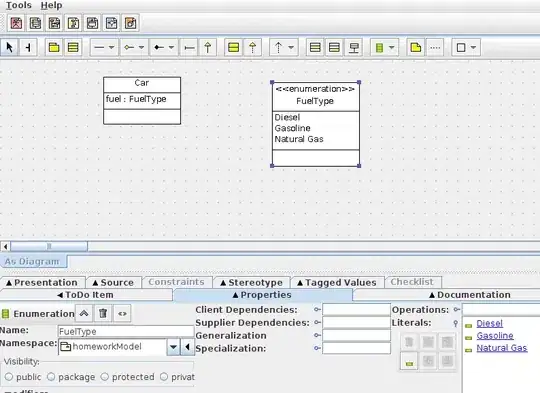
- You need to unpack the
keys and values of my_dict.
- From
python >=3.6 dicts are insertion ordered, so the extracted values don't require sorting.
- Tested in
python 3.8, pandas 1.3.1, matplotlib 3.4.2, and seaborn 0.11.1
my_dict = {21: ((0.667, 0.126), (0.63, 0.068)), 52: ((0.679, 0.059), (0.637, 0.078)), 73: ((0.612, 0.211), (0.519, 0.143)), 94: ((0.709, 0.09), (0.711, 0.097))}
x_vals = my_dict.keys()
line1 = [v[0][0] for v in my_dict.values()]
line2 = [v[1][0] for v in my_dict.values()]
errorbar1 = [v[0][1] for v in my_dict.values()]
errorbar2 = [v[1][1] for v in my_dict.values()]
plt.plot(x_vals, line1, linestyle='dotted')
plt.plot(x_vals, line2, linestyle='dotted')
plt.errorbar(x_vals, line1, yerr=errorbar1, fmt=' ')
plt.errorbar(x_vals, line2, yerr=errorbar2, fmt=' ')
plt.xlabel('x axis')
plt.ylabel('yaxis')
plt.show()
Using pandas
- Tested with
pandas 1.3.1 and matplotlib 3.4.2
- This reduces the code from 13 to 7 lines.
import pandas as pd
my_dict = {21: ((0.667, 0.126), (0.63, 0.068)), 52: ((0.679, 0.059), (0.637, 0.078)), 73: ((0.612, 0.211), (0.519, 0.143)), 94: ((0.709, 0.09), (0.711, 0.097))}
# load the dictionary into pandas
df = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(my_dict, orient='index', columns=['line1', 'line2'])
# display(df)
line1 line2
21 (0.667, 0.126) (0.63, 0.068)
52 (0.679, 0.059) (0.637, 0.078)
73 (0.612, 0.211) (0.519, 0.143)
94 (0.709, 0.09) (0.711, 0.097)
# separate the tuples to columns
for i, col in enumerate(df.columns, 1):
df[[col, f'errorbar{i}']] = pd.DataFrame(df[col].tolist(), index= df.index)
# display(df)
line1 line2 errorbar1 errorbar2
21 0.667 0.630 0.126 0.068
52 0.679 0.637 0.059 0.078
73 0.612 0.519 0.211 0.143
94 0.709 0.711 0.090 0.097
# plot
ax = df.plot(y=['line1', 'line2'], linestyle='dotted', ylabel='y-axis', xlabel='x-axis', title='title', figsize=(8, 6))
ax.errorbar(df.index, 'line1', yerr='errorbar1', data=df, fmt=' ')
ax.errorbar(df.index, 'line2', yerr='errorbar2', data=df, fmt=' ')
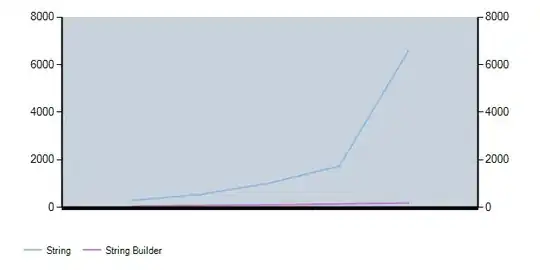
Update
- I realized that all of the previous code is to accommodate your other question.
- Everything from both questions can really be ignored, plotting is all about shaping the data to fit the plot API.
- If
rl from the other question is used, it can be directly converted to a long form, and plotted with seaborn.pointplot.
- As you can see in the previous plots, the error bars overlap, making the plot more difficult to read. Here
dodge is used to slightly offset the points, so the error bars don't overlap.
import seaborn as sns
import pandas
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# using rl from the other question convert to a long form
rl = [{21: (0.5714285714285714, 0.6888888888888889), 52: (0.6153846153846154, 0.7111111111111111), 73: (0.7123287671232876, 0.6222222222222222), 94: (0.7127659574468085, 0.6)}, {21: (0.6190476190476191, 0.6444444444444445), 52: (0.6923076923076923, 0.6444444444444445), 73: (0.3698630136986301, 0.35555555555555557), 94: (0.7978723404255319, 0.7777777777777778)}, {21: (0.8095238095238095, 0.5555555555555556), 52: (0.7307692307692307, 0.5555555555555556), 73: (0.7534246575342466, 0.5777777777777777), 94: (0.6170212765957447, 0.7555555555555555)}]
df = pd.DataFrame(rl).melt(var_name='Sample Size')
df[['Train', 'Test']] = pd.DataFrame(df['value'].tolist(), index= df.index)
df.drop('value', axis=1, inplace=True)
df = df.melt(id_vars='Sample Size', var_name='Score')
# display(df)
Sample Size Score value
0 21 Train 0.571429
1 21 Train 0.619048
2 21 Train 0.809524
3 52 Train 0.615385
4 52 Train 0.692308
# plot
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 5))
p = sns.pointplot(data=df, x='Sample Size', y='value', hue='Score', ci='sd', dodge=0.25, linestyles='dotted')
p.set(ylabel='Mean of Trials', title='Score Metrics')
# given df, you can still see the metrics with
dfg = df.groupby(['Sample Size', 'Score']).agg(['mean', 'std'])
# display(dfg)
value
mean std
Sample Size Score
21 Test 0.629630 0.067890
Train 0.666667 0.125988
52 Test 0.637037 0.078042
Train 0.679487 0.058751
73 Test 0.518519 0.142869
Train 0.611872 0.210591
94 Test 0.711111 0.096864
Train 0.709220 0.090478