You could use scipy.linalg.orthogonal_procrustes. Here's a demonstration. Note that the function generateAB only exists to generate the arrays A and B for the demo. The key steps of the calculation are to center A and B, and then call orthogonal_procrustes.
import numpy as np
from scipy.stats import ortho_group
from scipy.linalg import orthogonal_procrustes
def generateAB(shape, noise=0, rng=None):
# Generate A and B for the example.
if rng is None:
rng = np.random.default_rng()
m, n = shape
# Random matrix A
A = 3 + 2*rng.random(shape)
Am = A.mean(axis=0, keepdims=True)
# Random orthogonal matrix T
T = ortho_group.rvs(n, random_state=rng)
# Target matrix B
B = ((A - Am) @ T + rng.normal(scale=noise, size=A.shape)
+ 3*rng.random((1, n)))
# Include T in the return, but in a real problem, T would not be known.
return A, B, T
# For reproducibility, use a seeded RNG.
rng = np.random.default_rng(0x1ce1cebab1e)
A, B, T = generateAB((7, 5), noise=0.01, rng=rng)
# Find Q. Note that `orthogonal_procrustes` does not include
# dilation or translation. To handle translation, we center
# A and B by subtracting the means of the points.
A0 = A - A.mean(axis=0, keepdims=True)
B0 = B - B.mean(axis=0, keepdims=True)
Q, scale = orthogonal_procrustes(A0, B0)
with np.printoptions(precision=3, suppress=True):
print('T (used to generate B from A):')
print(T)
print('Q (computed by orthogonal_procrustes):')
print(Q)
print('\nCompare A0 @ Q with B0.')
print('A0 @ Q:')
print(A0 @ Q)
print('B0 (should be close to A0 @ Q if the noise parameter was small):')
print(B0)
Output:
T (used to generate B from A):
[[-0.873 0.017 0.202 -0.44 -0.054]
[-0.129 0.606 -0.763 -0.047 -0.18 ]
[ 0.055 -0.708 -0.567 -0.408 0.088]
[ 0.024 0.24 -0.028 -0.168 0.955]
[ 0.466 0.272 0.235 -0.78 -0.21 ]]
Q (computed by orthogonal_procrustes):
[[-0.871 0.022 0.203 -0.443 -0.052]
[-0.129 0.604 -0.765 -0.046 -0.178]
[ 0.053 -0.709 -0.565 -0.409 0.087]
[ 0.027 0.239 -0.029 -0.166 0.956]
[ 0.47 0.273 0.233 -0.779 -0.21 ]]
Compare A0 @ Q with B0.
A0 @ Q:
[[-0.622 0.224 0.946 1.038 0.578]
[ 0.263 0.143 -0.031 -0.949 0.492]
[-0.49 0.758 0.473 -0.221 -0.755]
[ 0.205 -0.74 0.065 -0.192 -0.551]
[-0.295 -0.434 -1.103 0.444 0.547]
[ 0.585 -0.378 -0.645 -0.233 0.651]
[ 0.354 0.427 0.296 0.113 -0.963]]
B0 (should be close to A0 @ Q if the noise parameter was small):
[[-0.627 0.226 0.949 1.032 0.576]
[ 0.268 0.135 -0.028 -0.95 0.492]
[-0.493 0.765 0.475 -0.201 -0.75 ]
[ 0.214 -0.743 0.071 -0.196 -0.55 ]
[-0.304 -0.433 -1.115 0.451 0.551]
[ 0.589 -0.375 -0.645 -0.235 0.651]
[ 0.354 0.426 0.292 0.1 -0.969]]
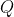 that would transform the Source Matrix
that would transform the Source Matrix 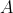 to nearly
to nearly 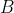 Using
Using