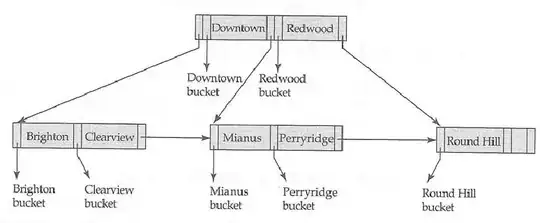
Okay, your primary problem is derefencing a NULL in reports.c at:
while (currNode != NULL) {
if (strcmp (currNode->data->country, currNode->next->data->country) ==
on your last node, the node->next pointer is NULL yet you attempt to access currNode->next->... Boom! SegFault!
You simply need to use currNode->next in your conditional, e.g.
while (currNode->next != NULL) {
if (strcmp (currNode->data->country, currNode->next->data->country) ==
Next, the link Why is while ( !feof (file) ) always wrong? explains why your read loop will cause problems. Always control your read-loop with the return of the input function, e.g.
while (fscanf (infile, "%s %s %s %s %d %d ", code, country, gender, degree,
&year, &numberOfGrads) == 6) {
if (!(data = initData (code, country, gender, degree, year, numberOfGrads)))
return 1;
addDataToList (list, data);
}
If you notice, the declaration for initData has changed. You have no valid way to indicate success or failure of mailloc in initData before you blindly start using *r. Instead in any function that allocates memory, takes user input, etc. (any function that is critical to the continued operation of your code), you need to choose a meaningful return type that you can use to indicate success/failure of your function.
There is no need to pass the address of the pointer data as a parameter. Instead, declare r local to your function and then return NULL on failure or an allocated block for assignment back in the caller. You can change the prototype to:
DataType *initData (char*, char*, char*, char*, int, int);
and then simply have the function return NULL on failure or r on success, e.g.
DataType *initData (char *co, char *c, char *g, char *d, int y, int n)
{
DataType *r = malloc (sizeof (DataType));
if (!r) {
perror ("malloc-initData");
return NULL;
}
strcpy (r->code, co);
strcpy (r->country, c);
strcpy (r->gender, g);
strcpy (r->degree, d);
r->year = y;
r->numberOfGrads = n;
return r;
}
Lastly, your addDataToList() function suffers from the same void type and no ability to indicate success/failure of malloc() (I'll let you rewrite this one). In the mean time, you must protect against an out-of-memory error. You can further vastly shorten how you add a node to your list. Doing both, and using the tail pointer for what a tail pointer is supposed to be used for, you could do:
void addDataToList (ListType * list, DataType * m)
{
NodeType *newNode = malloc (sizeof (NodeType));
if (!newNode) {
perror ("malloc-newNode");
exit (EXIT_FAILURE);
}
newNode->data = m;
newNode->prev = NULL;
newNode->next = NULL;
if (!list->head)
list->head = list->tail = newNode;
else {
newNode->prev = list->tail;
list->tail->next = newNode;
list->tail = newNode;
}
list->size++;
}
Use Header-Guards To Prevent Multiple Inclusions of the Header
When writing a header file, you only want it included in the compilation once (it can cause problems when included multiple times, e.g. redefinition of X, etc..) To ensure the header is only included once, you wrap the content in a
#infdef SOME_HEADER_LABEL_H
#define SOME_HEADER_LABEL_H 1
...
your header content
...
