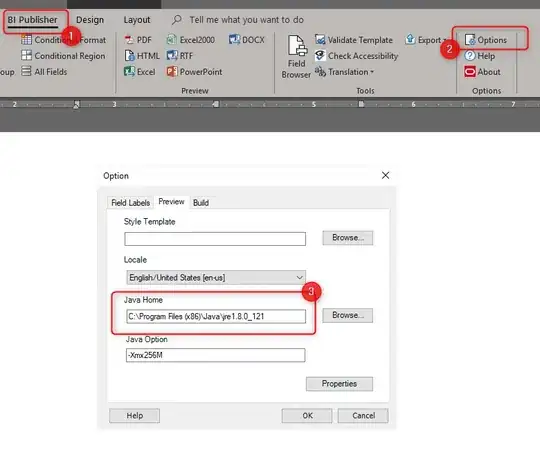
I want to change the graph color and gradient direction in the parts where graph goes below zero. Alternative image for illustration:
I have tried it using this code
def add_gradient_fill(ax: Optional[plt.Axes] = None, alpha_gradientglow: float = 1.0):
"""Add a gradient fill under each line,
i.e. faintly color the area below the line."""
if not ax:
ax = plt.gca()
lines = ax.get_lines()
for line in lines:
# don't add gradient fill for glow effect lines:
if hasattr(line, 'is_glow_line') and line.is_glow_line:
continue
fill_color = line.get_color()
zorder = line.get_zorder()
alpha = line.get_alpha()
alpha = 1.0 if alpha is None else alpha
rgb = mcolors.colorConverter.to_rgb(fill_color)
z = np.empty((100, 1, 4), dtype=float)
z[:, :, :3] = rgb
z[:, :, -1] = np.linspace(0, alpha, 100)[:, None]
x, y = line.get_data(orig=False)
x, y = np.array(x), np.array(y) # enforce x,y as numpy arrays
xmin, xmax = x.min(), x.max()
ymin, ymax = y.min(), y.max()
im = ax.imshow(z, aspect='auto',
extent=[xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax],
alpha=alpha_gradientglow,
origin='lower', zorder=zorder)
xy = np.column_stack([x, y])
xy = np.vstack([[xmin, ymin], xy, [xmax, ymin], [xmin, ymin]])
clip_path = Polygon(xy, facecolor='none', edgecolor='none', closed=True)
ax.add_patch(clip_path)
im.set_clip_path(clip_path)
ax.autoscale(True)
This code is also a part of a matplotlib theming library called mplcyberpunk.
This provides great looks to the plot, but as mentioned earlier, I want that the sub-zero parts of the graphs be in different color with gradient direction reversed.
How can this be possibly achieved?
PS: Sincerely, my question is different from other graph gradient questions, please don't close this.
Edit
Minimal reproducible code
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import mplcyberpunk as mplcp
x = range(-10, 11)
y = [(i ** 2) - 50 for i in x]
plt.style.use('cyberpunk')
###### just for setting the theme, ignore these lines #########
for param in ['figure.facecolor', 'axes.facecolor', 'savefig.facecolor']:
plt.rcParams[param] = '#303030'
for param in ['text.color', 'axes.labelcolor', 'xtick.color', 'ytick.color']:
plt.rcParams[param] = '#ffffff'
plt.subplots()[1].grid(color='#404040')
##################################################################
plt.plot(x, y)
mplcp.make_lines_glow()
mplcp.add_gradient_fill()
plt.show()
Update:
Well I somehow figured it out, but there are some visual defects that need focus. Here are the functions and output:
from itertools import groupby
import numpy as np
from matplotlib.lines import Line2D
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.colors as mcolors
from matplotlib.patches import Polygon
def add_glow_effects(n_glow_lines: int = 10,
diff_linewidth: float = 1.05,
alpha_line: float = 0.3,
change_line_color: bool = True,
color_positive: str = '#0000ff',
color_negative: str = '#ff0000',
alpha_gradientglow: float = 1.0, ):
make_lines_glow(n_glow_lines, diff_linewidth, alpha_line, change_line_color, color_positive, color_negative)
add_gradient_fill(alpha_gradientglow, color_positive, color_negative, )
def make_lines_glow(n_glow_lines: int = 10,
diff_linewidth: float = 1.05,
alpha_line: float = 0.3,
change_line_color: bool = True,
color_positive: str = '#0000ff',
color_negative: str = '#ff0000'):
ax = plt.gca()
lines = ax.get_lines()
alpha_value = alpha_line / n_glow_lines
for line_element in lines:
if not isinstance(line_element, Line2D):
continue
x, y = line_element.get_data(orig=False)
x, y = optimize_lines(list(x), list(y))
lines_list = list_form(x, y)
for line in lines_list:
if change_line_color:
y_avg = sum(line[1]) / len(line[1])
if y_avg >= 0:
color = color_positive
else:
color = color_negative
else:
color = line_element.get_color()
line = Line2D(line[0], line[1], linewidth=line_element.get_linewidth(), color=color)
data = list(line.get_data(orig=False))
linewidth = line.get_linewidth()
ax.plot(data[0], data[1], color=color, linewidth=linewidth)
for n in range(1, n_glow_lines + 1):
glow_line, = ax.plot(*data)
glow_line.update_from(line)
# line properties are copied as seen in this solution: https://stackoverflow.com/a/54688412/3240855
glow_line.set_alpha(alpha_value)
glow_line.set_linewidth(linewidth + (diff_linewidth * n))
