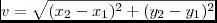I'm trying to compute the integral of a gaussian from an arbitrary point gamma as follows:
import numpy as np
from scipy.stats import norm
def func(mu, sigma, gamma):
x = np.linspace(mu-4*sigma, mu + 4*sigma, 100)
y = norm.pdf(x, mu, sigma)
area = y[x>=gamma].sum()
print(f"Area is ~ {area:.3f}")
plt.plot(x,y, label=f'μ0 = {mu}, σ={sigma}')
plt.fill_between(x[x>gamma],y[x>gamma], alpha=.5, label=f'area={area:.3f}')
plt.title("Example")
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.show()
# Execute the function
func(0,10,-20)
Output is: Area is ~ 1.211
The blue area is integrated but it adds more than one (far more), even when it's not the complete function.
I found this related but didn't help.
Why is it adding up more than one?