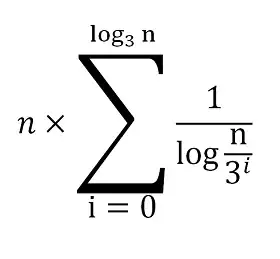I edited this post in order to ask a more clear question.
Starting from a figure plot generate by Matplotlib like this :

Bitmap data is returned by a function:
from PIL import Image
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
def fig2rgb ( fig ):
fig.tight_layout()
fig.canvas.draw ( )
pil_fig=Image.frombytes('RGB',
fig.canvas.get_width_height(),
fig.canvas.tostring_rgb() )
return pil_fig
figure = plt.etcetera ...
...
fig_datas=fig2rgb (figure)
I have another rectangular PIL image with definite dimension (height=a and width=b) which can be inclued in PIL figure generated before. How can we find an available rectangular zone with those finite dimensions in the whitespace of figure plot ?
The final result should be :
My initial hypothesis was to use a function that returns pixel coordinates of white space in figure and try to find x,y in them:
def getWhite_coords(rgb):
white_positions = [[x,y] for x in range(rgb.size[0]) for y in range(rgb.size[1]) \
if rgb.getdata()[x+y*rgb.size[0]] == (255,255,255)]
return np.array(white_positions)
white_space=getWhite_coords(fig_datas)
for y in range(a):
if all([x,y] in white_space for x in range(b)):
...
break
This method has not shown results for my aim.
All this presented above is trying to simulate what legend box does when its argument loc="best" is setted.
Do you have any proposals?
Thanks in advance for the reply