As the title mentioned, I have to remove adjacent duplicates in doubly linked list such that if input is 'google', the adjacent duplicates removal is google-->ggle-->le and hence output should be 'le'. I'm supposed to code it in C. I tried to perform delete operation as shown in this image-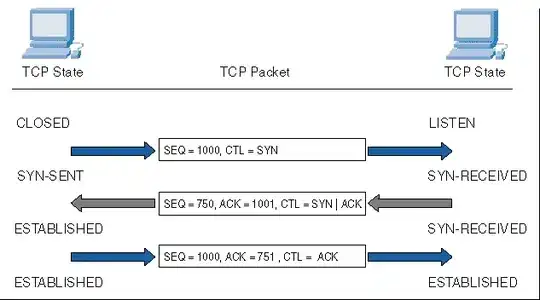 , except that I don't know how to continuously loop till all adjacent duplicates are removed (I don't know how to use recursion). I'm removing adjacent duplicates in remove_adjacent_duplicates() function, and since I don't know how to put terminating condition in loop, I've merely used while loop. I also don't know how to assign modified doubly linked list to original linked list named 'head', and so
, except that I don't know how to continuously loop till all adjacent duplicates are removed (I don't know how to use recursion). I'm removing adjacent duplicates in remove_adjacent_duplicates() function, and since I don't know how to put terminating condition in loop, I've merely used while loop. I also don't know how to assign modified doubly linked list to original linked list named 'head', and so head=current; in while loop (line 63 of code) is a wrong assignment as it finally prints empty(?) list. Please rectify my mistakes and give correct solution. Here's my code-
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
struct node {
char data;
struct node *next;
struct node *prev;
};
struct node *head, *tail = NULL; //Represent the head and tail of the doubly linked list
int len;
void addNode(char data) {
struct node *newNode = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node)); //Create new node
newNode->data = data;
if(head == NULL) { //If dll is empty
head = tail = newNode; //Both head and tail will point to newNode
head->prev = NULL; //head's previous will point to NULL
tail->next = NULL; //tail's next will point to NULL, as it is the last node of the list
}
else {
tail->next = newNode; //newNode will be added after tail such that tail's next points to newNode
newNode->prev = tail; //newNode's previous will point to tail
tail = newNode; //newNode will become new tail
tail->next = NULL; //As it is last node, tail's next will point to NULL
}
}
void remove_adjacent_duplicates() {
struct node *current, *index, *temp;
if(head == NULL) {
return;
}
else
{
current=head;
while(current != NULL)
{
if(current->data == current->next->data)
{
index = current->prev; //noting data previous to duplicate data
//printf("%c\n",index->data);
while(current->data == current->next->data && current!=NULL)
{
current=current->next; //iterating till all adjacent duplicates are found
//printf("*%c\n",current->data);
}
temp=current->next; //temp points to character next to latest adjacent duplicate
//printf("!%c\n",temp->data);
index->next=temp; //the 'next' pointer of struct node of data before duplicate points to node after all adjacent duplicates found currently
//printf("@%c\n",index->data);
temp->prev=index; //data's 'prev' pointer (right after adjacent duplicates) points to data present just before adjacent duplicates
//printf("#%c\n",temp->data);
head=current; //logical error
//printf("$%c\n",head->data);
free(current);
free(index);
free(temp);
break;
}
else
{
current=current->next;
}
}
}
}
void display() {
struct node *current = head; //head the global one
while(current != NULL) {
printf("%c<->", current->data); //Prints each node by incrementing pointer.
current = current->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
int main()
{
char s[100];
int i;
printf("Enter string: ");
scanf("%s",s);
len=strlen(s);
for(i=0;i<len;i++){
addNode(s[i]);
}
printf("Doubly linked list: \n");
display();
remove_adjacent_duplicates()
printf("Doubly linked list after removing adjacent duplicates: \n");
display();
return 0;
}