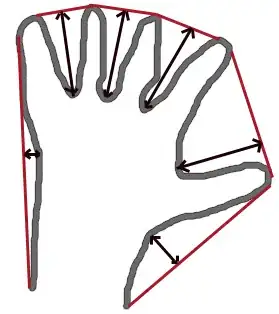
I'm trying to simulate some data for a project, and basically I need to draw an irregular oval-ish shape, then make a bunch of random points inside that shape, and I'm at a total loss for how to do this.
For now, I've made a spline shape, then plotted a bunch of points over it. Is there a way I can find the overlap? Or better, just generate random points in bounds of a pre-made shape?
(feel free to ditch my code if there is a better way to start - maybe it needs to be some kind of spatial object?)
set.seed(2)
shape <- data.frame(
x = c(2, 3, 2, 3, 2, 1, 0, 1),
y = c(1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 7, 5, 3 )
)
scatter = data.frame(
x = rnorm(100, mean = 1.5, sd = .6),
y = rnorm(100, mean = 5, sd = 2)
)
ggplot(data = shape,
aes(x=x,y=y)) +
ggforce::geom_bspline_closed(fill = "transparent", color = "black") +
geom_point(color = "blue") +
coord_equal() +
geom_point(data = scatter, shape = "*", size=3)