class Person {
constructor() {
let name = 'John';
}
talk() {
return "talking"
}
}
const me = new Person();
Person.prototype.walk = function walk() { return "walking"; };
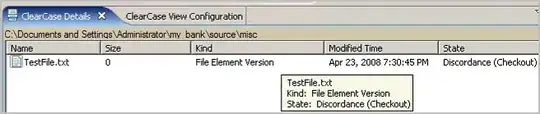
as you can see in the image below, why I am getting undefined for me.name (although it was present in the constructor)?
Why accessible through Person and why not with me?
Do we get only the prototype object properties to be accessed to me, or do we get constructor properties? If not then what's the use of passing them by default to the me instance as you can see in the image below?