#endif
That way on first inclusion, the compiler checks if SOME_HEADER_LABEL_H is defined, and if it isn't, it defines it with #define SOME_HEADER_LABEL_H 1 so that the next time it is included, it will simply skip the content. (the 1 isn't strictly necessary -- it can be omitted, but if you are going to define a constant, you may as well give it a value). For your header that could be:
#ifndef DEFS_H
#define DEFS_H 1
#define MAX_STR 32
typedef struct {
char code[MAX_STR];
char country[MAX_STR];
char gender[MAX_STR];
char degree[MAX_STR];
int year;
int numberOfGrads;
} DataType;
typedef struct Node {
DataType *data;
struct Node *prev;
struct Node *next;
} NodeType;
typedef struct {
int size;
NodeType *head;
NodeType *tail;
} ListType;
// void initData(DataType**, char*, char*, char*, char*, int, int);
DataType *initData (char*, char*, char*, char*, int, int);
void printData(const DataType*);
void addDataToList (ListType*, DataType*);
void reportOne(ListType*);
#endif
No Need To Allocate For data In main()
On second look, there is no need to allocated for DataType *data; in main() at all. It is a temporary, so just declare it with automatic storage type and reuse it for all input -- but you will need to allocate for newNode->data in addDataToList and memcpy rather than assign m. So either way is fine. (that code is shown commented in the update related to the report output shown in the edit below)
Avoid MagicNumbers and Hardcoded Filenames
In your code you hardcode "grad.dat" as the filename to read. That means you must recompile your code every time you want to read from another file. Instead, pass the filename to read as an argument to your program using int main (int argc, char **argv) -- that's what the parameters to main() are for. You can use a simple ternary to read from the filename given as an argument, or if no argument is given, read from "grad.dat" by default. That's fine, but define a constant for the filename, e.g.
#define DATAFILE "grad.dat"
...
/* do not hardcode filenames, you can use it as a default */
infile = fopen (argc > 1 ? argv[1] : DATAFILE, "r");
if (!infile) { /* good job validating fopen */
printf ("Error: could not open file\n");
exit (1);
}
Making reportOne() Summarize by Country
This took a bit more thinking to arrive at. There are several ways to go about it. You either use a slightly more complicated data structure to hold the summary data for each country along with the totalGradsCountry value, or you store only the summary of the country data, and then must traverse your list twice in reportOne(), once to sum totalGradsCountry, and then again to output the results using your totalGradsCountry.
Basically to capture the information while traversing the list a single time takes building an array of the unique countries along with the sums of L6, L7, and L8 captured along with the country (name) and optionally code (makes for a shorter strcmp to determine the country in the node). So you could use something like:
#define NSUM 2 /* initial no. of countrytype to allocate */
typedef struct { /* struct to hold summary of country data */
char code[MAX_STR],
country[MAX_STR];
double L6,
L7,
L8;
} countrytype;
typedef struct { /* struct to hold array of countries and totalgrads */
countrytype *countries;
double totalGradsAll;
} totaltype;
Then it is a matter of traversing your full list, and for each unique country, allocate storage for a countrytype and on the first node for that country, copy the code and country information, and for all remaining entries for that country add to the L6, L7, and L8 values and to the totalGradsAll sum. When allocating (and reallocating) for the countrytype, zeroing the memory allows you to check if code is the empty-string to know if you have the first-occurrence of that country.
The reportOne() function becomes:
void reportOne (ListType *list)
{
size_t used = 0, avail = NSUM; /* number used, number allocated */
totaltype total = { .countries = calloc (avail, sizeof(countrytype)) };
NodeType *node = list->head;
if (!total.countries) { /* validate initial allocation */
perror ("calloc-.countries");
return;
}
while (node) { /* loop over each node in list */
/* check if country code exists in summary list of countries */
size_t ndx = codeexists (total.countries, node->data->code, &used);
if (used == avail) /* check if realloc needed */
total.countries = addcountry (total.countries, &avail);
addtosum (&total, ndx, node->data); /* add current node info to summary */
node = node->next; /* advance to next node */
}
puts ( "\nCountry L6 L7 L8 Total\n"
"-------------------------------------------------------");
for (size_t i = 0; i < used; i++) { /* loop over countries in summary */
/* sum L6 + L7 + L8 for country */
double totalGradsCountry = total.countries[i].L6 + total.countries[i].L7 +
total.countries[i].L8;
/* output results */
printf ("%-15s %6.2f %6.2f %6.2f %7.2f\n",
total.countries[i].country,
total.countries[i].L6 / totalGradsCountry,
total.countries[i].L7 / totalGradsCountry,
total.countries[i].L8 / totalGradsCountry,
totalGradsCountry / total.totalGradsAll);
}
free (total.countries); /* free all memory allocated for summary */
}
Now you see several helper-functions that by putting them in functions help keep your reportOne logic readable. The helpers are codeexists() (e.g. does this country code already exist in the block of countrytype) Having it return the index to the country in the allocated block of countrytype allows you to simply update the L6, L7, and L8 at that index. If the index doesn't exist, it is a new country that you add to your used count to keep track of when a reallocation is needed. It is a simple function:
/* returns index of country matching code or next available index,
* incrementing the value at n (used) for each new index returned.
