I have a 2 points projection sketch based on two lines intersection algorithms.
For example, if there's a 3D point { x: -4, y: 2, z: -2 } and axes origin is pre-defined, I could find a = {x: -4, y: 2, z: 0} and b = {x: 0, y: 2, z: -2} points and find one possible intersection of line {vanishingPointX, a) and another line of {vanishingPointZ, b) and as you can see the code works fine.
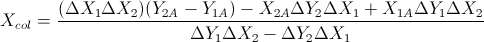
And the task is to add another 3-rd point, so the output should like this:

it's a rough illustration, some lines are distorted.
I have tried to project Y values along X-axis, but anyway neither there's no algorithm of three lines intersection nor these three lines don't intersect together at one point.
And the last but not least, I am aware that this problem could be solved with matrices, however, I'm trying to do it calculus-free.
const scale = 64.0;
const far = 6.0;
const cube = [
{ x: 1.0, y: 1.0, z: 1.0 },
{ x: 1.0, y: -1.0, z: 1.0 },
{ x: -1.0, y: -1.0, z: 1.0 },
{ x: -1.0, y: 1.0, z: 1.0 },
{ x: 1.0, y: 1.0, z: -1.0 },
{ x: 1.0, y: -1.0, z: -1.0 },
{ x: -1.0, y: -1.0, z: -1.0 },
{ x: -1.0, y: 1.0, z: -1.0 },
];
const sides = [0, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 0, 4, 5, 5, 6, 6, 7, 7, 4, 0, 4, 1, 5, 2, 6, 3, 7];
let vanishingPointZ = { x: -3.5, y: 2.0 };
let vanishingPointX = { x: 5.0, y: 2.0 };
let vanishingPointY = { x: 0.0, y: -6.0 };
let canvas = document.getElementById('canvas');
let ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
let zero = { x: canvas.width / 2, y: canvas.height / 2 };
draw();
function draw(){
ctx.font = '32px serif';
ctx.fillStyle = "#0F0"
ctx.fillText('X', zero.x + vanishingPointX.x * scale + 16, zero.y + vanishingPointX.y * scale + 16);
ctx.fillStyle = "#F0F";
ctx.fillText('Y', zero.x + vanishingPointY.x * scale + 32, zero.y + vanishingPointY.y * scale + 16);
ctx.fillStyle = "#00F";
ctx.fillText('Z', zero.x + vanishingPointZ.x * scale - 32, zero.y + vanishingPointZ.y * scale + 16);
cube.forEach((p_, i_) =>{
project(p_);
let pos = { x: zero.x + p_.dx * scale, y: zero.y + p_.dy * scale };
//to x
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(zero.x + vanishingPointX.x * scale, zero.y + vanishingPointX.y * scale);
ctx.lineTo(pos.x, pos.y);
ctx.closePath();
ctx.strokeStyle = "rgba(0, 255, 0, 0.33)";
ctx.stroke();
//to z
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(zero.x + vanishingPointZ.x * scale, zero.y + vanishingPointZ.y * scale);
ctx.lineTo(pos.x, pos.y);
ctx.closePath();
ctx.strokeStyle = "rgba(0, 0, 255, 0.33)";
ctx.stroke();
//to upper y
//to x
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(zero.x + vanishingPointY.x * scale, zero.y + vanishingPointY.y * scale);
ctx.lineTo(pos.x, pos.y);
ctx.closePath();
ctx.strokeStyle = "rgba(255, 0, 255, 0.33)";
ctx.stroke();
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.arc(pos.x, pos.y, 8, 0, Math.PI * 2);
ctx.closePath();
ctx.fillStyle = "#DEDEDE";
ctx.fill();
})
for(let i = 0; i < sides.length; i += 2){
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(zero.x + cube[sides[i]].dx * scale, zero.y + cube[sides[i]].dy * scale);
ctx.lineTo(zero.x + cube[sides[i + 1]].dx * scale, zero.y + cube[sides[i + 1]].dy * scale);
ctx.closePath();
ctx.strokeStyle = "#000";
ctx.stroke();
}
}
function project(p_){
let distX = Math.sqrt(Math.pow(vanishingPointX.x, 2), Math.pow(vanishingPointX.y - p_.y, 2));
let vx = { x: vanishingPointX.x, y: vanishingPointX.y - p_.y };
let nx = Math.exp( p_.x / far );
vx.x *= nx;
vx.y *= nx;
let x = { x: vanishingPointX.x - vx.x, y: vanishingPointX.y - vx.y };
let distZ = Math.sqrt(Math.pow(vanishingPointZ.x, 2), Math.pow(vanishingPointZ.y - p_.y, 2));
let vz = { x: vanishingPointZ.x, y: vanishingPointZ.y - p_.y };
let nz = Math.exp( p_.z / far );
vz.x *= nz;
vz.y *= nz;
let z = { x: vanishingPointZ.x - vz.x, y: vanishingPointZ.y - vz.y };
let out = twoLinesIntersection(vanishingPointZ, z, vanishingPointX, x);
//trying to calculate y projection and it seems that as standalone it work fine
let distY = Math.sqrt(Math.pow(vanishingPointY.x, 2), Math.pow(vanishingPointX.y - p_.x, 2));
let vy = { x: vanishingPointY.y, y: vanishingPointY.y - p_.x };
let ny = Math.exp( p_.y / far );
vy.x *= ny;
vy.y *= ny;
let y = { x: vanishingPointY.x - vy.x, y: vanishingPointY.y - vy.y };
p_.dx = out.x;
p_.dy = out.y;
}
function twoLinesIntersection(p1_, p4_, p3_, p2_){
let d1 = (p1_.x - p2_.x) * (p3_.y - p4_.y);
let d2 = (p1_.y - p2_.y) * (p3_.x - p4_.x);
let d = (d1) - (d2);
let u1 = (p1_.x * p2_.y - p1_.y * p2_.x);
let u4 = (p3_.x * p4_.y - p3_.y * p4_.x);
let u2x = p3_.x - p4_.x;
let u3x = p1_.x - p2_.x;
let u2y = p3_.y - p4_.y;
let u3y = p1_.y - p2_.y;
return { x: (u1 * u2x - u3x * u4) / d, y: (u1 * u2y - u3y * u4) / d };
}body { margin: 0; }<canvas id='canvas' width='800' height='800'></canvas>