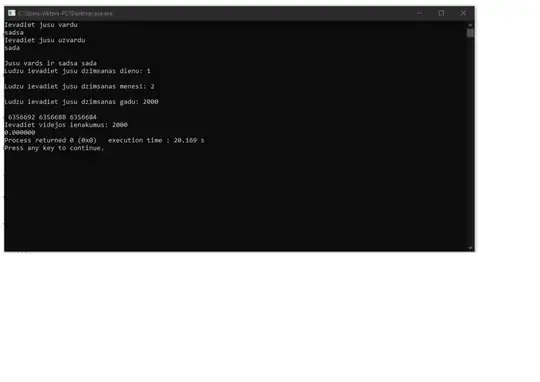
 Haven't used C in a while and get -1073741819 (0xC0000005) after I ask a user for the d, m, y inputs. I assume it's something to do with how I use pointers. I have created a different program using the pointers similarly, and it all worked fine and dandy. Don't really know what else to say. Why would the program not work. I feel like it's something ridiculously obvious and stupid, but I just can't see it. :D
Haven't used C in a while and get -1073741819 (0xC0000005) after I ask a user for the d, m, y inputs. I assume it's something to do with how I use pointers. I have created a different program using the pointers similarly, and it all worked fine and dandy. Don't really know what else to say. Why would the program not work. I feel like it's something ridiculously obvious and stupid, but I just can't see it. :D
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<ctype.h>
void date (int *d, int *m, int *y);
void name (char vards[20], char uzvards[20]);
void income (float *ienakums);
void writefile(int *y,int *m, int *d, char vards[20],char uzvards[20],float *ienakums);
int main(void) {
char Name[20], last[20];
int diena,menesis,gads;
float cash;
// step 1 - get name + check
name(&Name[20], &last[20]);
// step 2 - get date + check
date(&diena,&menesis,&gads);
// step 3 - get income + check
income(&cash);
// step 4 - write the file
writefile(&gads,&menesis,&diena,&Name[20],&last[20],&cash);
}
void name(char vards[20], char uzvards[20]){
int check = 1;
int counter = 0;
do{
printf("Ievadiet jusu vardu\n");
gets(vards);
for(int i=0; i<strlen(vards); i++)
{
if(isdigit(vards[i]) > 0)
{
counter++;
}
}
if(counter == 0)
{
check = 0;
}
else{
check = 1;
}
}while(check == 1);
check = 0;
do{
printf("Ievadiet jusu uzvardu\n");
gets(uzvards);
for(int i=0; i<strlen(vards); i++)
{
if(isdigit(vards[i]) > 0)
{
counter++;
}
}
if(counter == 0)
{
check = 0;
}
else{
check = 1;
}
}while(check == 1);
printf("\nJusu vards ir %s %s",vards,uzvards);
}
void date (int *d, int *m, int *y){
*d = 0;
*m = 0;
*y = 0;
do{
printf("\nLudzu ievadiet jusu dzimsanas dienu: ");
fflush(stdin);
scanf("%d", &d);
}while((d<=0) || (d>31));
do{
printf("\nLudzu ievadiet jusu dzimsanas menesi: ");
fflush(stdin);
scanf("%d", &m);
}while((m<=0) || (m>12));
do{
printf("\nLudzu ievadiet jusu dzimsanas gadu: ");
fflush(stdin);
scanf("%d", &y);
}while((y<1900) || (y>2021));
printf("\n %d %d %d",*d,*m,*y);
}
void income (float *ienakums){
//do{
printf("\nIevadiet videjos ienakumus: ");
fflush(stdin);
scanf("%f", &ienakums);
//}while(isdigit(ienakums) <= 0);
printf("%f",*ienakums);
}
void writefile(int *y,int *m, int *d, char vards[20],char uzvards[20],float *ienakums)
{
FILE *file = fopen("dati.txt", "a+");
fprintf(file, "\n\tVards:%s Uzvards:%s Dzimsanas Datums:%d %d %d Ienakums %.2f EUR \n", vards, uzvards, *d, *m, *y, *ienakums);
fclose(file);
}
The code now looks like this:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<ctype.h>
void date (int *d, int *m, int *y);
void name (char vards[20], char uzvards[20]);
void income (float *ienakums);
void writefile(int *y,int *m, int *d, char vards[20],char uzvards[20],float *ienakums);
int main(void) {
char Name[20], last[20];
int diena,menesis,gads;
float cash;
// step 1 - get name + check
name(Name, last);
// step 2 - get date + check
date(&diena,&menesis,&gads);
// step 3 - get income + check
income(&cash);
// step 4 - write the file
writefile(&gads,&menesis,&diena,Name,last,&cash);
}
void name(char vards[20], char uzvards[20]){
int check = 1;
int counter = 0;
do{
printf("Ievadiet jusu vardu\n");
gets(vards);
for(int i=0; i<strlen(vards); i++)
{
if(isdigit(vards[i]) > 0)
{
counter++;
}
}
if(counter == 0)
{
check = 0;
}
else{
check = 1;
}
}while(check == 1);
check = 0;
do{
printf("Ievadiet jusu uzvardu\n");
gets(uzvards);
for(int i=0; i<strlen(vards); i++)
{
if(isdigit(vards[i]) > 0)
{
counter++;
}
}
if(counter == 0)
{
check = 0;
}
else{
check = 1;
}
}while(check == 1);
printf("\nJusu vards ir %s %s",vards,uzvards);
}
void date (int *d, int *m, int *y){
*d = 0, *m = 0, *y =0;
do{
printf("\nLudzu ievadiet jusu dzimsanas dienu: ");
fflush(stdin);
scanf("%d", d);
}while((*d<=0) || (*d>31));
do{
printf("\nLudzu ievadiet jusu dzimsanas menesi: ");
fflush(stdin);
scanf("%d", m);
}while((*m<=0) || (*m>12));
do{
printf("\nLudzu ievadiet jusu dzimsanas gadu: ");
fflush(stdin);
scanf("%d", y);
}while((*y<1900) || (*y>2021));
printf("\n %d %d %d",d,m,y);
}
void income (float *ienakums){
//do{
printf("\nIevadiet videjos ienakumus: ");
fflush(stdin);
scanf("%f", ienakums);
//}while(isdigit(ienakums) <= 0);
printf("%f",ienakums);
}
void writefile(int *y,int *m, int *d, char vards[20],char uzvards[20],float *ienakums)
{
FILE *file = fopen("dati.txt", "a+");
fprintf(file, "\n\tVards:%s Uzvards:%s Dzimsanas Datums:%d %d %d Ienakums %.2f EUR \n", vards, uzvards, d, m, y, ienakums);
fclose(file);
}