*/
size_t codeexists (const countrytype *c, const char *code, size_t *n)
{
size_t i;
for (i = 0; i < *n; i++) /* loop over countries */
if (strcmp (c[i].code, code) == 0) /* if codes match, break to return index */
break;
if (i == *n) /* if code not found in countries */
*n += 1; /* new country found, increment n (used) */
return i; /* return index */
}
The next helper is addcountry() which when your used == avail (used blocks for countries equals the number allocated), a reallocation is needed and that is what addcountry() does, returing a pointer to the newly reallocated block for assignment (or exiting if an error occurs), e.g.
/* reallocate countries when used == available,
* new memory is zeroed for 1st char check in addtosum,
* program exits on memory failure.
*/
countrytype *addcountry (countrytype *c, size_t *avail)
{
/* always realloc using a temporary pointer */
void *tmp = realloc (c, 2 * *avail * sizeof *c);
if (!tmp) { /* validate reallocation */
perror ("realloc-countrytype");
exit (EXIT_FAILURE);
}
c = tmp; /* assing realloc'ed block to ptr */
memset (c + *avail, 0, *avail * sizeof *c); /* zero newly allocated memory */
*avail *= 2; /* update no. of countries avail */
return c; /* return pointer for assignment in caller */
}
The last helper is addtosum() which simply copies code and country names if needed and updates L6, L7, and L8 for the given index,
/* add current nodes information to the country and total sums */
void addtosum (totaltype *t, size_t ndx, DataType *d)
{
if (!*t->countries[ndx].code) { /* if new country, copy info */
strcpy (t->countries[ndx].code, d->code);
strcpy (t->countries[ndx].country, d->country);
}
switch (d->degree[1]) { /* switch on 2nd character */
case '6': t->countries[ndx].L6 += d->numberOfGrads; break;
case '7': t->countries[ndx].L7 += d->numberOfGrads; break;
case '8': t->countries[ndx].L8 += d->numberOfGrads; break;
default : fputs ("error: addtosum switch -- we shouldn't be here\n", stderr);
return;
}
t->totalGradsAll += d->numberOfGrads; /* add to total for all */
}
A switch() is used above on the 2nd character of the degree, e.g. 6, 7, or 8 to updated to appropriate value without needing to call strcmp() each time.
