95, alpha: 1)
collectionView.autoresizingMask = [.flexibleWidth, .flexibleHeight]
collectionView.register(GridCell.self, forCellWithReuseIdentifier: GridCell.reuseIdentifier)
collectionView.dataSource = self
view.addSubview(collectionView)
}
}
extension ViewController: UICollectionViewDataSource {
func numberOfSections(in collectionView: UICollectionView) -> Int {
return records.count
}
func collectionView(_ collectionView: UICollectionView, numberOfItemsInSection section: Int) -> Int {
return records[section].count
}
func collectionView(_ collectionView: UICollectionView, cellForItemAt indexPath: IndexPath) -> UICollectionViewCell {
let cell = collectionView.dequeueReusableCell(withReuseIdentifier: GridCell.reuseIdentifier, for: indexPath) as! GridCell
cell.setRecord(records[indexPath.section][indexPath.item])
return cell
}
}