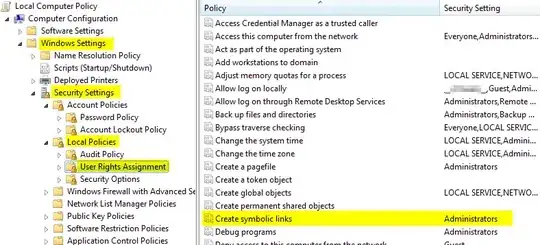
Like Gian Marco Gherardi answer but defines os.symlink on windows, so that your code can safely work on windows and linux:
import os
os_symlink = getattr(os, "symlink", None)
if callable(os_symlink):
pass
else:
def symlink_ms(source, link_name):
import ctypes
csl = ctypes.windll.kernel32.CreateSymbolicLinkW
csl.argtypes = (ctypes.c_wchar_p, ctypes.c_wchar_p, ctypes.c_uint32)
csl.restype = ctypes.c_ubyte
flags = 1 if os.path.isdir(source) else 0
if csl(link_name, source, flags) == 0:
raise ctypes.WinError()
os.symlink = symlink_ms
If you run your script as administrator everything is fine, if you want to run it as user -- you have to grant python a permission to make symlinks -- which only possible under windows vista+ ultimate or professional.
Edit:
Gian Marco Gherardi answer creates a link to a unix path: like/this and it doesn't work. The fix is to do source.replace('/', '\\'):
# symlink support under windows:
import os
os_symlink = getattr(os, "symlink", None)
if callable(os_symlink):
pass
else:
def symlink_ms(source, link_name):
import ctypes
csl = ctypes.windll.kernel32.CreateSymbolicLinkW
csl.argtypes = (ctypes.c_wchar_p, ctypes.c_wchar_p, ctypes.c_uint32)
csl.restype = ctypes.c_ubyte
flags = 1 if os.path.isdir(source) else 0
if csl(link_name, source.replace('/', '\\'), flags) == 0:
raise ctypes.WinError()
os.symlink = symlink_ms
Another way is to use window's vista+ mklink utility. But using this utility requires same permissions. Still:
# symlink support under windows:
import os
os_symlink = getattr(os, "symlink", None)
if callable(os_symlink):
pass
else:
def symlink_ms(source, link_name):
os.system("mklink {link} {target}".format(
link = link_name,
target = source.replace('/', '\\')))
os.symlink = symlink_ms
Edit 2:
Here's what I'm finally using: this script makes a link under windows if the user has a privilage to do so, otherwise it just doesn't make a link:
import os
if os.name == "nt":
def symlink_ms(source, link_name):
import ctypes
csl = ctypes.windll.kernel32.CreateSymbolicLinkW
csl.argtypes = (ctypes.c_wchar_p, ctypes.c_wchar_p, ctypes.c_uint32)
csl.restype = ctypes.c_ubyte
flags = 1 if os.path.isdir(source) else 0
try:
if csl(link_name, source.replace('/', '\\'), flags) == 0:
raise ctypes.WinError()
except:
pass
os.symlink = symlink_ms