Putting It Altogether
Those are the changes needed. So your defs.h becomes:
#ifndef DEFS_H
#define DEFS_H 1
#define MAX_STR 32
typedef struct {
char code[MAX_STR];
char country[MAX_STR];
char gender[MAX_STR];
char degree[MAX_STR];
int year;
int numberOfGrads;
} DataType;
typedef struct Node {
DataType *data;
struct Node *prev;
struct Node *next;
} NodeType;
typedef struct {
int size;
NodeType *head;
NodeType *tail;
} ListType;
// void initData (DataType*, char*, char*, char*, char*, int, int);
DataType *initData (char*, char*, char*, char*, int, int);
void printData (const DataType*);
void addDataToList (ListType*, DataType*);
void reportOne (ListType*);
// void reportTwo (ListType*);
#endif
Your main.c (with the code commented out showing to use data with automatic storage duration) becaomes:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "defs.h"
#define DATAFILE "grad.dat"
int main (int argc, char **argv)
{
FILE *infile;
DataType *data;
ListType *list = malloc (sizeof *list);
char code[MAX_STR];
char country[MAX_STR];
char gender[MAX_STR];
char degree[MAX_STR];
int year;
int numberOfGrads;
char input[MAX_STR];
if (!list) { /* validate EVERY allocation */
perror ("malloc-list");
return 1;
}
list->size = 0;
list->head = NULL;
list->tail = NULL;
/* do not hardcode filenames, you can use it as a default */
infile = fopen (argc > 1 ? argv[1] : DATAFILE, "r");
if (!infile) { /* good job validating fopen */
printf ("Error: could not open file\n");
exit (1);
}
/* always control read-loop with return of the input function itself */
while (fscanf (infile, "%s %s %s %s %d %d ", code, country, gender, degree,
&year, &numberOfGrads) == 6) {
if (!(data = initData (code, country, gender, degree, year, numberOfGrads)))
return 1;
addDataToList (list, data);
}
fclose (infile);
while (1) {
fputs ( "\n 0. Quit \n"
" 1 = Top 5 and bottom 5 countries of female graduates\n"
"Enter a selection: ", stdout);
if (scanf ("%s", input) != 1) {
puts ("(user canceled input)");
return 1;
}
if (strcmp (input, "1") == 0) {
reportOne (list);
}
else if (strcmp (input, "0") == 0) {
break;
}
}
}
DataType *initData (char *co, char *c, char *g, char *d, int y, int n)
{
DataType *r = malloc (sizeof (DataType));
if (!r) {
perror ("malloc-initData");
return NULL;
}
strcpy (r->code, co);
strcpy (r->country, c);
strcpy (r->gender, g);
strcpy (r->degree, d);
r->year = y;
r->numberOfGrads = n;
return r;
}
/* initData for use of data with automatic storage in main */
// void initData (DataType *r, char *co, char *c, char *g, char *d, int y, int n)
// {
// strcpy (r->code, co);
// strcpy (r->country, c);
// strcpy (r->gender, g);
// strcpy (r->degree, d);
// r->year = y;
// r->numberOfGrads = n;
// }
void printData (const DataType * data)
{
printf ("%s %s %s %s %d %d\n", data->code, data->country, data->gender,
data->degree, data->year, data->numberOfGrads);
}
void addDataToList (ListType * list, DataType * m)
{
NodeType *newNode = malloc (sizeof (NodeType));
if (!newNode) {
perror ("malloc-newNode");
exit (EXIT_FAILURE);
}
/* allocation and copy if using data with automatic storage in main */
// if (!(newNode->data = malloc (sizeof *newNode->data))) {
// perror ("malloc-newNode->data");
// exit (EXIT_FAILURE);
// }
// memcpy (newNode->data, m, sizeof *m);
newNode->data = m;
newNode->prev = NULL;
newNode->next = NULL;
if (!list->head)
list->head = list->tail = newNode;
else {
newNode->prev = list->tail;
list->tail->next = newNode;
list->tail = newNode;
}
list->size++;
}
Finally the updated reports.c becomes:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "defs.h"
#define NSUM 2 /* initial no. of countrytype to allocate */
typedef struct { /* struct to hold summary of country data */
char code[MAX_STR],
country[MAX_STR];
double L6,
L7,
L8;
} countrytype;
typedef struct { /* struct to hold array of countries and totalgrads */
countrytype *countries;
double totalGradsAll;
} totaltype;
/* returns index of country matching code or next available index,
* incrementing the value at n (used) for each new index returned.
*/
size_t codeexists (const countrytype *c, const char *code, size_t *n)
{
size_t i;
for (i = 0; i < *n; i++) /* loop over countries */
if (strcmp (c[i].code, code) == 0) /* if codes match, break to return index */
break;
if (i == *n) /* if code not found in countries */
*n += 1; /* new country found, increment n (used) */
return i; /* return index */
}
/* reallocate countries when used == available,
* new memory is zeroed for 1st char check in addtosum,
* program exits on memory failure.
