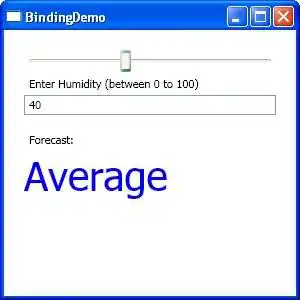
The following code is inspired by the multicolored-line example from the matplotlib docs. First the horizontal line segments are drawn and colored using their y-value. The vertical segments are subdivided in small chunks to colored individually.
vmin of the norm is set a bit lower to avoid the too-light range of the colormap.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.collections import LineCollection
import numpy as np
x = np.arange(50)
y = np.random.randint(-3, 4, x.size).cumsum()
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
norm = plt.Normalize(y.min() - y.ptp() * .2, y.max())
cmap = 'inferno_r' # 'Reds'
horizontal_lines = np.array([x[:-1], y[:-1], x[1:], y[:-1]]).T.reshape(-1, 2, 2)
hor_lc = LineCollection(horizontal_lines, cmap=cmap, norm=norm)
hor_lc.set_array(y[:-1])
ax.add_collection(hor_lc)
factor = 10
long_y0 = np.linspace(y[:-1], y[1:], factor)[:-1, :].T.ravel()
long_y1 = np.linspace(y[:-1], y[1:], factor)[1:, :].T.ravel()
long_x = np.repeat(x[1:], factor - 1)
vertical_lines = np.array([long_x, long_y0, long_x, long_y1]).T.reshape(-1, 2, 2)
ver_lc = LineCollection(vertical_lines, cmap=cmap, norm=norm)
ver_lc.set_array((long_y0 + long_y1) / 2)
ax.add_collection(ver_lc)
ax.scatter(x, y, c=y, cmap=cmap, norm=norm)
plt.autoscale() # needed in case the scatter plot would be omited
plt.show()
Here is another example, with a black background. In this case the darkest part of the colormap is avoided. The changed code parts are:
y = np.random.randint(-9, 10, x.size)
ax.patch.set_color('black')
norm = plt.Normalize(y.min(), y.max() + y.ptp() * .2)
cmap = 'plasma_r'
Here is an example with a TwoSlopeNorm and the blue-white-red colormap:
from matplotlib.colors import TwoSlopeNorm
y = np.random.uniform(-1, 1, x.size * 10).cumsum()[::10]
y = (y - y.min()) / y.ptp() * 15 - 5
norm = TwoSlopeNorm(vmin=-5, vcenter=0, vmax=10)
cmap = 'bwr'