I am attempting to project a world map in a Robinson projection where the central meridian is different from 0. According to this StackOverFlow thread, it should be an easy thing (albeit the example uses sp).
Here is my reproducible code:
library(sf)
library(ggplot2)
library(rnaturalearth)
world <- ne_countries(scale = 'small', returnclass = 'sf')
# Notice +lon_0=180 instead of 0
world_robinson <- st_transform(world, crs = '+proj=robin +lon_0=180 +x_0=0 +y_0=0 +ellps=WGS84 +datum=WGS84 +units=m +no_defs')
ggplot() +
geom_sf(data = world_robinson)
This is the result. Polygons are closing themselves from one side to the other of the projection.
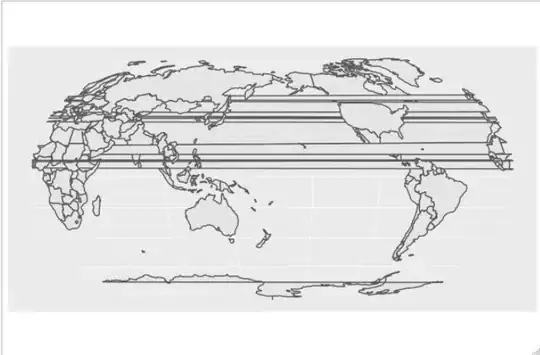
Trying with sp gives the same effect. I also tried with a shapefile including only polygons from coastlines (no political borders) from http://www.naturalearthdata.com/ and the effect is similar.
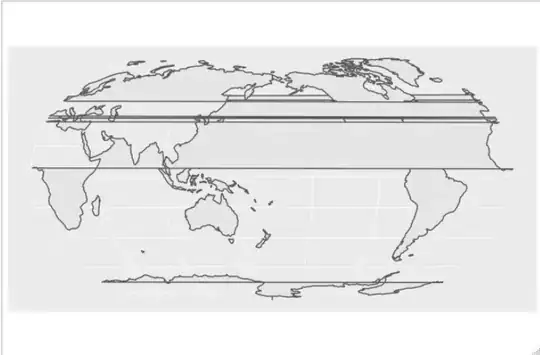
I tried to run my snippet on two independent R installations on Mac OS X and Ubuntu 18.04.