I finally managed to make Nginx Ingress Controller and L7 HTTP(S) Load Balancer work together.
Based on the @rrob repply with his own question I managed to make it work. The only difference is that his solution will install a classic HTTP(S) LoadBalancer, instead of the new version and also I cover the creation of the IP Address, the self-signed Certificate, and the HTTP Proxy redirect from HTTP to HTTPS. I will plcae here the detailed steps that worked for me.
This steps assume we already have a Cluster created with VPC-native traffic routing enabled.
Before the need of the HTTP(S) LoadBalancer, I would just apply the manifests provided by the NGINX DOCS page for the installation of the Nginx Ingress Controller and It would create a service of type LoadBalancer which would, then, create a regional L4 LoadBalancer automatically.
But now that I need need to have Cloud Armor and WAF, the L4 Loadbalancer doesn't support it. A HTTPS(S) Load Balancer is needed in order for Cloud Armor to work.
In order to have Nginx Ingress controller working with the new HTTPS(S) LoadBalancer we need to change the type: LoadBalancer on the Nginx Ingress Controller service to ClusterIP instead, and add the NEG annotation to it cloud.google.com/neg: '{"exposed_ports": {"80":{"name": "ingress-nginx-80-neg"}}}'. With this net annotation, GCP will automatically create a Network Endpoint Group that will point to the Nginx Ingress Controller service running in GKE. This Network Endpoint Group will serve as the backend of our HTTPS Load Balancer.
NOTE: When using the cloud.google.com/neg annotation, GCP will create one Network Endpoint Group for each region containing nodes with Nginx Ingress Controller pods. For exmple, if you set your NodePool to spread across us-central1-a, us-central1-b and us-central1-f, GCP will create three Network Endpoint Groups if you have one Ingress Controller replica in each node. So when you set the Load Balancer's back end, you need to add all of them as backends as It's explained in STEP 5.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
annotations:
labels:
helm.sh/chart: ingress-nginx-4.0.15
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/instance: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/version: 1.1.1
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: Helm
app.kubernetes.io/component: controller
name: ingress-nginx-controller
namespace: ingress-nginx
annotations:
cloud.google.com/neg: '{"exposed_ports": {"80":{"name": "ingress-nginx-80-neg"}}}'
spec:
type: ClusterIP
ipFamilyPolicy: SingleStack
ipFamilies:
- IPv4
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
protocol: TCP
targetPort: http
appProtocol: http
- name: https
port: 443
protocol: TCP
targetPort: https
appProtocol: https
selector:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/instance: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/component: controller
If you install the Nginx Ingress Controller using HELM you need to overwrite the config to add the NEG annotation to the service. So the values.yaml would look something like this:
controller:
service:
type: ClusterIP
annotations:
cloud.google.com/neg: '{"exposed_ports": {"80":{"name": "ingress-nginx-80-neg"}}}'
To install it, add the ingress-nginx to the helm repository:
helm repo add ingress-nginx https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx
helm repo update
Then install it:
helm install -f values.yaml ingress-nginx ingress-nginx/ingress-nginx
The next steps will be:
PROJECT_ID=<project-id>
ZONE=us-central1-a
CLUSTER_NAME=<cluster-name>
HEALTH_CHECK_NAME=nginx-ingress-controller-health-check
NETWORK_NAME=<network-name>
CERTIFICATE_NAME=self-managed-exp-<day>-<month>-<year>
GKE_NODE_METADATA=$(kubectl get nodes -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata}')
GKE_SAMPLE_NODE_NAME=$(echo $GKE_NODE_METADATA | jq -r .name)
GKE_SAMPLE_NODE_ZONE=$(echo $GKE_NODE_METADATA | jq -r .labels | jq -r '."topology.kubernetes.io/zone"')
NETWORK_TAGS=$(gcloud compute instances describe \
$GKE_SAMPLE_NODE_NAME --project $PROJECT_ID \
--zone=$GKE_SAMPLE_NODE_ZONE --format="value(tags.items[0])")
- Create an Static IP Address (skip if you already have):
Has to be Premium tier and Global
gcloud compute addresses create ${CLUSTER_NAME}-loadbalancer-ip \
--global \
--ip-version IPV4
- Create a Firewall rule allowing the L7 HTTP(S) Load Balancer to access our cluster
gcloud compute firewall-rules create ${CLUSTER_NAME}-allow-tcp-loadbalancer \
--allow tcp:80 \
--source-ranges 130.211.0.0/22,35.191.0.0/16 \
--target-tags $NETWORK_TAGS \
--network $NETWORK_NAME
- Create a Health Check for our to-be-created Backend Service
gcloud compute health-checks create http ${CLUSTER_NAME}-nginx-health-check \
--port 80 \
--check-interval 60 \
--unhealthy-threshold 3 \
--healthy-threshold 1 \
--timeout 5 \
--request-path /healthz
- Create a Backend Service which is used to inform the LoadBalancer how to connect and distribute trafic to the pods.
gcloud compute backend-services create ${CLUSTER_NAME}-backend-service \
--load-balancing-scheme=EXTERNAL \
--protocol=HTTP \
--port-name=http \
--health-checks=${CLUSTER_NAME}-nginx-health-check \
--global
- Now it's the time we add the Nginx NEG service (the one annotated earlier) to the back end service created on the previous step:
As explained earlier, a Network Endpoint Group will be created for each zone that contains Nginx Ingress Controller pods. So the current layout of my setup is:
a. **Node Pool** configured to span across **us-central1-a** and **us-central1-c**.
b. **Nginx Ingress Controller** configured to have 4 replicas.
c. **Node 1** in **us-central1-a** will have 2 replicas.
d. **Node 2** in **us-central1-c** will have 2 replicas.
e. GCP generated two Network Endpoint Groups. One for **us-central1-a** and other for **us-central1-c**.
