I'm trying to create a model that can be used for both a QTableView and QTreeView. As an example, my data is something like:
| ID | Location | Name |
|---|---|---|
| 101 | 201 | Apple |
| 201 | None | Kitchen |
| 102 | 201 | Banana |
| 301 | None | Cellar |
| 302 | 301 | Potatoes |
| 202 | 302 | Nail |
So every entry has a location which is itself an entry in the model. For the QTableView, I'd like to simply display all entries under each other as shown above, while for the QTreeView I'd like something like
- 201: Kitchen
- 101: Apple
- 102: Banana
- 301: Cellar
- 302: Potatoes
- 202: Nail
- 302: Potatoes
My problem however is that I can't figure out how to implement QAbstractProxyModel.maptoSource() or mapfromSource() as I lose information about the parent in the QTableView. Reading https://www.qtcentre.org/threads/26163-Map-table-to-tree-through-model-view-possible it seems that perhaps this is not possible at all. However the QAbstractProxyModel explicitly says that's it's meant for showing data in both views. Can anyone point me in the right direction or knows whether it's possible to implement a model like this? Especially in Python, I can't find any examples unfortunately.
I really like the idea of just using an unindented TreeView as a sort of TableView. Unfortunately I'm still having trouble creating the model. Currently, only the top entries are being shown.
class MyModel(qtg.QStandardItemModel):
def __init__(
self,
engine
):
self.engine = engine
self.hierarchy_key = 'location_id'
self.column_names = ['id', 'location_id', 'name', 'quantity']
super().__init__(0, len(self.fields))
self.setHorizontalHeaderLabels(self.column_names)
self.root = self.invisibleRootItem()
self.build_model()
def build_model(self):
def add_children_to_tree(entries, parent_item):
for entry in entries:
items = []
for col in self.column_names:
text = getattr(entry, col)
item = qtg.QStandardItem(text)
items.append(qtg.QStandardItem(text))
parent_item.appendRow(items)
item = items[1] #the location_id item
parent_item.setChild(item.index().row(), item.index().column(), item)
with session_scope(self.engine) as session:
child_entries = (
session.query(self.entry_type)
.filter(
getattr(getattr(self.entry_type, self.hierarchy_key), "is_")(
entry.id
)
)
.all()
)
if child_entries:
add_children_to_tree(child_entries, item)
self.removeRows(0, self.rowCount())
with session_scope(self.engine) as session:
root_entries = session.query(self.entry_type).filter(getattr(getattr(self.entry_type, self.hierarchy_key), "is_")(None)).all()
if not isinstance(root_entries, list):
root_entries = [root_entries]
add_children_to_tree(root_entries, self.root)
The idea is that the session query results in a list of entries. Each entry is a record in the database with the attributes "id", "location_id", etc. Each attribute thus is an Item and the list of items creates a row in the model. I can't figure out how one makes the row of items a child of another row in the way it's shown here:
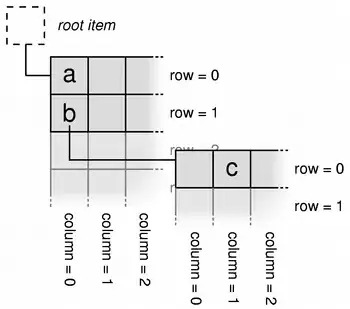 I assume the setChild() function needs to be called differently?
I assume the setChild() function needs to be called differently?