I am developing a site where the users will be able to click a "Forgot My Password" button to reset their passwords.
Currently, once the email has been validated, the following code should generate a token to be emailed to the user:
if(validUser != null)
{
var generationTime = DateTime.Now;
var pwToken = await _userManager.GeneratePasswordResetTokenAsync(validUser);
await _userManager.UpdateAsync(validUser);
var url = $"https://{Request.Host}/verify/{HttpUtility.UrlEncode(pwToken)}";
//EmailHelper.SendMagicLinkEmail(validUser, url, Request);
return new RedirectResult("/");
}
All information online regarding this seems to suggest that this is the way to do things. I have set up the Default token providers in the Startup.csfile too:
identityOptions: o => {
o.User.RequireUniqueEmail = true;
o.Tokens.PasswordResetTokenProvider = TokenOptions.DefaultProvider;
o.Tokens.EmailConfirmationTokenProvider = TokenOptions.DefaultProvider;
},
Yet when a token is generated it produces a large token such as this:
CfDJ8CnvAYtZf+1IjXpKUM7+umDYEaImg2SPFglPX3Y8RmYpEfg5zpK8xL54lvlbJUd54CaIzzYlff/GU+xKKS8mmG5UdC1zdk24nOsJNpIlmC3P5V72BchS4P9DGFTR77XiKbMAAYymnMomS2zCdTKh+E4bn9RI6FVinMecG1HR7nSHmOI2McbXHBFTanI/0uwxH5WI/Dj4AFTBP39ni7mfKkeWz2nJ5pTemELJJ6pYP50+
The problem here is obviously the forward slashes, which cause issues with routing so are encoded out here:
var url = $"https://{Request.Host}/verify/{HttpUtility.UrlEncode(pwToken)}";
The problem is that even with that, .Net Core seems to un-encode it and produce the following error when the generated link is accessed:
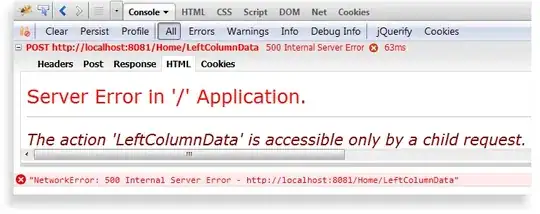
This error isn't necessarily the issue, and I do understand it's importance. Yet I can't seem to find any explanation as to why this token is behaving this way. All online examples seem to produce a fairly standard GUID style token, not something such as this.
Does anyone know why this might be happening?
Cheers