So for the example bellow, I bind the two NEGs for each zone, as backend services to my Load Balancer.
# us-central1-a
gcloud compute backend-services add-backend ${CLUSTER_NAME}-backend-service \
--network-endpoint-group=ingress-nginx-80-neg \
--network-endpoint-group-zone=us-central1-a \
--balancing-mode=RATE \
--capacity-scaler=1.0 \
--max-rate-per-endpoint=100 \
--global
# us-central1-c
gcloud compute backend-services add-backend ${CLUSTER_NAME}-backend-service \
--network-endpoint-group=ingress-nginx-80-neg \
--network-endpoint-group-zone=us-central1-c \
--balancing-mode=RATE \
--capacity-scaler=1.0 \
--max-rate-per-endpoint=100 \
--global
- Create the load balancer itself (URL MAPS)
gcloud compute url-maps create ${CLUSTER_NAME}-loadbalancer \
--default-service ${CLUSTER_NAME}-backend-service
- Create a Self Managed Certificate (it may be a Google-managed certificate but here we will cover the self-managed). Can also create from Console HERE.
gcloud compute ssl-certificates create $CERTIFICATE_NAME \
--certificate=my-cert.pem \
--private-key=my-privkey.pem \
--global
Finally, I will setup the Loadbalancer frontend through the Console interface which is way easier.
To create the LoadBalancer front end, enter the Loadbalancer on Console and click on "Edit".
The Frontend configuration tab will be incomplete. Go there 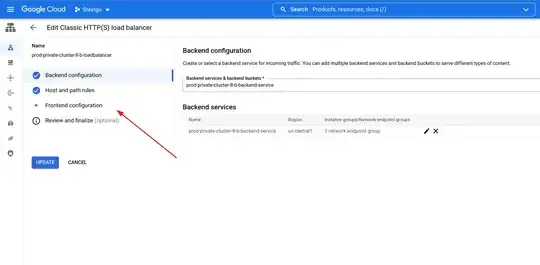
Click on "ADD FRONTEND IP AND PORT"
Give it a name and select HTTPS on the field Protocol.
On IP Address change from Ephemeral to your previously allocated static IP
Select your certificate and mark Enable HTTP to HTTPS redirect if you want. (I did)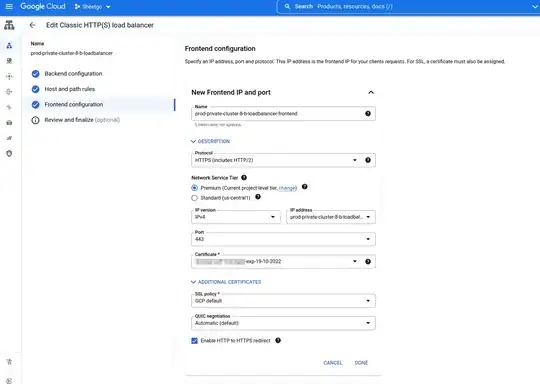
Save the LoadBalancer.
The entering the LoadBalancer page we should see our nginx instance(s) healthy and green. In my case I've setup the Nginx Ingress Controller to have 4 replicas:
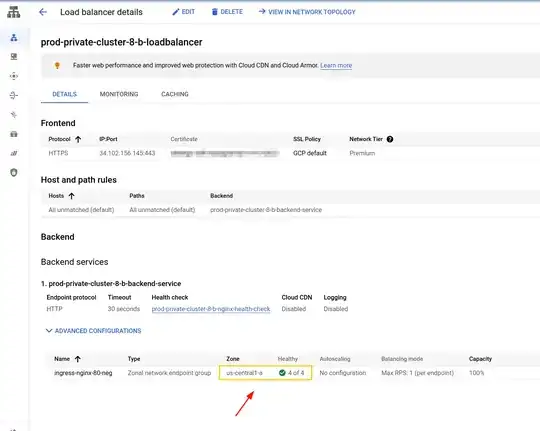
Finally, we just need to point our domains to the LoadBalancer IP and create our Ingress file.
NOTE: The Ingress now won't handle the certificate. The certificate will now be managed by the LoadBalancer externally. So the Ingress won't have the tls definition:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/upstream-fail-timeout: "1200"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/configuration-snippet: |
set $http_origin "${scheme}://${host}";
more_set_headers "server: hide";
more_set_headers "X-Content-Type-Options: nosniff";
more_set_headers "Referrer-Policy: strict-origin";
name: ingress-nginx
namespace: prod
spec:
rules:
- host: app.mydomain.com
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: frontend
port:
number: 80


