Looks like you can use the %in% operator or the st_difference function. If using st_difference, you might need to st_combine each set individually if the points are sf but not if they're sfc.
The methods may differ a little depending on the type of data you're using. Are they just points(sfc), or are they points associated with data(sf)?
*Edit for your reproducible example:
library(dplyr)
library(ggplot2)
library(sp)
library(sf)
data(meuse)
coordinates(meuse) = ~x+y
A <- st_as_sf(meuse) %>% select(geometry) #155 obs
B <- filter(A, row_number()<= 100)%>% select(geometry) #100 obs
diff_meuse <- st_difference(st_combine(A), st_combine(B)) %>% st_cast('POINT')
diff_meuse
#> Geometry set for 55 features
#> Geometry type: POINT
#> Dimension: XY
#> Bounding box: xmin: 178786 ymin: 329714 xmax: 180923 ymax: 333116
#> CRS: NA
#> First 5 geometries:
#> POINT (178786 329822)
#> POINT (178875 330311)
#> POINT (179024 329733)
#> POINT (179030 330082)
#> POINT (179034 330561)
ggplot() +
geom_sf(data = A, size = 4, alpha = .3) +
geom_sf(data = diff_meuse, color = 'red')

Created on 2022-03-31 by the reprex package (v2.0.1)
``` r
library(sf)
library(ggplot2)
set.seed(10)
# using nc data incl w/sf
nc <- st_read(system.file("shape/nc.shp", package="sf"))
#> Reading layer `nc' from data source
#> using driver `ESRI Shapefile'
#> Simple feature collection with 100 features and 14 fields
#> Geometry type: MULTIPOLYGON
#> Dimension: XY
#> Bounding box: xmin: -84.32385 ymin: 33.88199 xmax: -75.45698 ymax: 36.58965
#> Geodetic CRS: NAD27
a_b <- st_sample(nc, size = 20)
a <- a_b[1:20]
b <- a_b[1:5]
diff <- a[!a%in%b]
head(diff)
#> Geometry set for 6 features
#> Geometry type: POINT
#> Dimension: XY
#> Bounding box: xmin: -81.98142 ymin: 34.15653 xmax: -78.5457 ymax: 36.41477
#> Geodetic CRS: NAD27
#> First 5 geometries:
#> POINT (-78.5457 34.15653)
#> POINT (-79.28979 36.045)
#> POINT (-79.03986 36.41477)
#> POINT (-80.52165 35.15185)
#> POINT (-81.98142 35.45012)
## or using st_difference
diff_st <- st_difference(st_combine(a), st_combine(b))
head(st_cast(diff_st, 'POINT'))
#> Geometry set for 6 features
#> Geometry type: POINT
#> Dimension: XY
#> Bounding box: xmin: -82.19945 ymin: 35.11489 xmax: -80.52165 ymax: 35.93451
#> Geodetic CRS: NAD27
#> First 5 geometries:
#> POINT (-82.19945 35.93451)
#> POINT (-80.57638 35.60809)
#> POINT (-80.72523 35.14048)
#> POINT (-80.78783 35.11489)
#> POINT (-80.52165 35.15185)
ggplot() +
geom_sf(data = diff, color = "black", alpha = .2, size = 6) +
geom_sf(data = diff_st, color = "black", alpha = .8, size = 4) +
geom_sf(data = a, color = 'red', size = 1)
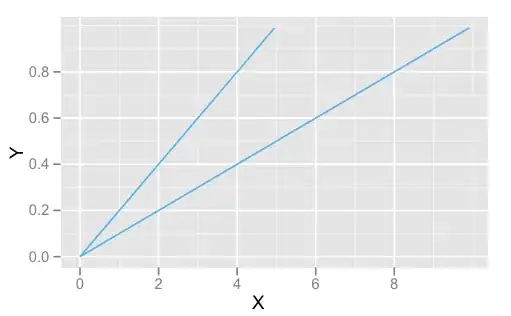
Created on 2022-03-31 by the reprex package (v2.0.1)