I ran in the same issue.
This is what worked for me:
Setting up Properties of Windows Authentication in IIS
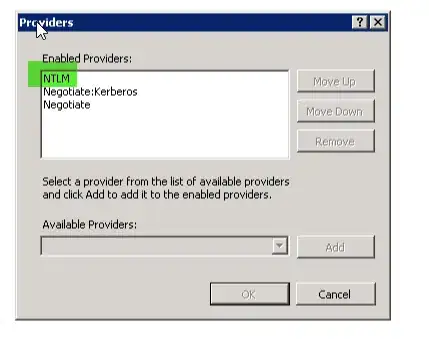
NTLM has to be the topmost.
Further Web.config modifications, make sure you already have or add if these do not exist:
<system.web>
<authentication mode="Windows" />
<identity impersonate="true"/>
</system.web>
<!-- you need the following lines of code to bypass errors, concerning type of Application Pool (integrated pipeline or classic) -->
<system.webServer>
<validation validateIntegratedModeConfiguration="false"/>
</system.webServer>
See below a legit explanation for the two nodes and
Difference between <system.web> and <system.webServer>?
And, of course , you get the username by
//I am using the following to get the index of the separator "\\" and remove the Domain name from the string
int indexOfSlashChar = HttpContext.Current.User.Identity.Name.IndexOf("\\");
loggedInWindowsUserName = HttpContext.Current.User.Identity.Name.Substring(indexOfSlashChar + 1);




