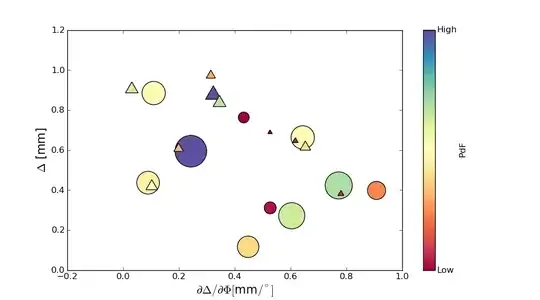
You can apply 2 or more materials like this
const geometry = new THREE.BoxBufferGeometry(boxWidth, boxHeight, boxDepth);
// prepare geometry to use 2 materials
geometry.clearGroups();
geometry.addGroup( 0, Infinity, 0 );
geometry.addGroup( 0, Infinity, 1 );
const loader = new THREE.TextureLoader();
// create 2 materials
const material0 = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({
color: 'orange',
});
const material1 = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({
map: loader.load('https://i.imgur.com/iFom4eT.png'),
transparent: true,
});
// apply 2 materials to geometry
const materials = [material0, material1];
const cube = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, materials);
Example, note it uses BoxBufferGeometry not BoxGeometry
function main() {
const canvas = document.querySelector('#c');
const renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({canvas});
const fov = 75;
const aspect = 2; // the canvas default
const near = 0.1;
const far = 5;
const camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(fov, aspect, near, far);
camera.position.z = 2;
const scene = new THREE.Scene();
scene.background = new THREE.Color('purple');
const boxWidth = 1;
const boxHeight = 1;
const boxDepth = 1;
const geometry = new THREE.BoxBufferGeometry(boxWidth, boxHeight, boxDepth);
// prepare geometry to use 2 materials
geometry.clearGroups();
geometry.addGroup( 0, Infinity, 0 );
geometry.addGroup( 0, Infinity, 1 );
const loader = new THREE.TextureLoader();
// create 2 materials
const material0 = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({
color: 'orange',
});
const material1 = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({
map: loader.load('https://i.imgur.com/hrzoDMj.png'),
transparent: true,
});
// apply 2 materials to geometry
const materials = [material0, material1];
const cube = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, materials);
scene.add(cube);
function render(time) {
time *= 0.001; // convert time to seconds
if (resizeRendererToDisplaySize(renderer)) {
const canvas = renderer.domElement;
camera.aspect = canvas.clientWidth / canvas.clientHeight;
camera.updateProjectionMatrix();
}
cube.rotation.x = time;
cube.rotation.y = time;
renderer.render(scene, camera);
requestAnimationFrame(render);
}
requestAnimationFrame(render);
}
function resizeRendererToDisplaySize(renderer) {
const canvas = renderer.domElement;
const width = canvas.clientWidth;
const height = canvas.clientHeight;
const needResize = canvas.width !== width || canvas.height !== height;
if (needResize) {
renderer.setSize(width, height, false);
}
return needResize;
}
main();
body { margin: 0; }
#c { width: 100vw; height: 100vh; display: block; }
<script src="https://threejsfundamentals.org/threejs/resources/threejs/r110/build/three.min.js"></script>
<canvas id="c"></canvas>
note that if you put a color and a texture (map) in a single material the 2 colors, (1) the color you specified and (2) the color from the texture, are multiplied with each other. So, wherever the texture has zeros, RGBA = 0,0,0,0 then the result is 0,0,0,0 as anything multiplied by zero is zero. This is why you got the results you got originally where outside the question mark is transparent and inside is orange.
Knowing this you can use your white question mark and change its color by setting the color on the material that is using the texture.
function main() {
const canvas = document.querySelector('#c');
const renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({canvas});
const fov = 75;
const aspect = 2; // the canvas default
const near = 0.1;
const far = 5;
const camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(fov, aspect, near, far);
camera.position.z = 2;
const scene = new THREE.Scene();
scene.background = new THREE.Color('purple');
const boxWidth = 1;
const boxHeight = 1;
const boxDepth = 1;
const geometry = new THREE.BoxBufferGeometry(boxWidth, boxHeight, boxDepth);
// prepare geometry to use 2 materials
geometry.clearGroups();
geometry.addGroup( 0, Infinity, 0 );
geometry.addGroup( 0, Infinity, 1 );
const loader = new THREE.TextureLoader();
// create 2 materials
const material0 = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({
color: 'orange',
});
const material1 = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({
map: loader.load('https://i.imgur.com/hrzoDMj.png'),
transparent: true,
});
// apply 2 materials to geometry
const materials = [material0, material1];
const cube = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, materials);
scene.add(cube);
function render(time) {
time *= 0.001; // convert time to seconds
if (resizeRendererToDisplaySize(renderer)) {
const canvas = renderer.domElement;
camera.aspect = canvas.clientWidth / canvas.clientHeight;
camera.updateProjectionMatrix();
}
material1.color.setHSL(time, 1, 0.5);
cube.rotation.x = time;
cube.rotation.y = time;
renderer.render(scene, camera);
requestAnimationFrame(render);
}
requestAnimationFrame(render);
}
function resizeRendererToDisplaySize(renderer) {
const canvas = renderer.domElement;
const width = canvas.clientWidth;
const height = canvas.clientHeight;
const needResize = canvas.width !== width || canvas.height !== height;
if (needResize) {
renderer.setSize(width, height, false);
}
return needResize;
}
main();
body { margin: 0; }
#c { width: 100vw; height: 100vh; display: block; }
<script src="https://threejsfundamentals.org/threejs/resources/threejs/r110/build/three.min.js"></script>
<canvas id="c"></canvas>