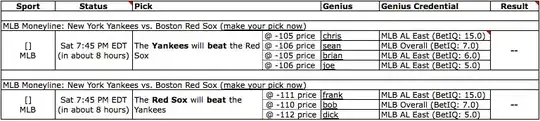
This can also be accomplished using Power Query, available in Windows Excel 2010+ and Excel 365 (Windows or Mac)
To use Power Query
- Select some cell in your Data Table
Data => Get&Transform => from Table/Range- When the PQ Editor opens:
Home => Advanced Editor
- Make note of the Table Name in Line 2
- Paste the M Code below in place of what you see
- Change the Table name in line 2 back to what was generated originally.
- Read the comments and explore the
Applied Steps to understand the algorithm
M Code
If your column names are not auto-generated, you may need to edit Column1 and Column2 to whatever the actual column names are (eg: Column1=>ColumnA)
let
//change Table name in next line to actual table name
Source = Excel.CurrentWorkbook(){[Name="Table7"]}[Content],
//set data types
#"Changed Type" = Table.TransformColumnTypes(Source,{
{"Column1", type text}, {"Column2", type text}}),
//for each entry in Column 1, create a List of all the entries in Column 2
//then remove column 2 and expand the custom column
#"Added Custom" = Table.AddColumn(#"Changed Type", "List of all in Column2",
each #"Changed Type"[Column2]),
#"Removed Columns" = Table.RemoveColumns(#"Added Custom",{"Column2"}),
#"Expanded List of all in Column2" = Table.ExpandListColumn(
#"Removed Columns", "List of all in Column2"),
//remove the rows with nulls
// (happens if one column longer than the other
#"Filtered Rows" = Table.SelectRows(#"Expanded List of all in Column2",
each ([Column1] <> null) and ([List of all in Column2] <> null)),
//merge the two columns with space delimiter to get Results
#"Merged Columns" = Table.CombineColumns(#"Filtered Rows",
{"Column1", "List of all in Column2"},
Combiner.CombineTextByDelimiter(" ", QuoteStyle.None),"Result")
in
#"Merged Columns"