# mark the glow lines, to disregard them in the underglow function.
glow_line.is_glow_line = True
# noinspection PyArgumentList
def add_gradient_fill(alpha_gradientglow: float = 1.0,
color_positive: str = '#00ff00',
color_negative: str = '#ff0000'):
"""Add a gradient fill under each line,
i.e. faintly color the area below the line."""
ax = plt.gca()
lines = ax.get_lines()
for line_element in lines:
if not isinstance(line_element, Line2D):
continue
x, y = line_element.get_data(orig=False)
x, y = optimize_lines(list(x), list(y))
lines_list = list_form(x, y)
for line in lines_list:
y_avg = sum(line[1]) / len(line[1])
# don't add gradient fill for glow effect lines:
if hasattr(line, 'is_glow_line') and line.is_glow_line:
continue
line = Line2D(line[0], line[1], linewidth=line_element.get_linewidth())
zorder = line.get_zorder()
alpha = line_element.get_alpha()
alpha = 1.0 if alpha is None else alpha
x, y = line.get_data(orig=False)
x, y = np.array(x), np.array(y) # enforce x,y as numpy arrays
xmin, xmax = x.min(), x.max()
ymin, ymax = y.min(), y.max()
xy = np.column_stack([x, y])
if y_avg >= 0:
fill_color = color_positive
linspace = np.linspace(0, alpha, 100)[:, None]
xy = np.vstack([[xmin, ymin], xy, [xmax, ymin], [xmin, ymin]])
else:
fill_color = color_negative
linspace = np.linspace(alpha, 0, 100)[:, None]
xy = np.vstack([[xmin, ymax], xy, [xmax, ymax], [xmin, ymax]])
rgb = mcolors.colorConverter.to_rgb(fill_color)
z = np.empty((100, 1, 4), dtype=float)
z[:, :, :3] = rgb
z[:, :, -1] = linspace
im = ax.imshow(z, aspect='auto',
extent=[xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax],
alpha=alpha_gradientglow,
origin='lower', zorder=zorder)
clip_path = Polygon(xy, facecolor='none', edgecolor='none', closed=True)
ax.add_patch(clip_path)
im.set_clip_path(clip_path)
ax.autoscale(True)
def optimize_lines(x: list, y: list):
y = [list(element) for index, element in groupby(y, lambda a: a >= 0)]
indexes = [0]
for i in y:
indexes.append(len(i) + indexes[-1])
# from https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/python-group-consecutive-elements-by-sign/
x = [x[indexes[i]:indexes[i + 1]] for i, _ in enumerate(indexes) if i != len(indexes) - 1]
for i in range(len(y) - 1):
if y[i][-1] == 0 and y[i + 1][0] == 0:
continue
a = y[i][-1]
b = y[i + 1][0]
diff = abs(a) + abs(b)
a_ = (abs(0 - a)) / diff
b_ = abs(0 - b) / diff
x[i].append(x[i][-1] + a_)
x[i + 1].insert(0, x[i + 1][0] - b_)
y[i].append(0)
y[i + 1].insert(0, 0)
x = [list(i) for i in x]
y = [list(i) for i in y]
# input: x=[1,2,3,4,5], y=[1,2,-5,0,2]
# output: x=[[1, 2, 2.2857142857142856], [2.2857142857142856, 3, 4.0], [4.0, 4, 5]],
# y=[[1, 2, 0], [0, -5, 0], [0, 0, 2]]
return list(x), list(y)
def list_form(x: list[list], y: list[list]):
lst = []
for i in range(len(x)):
lst.append([x[i], y[i]])
return lst
Notice how the glow from function is collected at the left side of graph. also, at the end of the graph these is a tiny purple triangle that is offset by one corner.