According to the documentation, a View (editor) receives commands from the Keyboard (IME) through an InputConnection and sends commands to the Keyboard through an InputMethodManager.
I will show the entire code below, but here are the steps.
1. Make the Keyboard to appear
Since the view is sending a command to the keyboard it needs to use an InputMethodManager. For the sake of the example, we will say that when the view is tapped it will show the keyboard (or hide it if it is already showing).
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
if (event.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_UP) {
InputMethodManager imm = (InputMethodManager) getContext().getSystemService(Context.INPUT_METHOD_SERVICE);
imm.toggleSoftInput(InputMethodManager.SHOW_IMPLICIT, InputMethodManager.HIDE_IMPLICIT_ONLY);
}
return true;
}
The view also needs to have had setFocusableInTouchMode(true) set previously.
2. Receive input from the keyboard
In order for the view to receive input from the keyboard, it needs to override onCreateInputConnection(). This returns the InputConnection that the Keyboard uses to communicate with the view.
@Override
public InputConnection onCreateInputConnection(EditorInfo outAttrs) {
outAttrs.inputType = InputType.TYPE_CLASS_TEXT;
return new MyInputConnection(this, true);
}
The outAttrs specify what kind of keyboard the view is requesting. Here we are just requesting a normal text keyboard. Choosing TYPE_CLASS_NUMBER would display a number pad (if available). There are lots of other options. See EditorInfo.
You must return an InputConnection, which is usually a custom subclass of BaseInputConnection. In that subclass you provide a reference to your editable string, which the keyboard will make updates to. Since a SpannableStringBuilder implements the Editable interface, we will use that in our basic example.
public class MyInputConnection extends BaseInputConnection {
private SpannableStringBuilder mEditable;
MyInputConnection(View targetView, boolean fullEditor) {
super(targetView, fullEditor);
MyCustomView customView = (MyCustomView) targetView;
mEditable = customView.mText;
}
@Override
public Editable getEditable() {
return mEditable;
}
}
All we did here was provide the input connection with a reference to the text variable in our custom view. The BaseInputConnection will take care of editing that mText. This could very well be all that you need to do. However, you can check out the source code and see which methods say "default implementation", especially "default implementation does nothing." These are other methods you may want to override depending on how involved your editor view is going to be. You should also look through all the method names in the documentation. A number of them have notes to "editor authors". Pay special attention to those.
Some keyboards don't send certain input through the InputConnection for some reason (for example delete, enter, and some number pad keys). For those I added an OnKeyListener. Testing this setup on five different soft keyboards, everything seemed to work. Supplemental answers related to this are here:
Full project code
Here is my full example for reference.
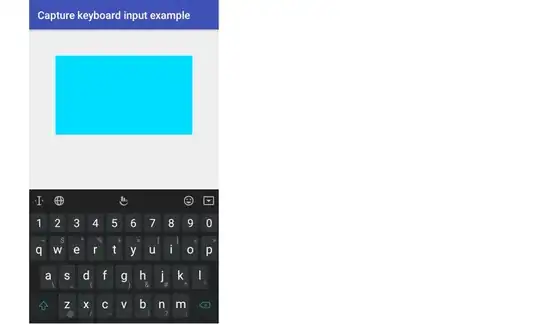
MyCustomView.java
public class MyCustomView extends View {
SpannableStringBuilder mText;
public MyCustomView(Context context) {
this(context, null, 0);
}
public MyCustomView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public MyCustomView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
init();
}
private void init() {
setFocusableInTouchMode(true);
mText = new SpannableStringBuilder();
// handle key presses not handled by the InputConnection
setOnKeyListener(new OnKeyListener() {
public boolean onKey(View v, int keyCode, KeyEvent event) {
if (event.getAction() == KeyEvent.ACTION_DOWN) {
if (event.getUnicodeChar() == 0) { // control character
if (keyCode == KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DEL) {
mText.delete(mText.length() - 1, mText.length());
Log.i("TAG", "text: " + mText + " (keycode)");
return true;
}
// TODO handle any other control keys here
} else { // text character
mText.append((char)event.getUnicodeChar());
Log.i("TAG", "text: " + mText + " (keycode)");
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
});
}
// toggle whether the keyboard is showing when the view is clicked
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
if (event.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_UP) {
InputMethodManager imm = (InputMethodManager) getContext().getSystemService(Context.INPUT_METHOD_SERVICE);
imm.toggleSoftInput(InputMethodManager.SHOW_IMPLICIT, InputMethodManager.HIDE_IMPLICIT_ONLY);
}
return true;
}
@Override
public InputConnection onCreateInputConnection(EditorInfo outAttrs) {
outAttrs.inputType = InputType.TYPE_CLASS_TEXT;
// outAttrs.inputType = InputType.TYPE_CLASS_NUMBER; // alternate (show number pad rather than text)
return new MyInputConnection(this, true);
}
}
MyInputConnection.java
public class MyInputConnection extends BaseInputConnection {
private SpannableStringBuilder mEditable;
MyInputConnection(View targetView, boolean fullEditor) {
super(targetView, fullEditor);
MyCustomView customView = (MyCustomView) targetView;
mEditable = customView.mText;
}
@Override
public Editable getEditable() {
return mEditable;
}
// just adding this to show that text is being committed.
@Override
public boolean commitText(CharSequence text, int newCursorPosition) {
boolean returnValue = super.commitText(text, newCursorPosition);
Log.i("TAG", "text: " + mEditable);
return returnValue;
}
}
activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="com.example.editorview.MainActivity">
<com.example.editorview.MyCustomView
android:id="@+id/myCustomView"
android:background="@android:color/holo_blue_bright"
android:layout_margin="50dp"
android:layout_width="300dp"
android:layout_height="150dp"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
/>
</RelativeLayout>
There is nothing special in the MainActivity.java code.
Please leave a comment if this doesn't work for you. I am using this basic solution for a custom EditText in a library I am making and if there are any edge cases in which it doesn't work, I want to know. If you would like to view that project, the custom view is here. It's InputConnection is here.
Related