*/
countrytype *addcountry (countrytype *c, size_t *avail)
{
/* always realloc using a temporary pointer */
void *tmp = realloc (c, 2 * *avail * sizeof *c);
if (!tmp) { /* validate reallocation */
perror ("realloc-countrytype");
exit (EXIT_FAILURE);
}
c = tmp; /* assing realloc'ed block to ptr */
memset (c + *avail, 0, *avail * sizeof *c); /* zero newly allocated memory */
*avail *= 2; /* update no. of countries avail */
return c; /* return pointer for assignment in caller */
}
/* add current nodes information to the country and total sums */
void addtosum (totaltype *t, size_t ndx, DataType *d)
{
if (!*t->countries[ndx].code) { /* if new country, copy info */
strcpy (t->countries[ndx].code, d->code);
strcpy (t->countries[ndx].country, d->country);
}
switch (d->degree[1]) { /* switch on 2nd character */
case '6': t->countries[ndx].L6 += d->numberOfGrads; break;
case '7': t->countries[ndx].L7 += d->numberOfGrads; break;
case '8': t->countries[ndx].L8 += d->numberOfGrads; break;
default : fputs ("error: addtosum switch -- we shouldn't be here\n", stderr);
return;
}
t->totalGradsAll += d->numberOfGrads; /* add to total for all */
}
void reportOne (ListType *list)
{
size_t used = 0, avail = NSUM; /* number used, number allocated */
totaltype total = { .countries = calloc (avail, sizeof(countrytype)) };
NodeType *node = list->head;
if (!total.countries) { /* validate initial allocation */
perror ("calloc-.countries");
return;
}
while (node) { /* loop over each node in list */
/* check if country code exists in summary list of countries */
size_t ndx = codeexists (total.countries, node->data->code, &used);
if (used == avail) /* check if realloc needed */
total.countries = addcountry (total.countries, &avail);
addtosum (&total, ndx, node->data); /* add current node info to summary */
node = node->next; /* advance to next node */
}
puts ( "\nCountry L6 L7 L8 Total\n"
"-------------------------------------------------------");
for (size_t i = 0; i < used; i++) { /* loop over countries in summary */
/* sum L6 + L7 + L8 for country */
double totalGradsCountry = total.countries[i].L6 + total.countries[i].L7 +
total.countries[i].L8;
/* output results */
printf ("%-15s %6.2f %6.2f %6.2f %7.2f\n",
total.countries[i].country,
total.countries[i].L6 / totalGradsCountry,
total.countries[i].L7 / totalGradsCountry,
total.countries[i].L8 / totalGradsCountry,
totalGradsCountry / total.totalGradsAll);
}
free (total.countries); /* free all memory allocated for summary */
}
Note -- all memory used in reportOne() is freed before returning. You need to make sure you clean up after the remainder of your code as well.
Take your time to work through how the countrytype and totaltype structures are used to produce the final output. There is a lot there, so just Slow Down and take it line-by-line and follow it trough.
Example Use/Output
With the limited sample data provided, you would receive:
$ ./bin/main
0. Quit
1 = Top 5 and bottom 5 countries of female graduates
Enter a selection: 1
Country L6 L7 L8 Total
-------------------------------------------------------
Australia 1.00 0.00 0.00 0.09
Belgium 0.96 0.03 0.01 0.01
Brazil 1.00 0.00 0.00 0.87
Canada 1.00 0.00 0.00 0.03
0. Quit
1 = Top 5 and bottom 5 countries of female graduates
Enter a selection:
Which given the values in the sample-data looks like it is what would be expected. Confirming is left to you.
Your code should run fine with those changes. If it doesn't, drop a comment, I may have forgotten a change or two. Let me know if you have further questions.